一个程序从源码到被执行,当中经历了3个过程:
- 编译:将.c文件编译成.o文件,不关心.o文件之间的联系.
- 静态链接:将所有.o文件合并成一个.so或.out文件,处理所有.o文件节区在目标文件中的布局.
- 动态链接:将.so或a.out文件加载到内存,处理加载文件在的内存中的布局.
什么是重定位
重定位就是把程序的逻辑地址空间变换成内存中的实际物理地址空间的过程。它是实现多道程序在内存中同时运行的基础。重定位有两种,分别是动态重定位与静态重定位。
- 1.静态重定位:即在程序装入内存的过程中完成,是指在程序开始运行前,程序中的各个地址有关的项均已完成重定位,地址变换通常是在装入时一次完成的,以后不再改变,故称为静态重定位。也就是在生成可执行/共享目标文件的同时已完成地址的静态定位,它解决了可执行文件/共享目标文件的内部矛盾.
- 2.动态重定位:它不是在程序装入内存时完成的,而是CPU每次访问内存时 由动态地址变换机构(硬件)自动进行把相对地址转换为绝对地址。动态重定位需要软件和硬件相互配合完成。也就是说可执行文件/共享目标文件的外部矛盾需要外部环境解决,它向外提供了一份入住地球村的外交说明.即本篇最后部分内容.
重定位十种类型
- 重定位有10种类型,在实际中请对号入座,这些类型部分在本篇能见到,如下:


解读
- fPIC的全称是 Position Independent Code, 用于生成位置无关代码。
objdump命令
objdump命令是Linux下的反汇编目标文件或者可执行文件的命令,它以一种可阅读的格式让你更多地了解二进制文件可能带有的附加信息.本篇将用它说明静态重定位的实现细节和动态重定位前置条件准备.先整体走读下objdump命令
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump
Usage: objdump <option(s)> <file(s)>
Display information from object <file(s)>.
At least one of the following switches must be given:
-a, --archive-headers Display archive header information
-f, --file-headers Display the contents of the overall file header
-p, --private-headers Display object format specific file header contents
-P, --private=OPT,OPT... Display object format specific contents
-h, --[section-]headers Display the contents of the section headers
-x, --all-headers Display the contents of all headers
-d, --disassemble Display assembler contents of executable sections
-D, --disassemble-all Display assembler contents of all sections
--disassemble=<sym> Display assembler contents from <sym>
-S, --source Intermix source code with disassembly
--source-comment[=<txt>] Prefix lines of source code with <txt>
-s, --full-contents Display the full contents of all sections requested
-g, --debugging Display debug information in object file
-e, --debugging-tags Display debug information using ctags style
-G, --stabs Display (in raw form) any STABS info in the file
-W[lLiaprmfFsoRtUuTgAckK] or
--dwarf[=rawline,=decodedline,=info,=abbrev,=pubnames,=aranges,=macro,=frames,
=frames-interp,=str,=loc,=Ranges,=pubtypes,
=gdb_index,=trace_info,=trace_abbrev,=trace_aranges,
=addr,=cu_index,=links,=follow-links]
Display DWARF info in the file
--ctf=SECTION Display CTF info from SECTION
-t, --syms Display the contents of the symbol table(s)
-T, --dynamic-syms Display the contents of the dynamic symbol table
-r, --reloc Display the relocation entries in the file
-R, --dynamic-reloc Display the dynamic relocation entries in the file
@<file> Read options from <file>
-v, --version Display this program's version number
-i, --info List object formats and architectures supported
-H, --help Display this information
objdump -S ./obj/main.o
main.o是个可重定位文件,通过 readelf 可知
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# readelf -h ./obj/main.o
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -S ./obj/main.o
./obj/main.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <main>:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "part.h"
extern int g_int;
extern char *g_str;
int main() {
0: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
4: 55 push %rbp
5: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
8: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
int loc_int = 53;
c: c7 45 f4 35 00 00 00 movl $0x35,-0xc(%rbp)
char *loc_str = "harmony os";
13: 48 8d 05 00 00 00 00 lea 0x0(%rip),%rax # 1a <main+0x1a>
1a: 48 89 45 f8 mov %rax,-0x8(%rbp)
printf("main 开始 - 全局 g_int = %d, 全局 g_str = %s.\n", g_int, g_str);
