为什么存在动态内存分配
我们已经掌握的内存开辟方式有:
int val = 20;//在栈空间上开辟四个字节
char arr[10] = {0};//在栈空间上开辟10个字节的连续空间
但是上述的开辟空间的方式有两个特点:
- 空间开辟大小是固定的。
- 数组在申明的时候,必须指定数组的长度,它所需要的内存在编译时分配。
但是对于空间的需求,不仅仅是上述的情况。有时候我们需要的空间大小在程序运行的时候才能知道,
那数组的编译时开辟空间的方式就不能满足了。
这时候就只能试试动态存开辟了
动态内存管理函数
malloc
c库函数
void *malloc(size_t size)
分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。
如果开辟成功,则返回一个指向开辟好空间的指针。
如果开辟失败,则返回一个NULL指针,因此malloc的返回值一定要做检查。
返回值的类型是 void* ,所以malloc函数并不知道开辟空间的类型,具体在使用的时候使用者自己
来决定。
如果参数 size 为0,malloc的行为是标准是未定义的,取决于编译器。
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char *str;
/* 最初的内存分配 */
str = (char *) malloc(15);
strcpy(str, "runoob");
printf("String = %s, Address = %u\n", str, str);
/* 重新分配内存 */
str = (char *) realloc(str, 25);
strcat(str, ".com");
printf("String = %s, Address = %u\n", str, str);
free(str);
return(0);
}
这段代码将生成以下结果
String = runoob, Address = 3662685808
String = runoob.com, Address = 3662685808
free
C 库函数
void free(void *ptr)
释放之前调用 calloc、malloc 或 realloc 所分配的内存空间。
如果参数 ptr 指向的空间不是动态开辟的,那free函数的行为是未定义的。
如果参数 ptr 是NULL指针,则函数什么事都不做。
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *str;
/* 最初的内存分配 */
str = (char *) malloc(15);
strcpy(str, "runoob");
printf("String = %s, Address = %p\n", str, str);
/* 重新分配内存 */
str = (char *) realloc(str, 25);
strcat(str, ".com");
printf("String = %s, Address = %p\n", str, str);
/* 释放已分配的内存 */
free(str);
return(0);
}
运行这段代码将产生以下结果
String = runoob, Address = 0x7fe4e4c02b10
String = runoob.com, Address = 0x7fe4e4c02b10
calloc
C 库函数
void *calloc(size_t nitems, size_t size)
分配所需的内存空间,并返回一个指向它的指针。malloc 和 calloc 之间的不同点是,malloc 不会设置内存为零,而 calloc 会设置分配的内存为零。
函数的功能是为 num 个大小为 size 的元素开辟一块空间,并且把空间的每个字节初始化为0。
与函数 malloc 的区别只在于 calloc 会在返回地址之前把申请的空间的每个字节初始化为全0。
举个例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int i, n;
int *a;
printf("要输入的元素个数:");
scanf("%d",&n);
a = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
printf("输入 %d 个数字:\n",n);
for( i=0 ; i < n ; i++ )
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
printf("输入的数字为:");
for( i=0 ; i < n ; i++ ) {
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
free (a); // 释放内存
return(0);
}
将产生以下结果:
要输入的元素个数:3
输入 3 个数字:
22
55
14
输入的数字为:22 55 14
realloc
C 库函数
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
尝试重新调整之前调用 malloc 或 calloc 所分配的 ptr 所指向的内存块的大小。
ptr 是要调整的内存地址
size 调整之后新大小
返回值为调整之后的内存起始位置。
这个函数调整原内存空间大小的基础上,还会将原来内存中的数据移动到 新 的空间。
realloc在调整内存空间的是存在两种情况:
原有空间之后有足够大的空间

原有空间之后没有足够大的空间
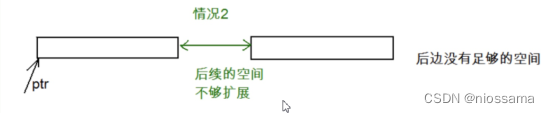
当是情况2 的时候,原有空间之后没有足够多的空间时,扩展的方法是:在堆空间上另找一个合适大小
的连续空间来使用。这样函数返回的是一个新的内存地址
举个例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *str;
/* 最初的内存分配 */
str = (char *) malloc(15);
strcpy(str, "runoob");
printf("String = %s, Address = %p\n", str, str);
/* 重新分配内存 */
str = (char *) realloc(str, 25);
strcat(str, ".com");
printf("String = %s, Address = %p\n", str, str);
free(str);
return(0);
}
运行的结果是
String = runoob, Address = 0x7fa2f8c02b10
String = runoob.com, Address = 0x7fa2f8c02b10
常见的动态内存错误
对NULL指针的解引用操作
oid test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(INT_MAX/4);
*p = 20;//如果p的值是NULL,就会有问题
free(p);
}
修改
oid test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(INT_MAX/4);
if(p==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
*p = 20;//如果p的值是NULL,就会有问题
free(p);
}
对动态开辟空间的越界访问
void test()
{
int i = 0;
int *p = (int *)malloc(10*sizeof(int));
if(NULL == p)
{
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for(i=0; i<=10; i++)
{
*(p+i) = i;//当i是10的时候越界访问
}
free(p);
}
对非动态开辟的内存使用free释放
void test()
{
int a = 10;
int *p = &a;
free(p);//ok?
}
使用free释放一块动态开辟内存的一部分
void test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(100);
p++;
free(p);//p不再指向动态内存的起始位置
}
对同一块动态内存多次释放
void test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(100);
free(p);
free(p);//重复释放
}
动态开辟内存忘记释放
void test()
{
int *p = (int *)malloc(100);
if(NULL != p)
{
*p = 20;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
while(1);
}





















 456
456











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








