5
目录
包 |
包是组织类的一种方式,包的主要目的是保证类的唯一性。
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Date date=new java.util.Date();
System.out.println(date.getTime());
}
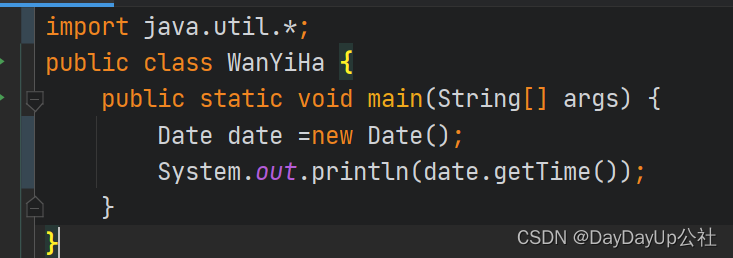
import java.util.Date;
public class WanYiHa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date =new Date();
System.out.println(date.getTime());
}
}

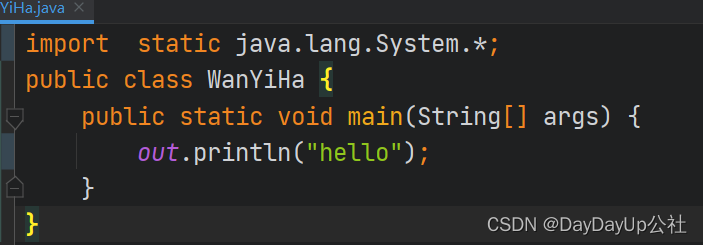
静态导入 |
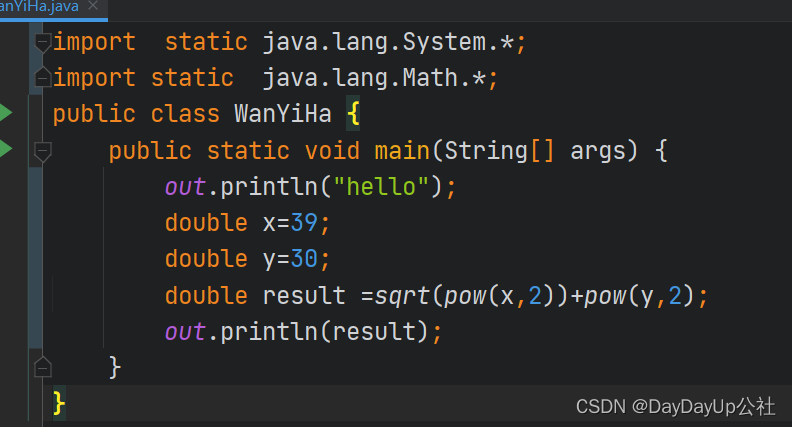
继承 |

package Animal;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat=new Cat("小猫");
cat.eat("吃的 ");
Bird bird=new Bird("小鸟");
bird.eat("吃的");
}
}
class Animal {
public String name;
public Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(this.name+"正在吃"+food);
}
}
// extends : 拓展的意思。
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name) {
// super 调用父类的构造方法
super(name);
}
}
class Bird extends Animal{
public Bird(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void fly(){
System.out.println(this.name+"正在飞");
}
}class被 public修饰的化,不同位置的包之间都可以extends;
protected 不能修饰class ;

protected修饰父类一个非本质属性之后,A包的子包B下的类继承了A包目录下的父类,也可以访问这个被protected修饰的非本质属性。


向上转型 :
在主方法中用
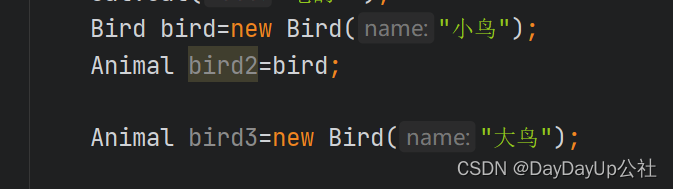

 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Cat cat=new Cat("小猫");
// cat.eat("吃的 ");
// bird.eat("吃的");
Animal bird3=new Bird("大鸟");
feed(bird3);
}
public static void feed(Animal animal){
animal.eat("谷子");
}
}
class Animal {
public String name;
public Animal(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(this.name+"正在吃"+food);
}
} 动态绑定 |
就是看对象选方法
package Animal;
public class Animal {
// protected 修饰,子类可以使用 这条String 属性。
protected String name;
// Animal 的构造方法 ,所以在new的时候初始化,给Animal 的对象都要求附一个名字; 比如"豆豆,鹦鹉"
public Animal (String name){
this.name=name;
}
// 父类有一个eat方法,和子类的不干预。 在使用 Animal 的对象时,调用这个eat() 方法
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println(th







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 2268
2268











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