1e: 48 8b 15 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rdx # 25 <main+0x25>
25: 8b 05 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%eax # 2b <main+0x2b>
2b: 89 c6 mov %eax,%esi
2d: 48 8d 3d 00 00 00 00 lea 0x0(%rip),%rdi # 34 <main+0x34>
34: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
39: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 3e <main+0x3e>
func_int(loc_int);
3e: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
41: 89 c7 mov %eax,%edi
43: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 48 <main+0x48>
func_str(loc_str);
48: 48 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax
4c: 48 89 c7 mov %rax,%rdi
4f: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 54 <main+0x54>
printf("main 结束 - 全局 g_int = %d, 全局 g_str = %s.\n", g_int, g_str);
54: 48 8b 15 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rdx # 5b <main+0x5b>
5b: 8b 05 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%eax # 61 <main+0x61>
61: 89 c6 mov %eax,%esi
63: 48 8d 3d 00 00 00 00 lea 0x0(%rip),%rdi # 6a <main+0x6a>
6a: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
6f: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 74 <main+0x74>
return 0;
74: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
79: c9 leaveq
7a: c3 retq
解读
- 注意那些 00 00 00 00部分,这些都是编译器暂时无法确定的内容.肉眼计算下此时OFFSET偏移位为 0x16,0x21,即下表内容
objdump -r ./obj/main.o
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -r ./obj/main.o
./obj/main.o: file format elf64-x86-64
RELOCATION RECORDS FOR [.text]:
OFFSET TYPE VALUE
0000000000000016 R_X86_64_PC32 .rodata-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000021 R_X86_64_PC32 g_str-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000027 R_X86_64_PC32 g_int-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000030 R_X86_64_PC32 .rodata+0x000000000000000c
000000000000003a R_X86_64_PLT32 printf-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000044 R_X86_64_PLT32 func_int-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000050 R_X86_64_PLT32 func_str-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000057 R_X86_64_PC32 g_str-0x0000000000000004
000000000000005d R_X86_64_PC32 g_int-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000066 R_X86_64_PC32 .rodata+0x0000000000000044
0000000000000070 R_X86_64_PLT32 printf-0x0000000000000004
解读
0x16,0x21对应的这些值都是 0,也就是说对于编译器不能确定的地址都这设置为空(0x000000),同时编译器都生成一一对应的记录,该记录告诉链接器在进行链接时要修正这条指令中函数的内存地址,并告知是什么重定位类型,要去哪里找数据填充.
- 外部全局变量重定位g_str,g_int
0000000000000021 R_X86_64_PC32 g_str-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000027 R_X86_64_PC32 g_int-0x0000000000000004
---
1e: 48 8b 15 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rdx # 25 <main+0x25>
25: 8b 05 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%eax # 2b <main+0x2b>
编译器连g_str在哪个.o文件都不知道,当然更不知道g_str运行时的地址,所以在g.o文件中设置一个重定位,要求后续过程根据"S(g_str内存地址)-A(0x04)",修改main.o镜像中0x21偏移处的值.
- 函数重定位,重定位类型为 R_X86_64_PLT32
000000000000003a R_X86_64_PLT32 printf-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000044 R_X86_64_PLT32 func_int-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000050 R_X86_64_PLT32 func_str-0x0000000000000004
0000000000000070 R_X86_64_PLT32 printf-0x0000000000000004
---
39: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 3e <main+0x3e>
43: e8 00 00 00 00 callq 48 <main+0x48>
同样编译器连``func_int,printf`在哪个.o文件都不知道,当然更不知道它们的运行时的地址,所以在main.o文件中设置一个重定位,后续将 修改main.o镜像中3a偏移处的值.
- 另一部分数据由本.o自己提供,如下
objdump -sj .rodata ./obj/main.o
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -sj .rodata ./obj/main.o
./obj/main.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Contents of section .rodata:
0000 6861726d 6f6e7920 6f730000 00000000 harmony os......
0010 6d61696e 20e5bc80 e5a78b20 2d20e585 main ...... - ..
0020 a8e5b180 20675f69 6e74203d 2025642c .... g_int = %d,
0030 20e585a8 e5b18020 675f7374 72203d20 ...... g_str =
0040 25732e0a 00000000 6d61696e 20e7bb93 %s......main ...
0050 e69d9f20 2d20e585 a8e5b180 20675f69 ... - ...... g_i
0060 6e74203d 2025642c 20e585a8 e5b18020 nt = %d, ......
0070 675f7374 72203d20 25732e0a 00 g_str = %s...
解读
- 内部变量重定位.
13: 48 8d 05 00 00 00 00 lea 0x0(%rip),%rax # 1a <main+0x1a>
---
0000000000000016 R_X86_64_PC32 .rodata-0x0000000000000004
因为是局部变量,编译器知道数据放在了 .rodata区,要求后续过程根据 “S(main.o镜像中.rodata的内存地址)-A(0x04)”,修改main.o镜像中0x16偏移处的值.
再分析经过静态链接之后的可执行文件
objdump -S ./bin/weharmony
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -S ./bin/weharmony
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000001188 <func_str>:
void func_str(char *str) {
1188: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
118c: 55 push %rbp
118d: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
1190: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
1194: 48 89 7d f8 mov %rdi,-0x8(%rbp)
g_str = str;
1198: 48 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax
119c: 48 89 05 75 2e 00 00 mov %rax,0x2e75(%rip) # 4018 <g_str>
printf("func_str g_str = %s.\n", g_str);
11a3: 48 8b 05 6e 2e 00 00 mov 0x2e6e(%rip),%rax # 4018 <g_str>
11aa: 48 89 c6 mov %rax,%rsi
11ad: 48 8d 3d 83 0e 00 00 lea 0xe83(%rip),%rdi # 2037 <_IO_stdin_used+0x37>
11b4: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
11b9: e8 92 fe ff ff callq 1050 <printf@plt>
11be: 90 nop
11bf: c9 leaveq
11c0: c3 retq
00000000000011c1 <main>:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "part.h"
extern int g_int;
extern char *g_str;
int main() {
11c1: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
11c5: 55 push %rbp
11c6: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
11c9: 48 83 ec 10 sub $0x10,%rsp
int loc_int = 53;
11cd: c7 45 f4 35 00 00 00 movl $0x35,-0xc(%rbp)
char *loc_str = "harmony os";
11d4: 48 8d 05 75 0e 00 00 lea 0xe75(%rip),%rax # 2050 <_IO_stdin_used+0x50>
11db: 48 89 45 f8 mov %rax,-0x8(%rbp)
printf("main 开始 - 全局 g_int = %d, 全局 g_str = %s.\n", g_int, g_str);
11df: 48 8b 15 32 2e 00 00 mov 0x2e32(%rip),%rdx # 4018 <g_str>
11e6: 8b 05 24 2e 00 00 mov 0x2e24(%rip),%eax # 4010 <g_int>
11ec: 89 c6 mov %eax,%esi
11ee: 48 8d 3d 6b 0e 00 00 lea 0xe6b(%rip),%rdi # 2060 <_IO_stdin_used+0x60>
11f5: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
11fa: e8 51 fe ff ff callq 1050 <printf@plt>
func_int(loc_int);
11ff: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
1202: 89 c7 mov %eax,%edi
1204: e8 40 ff ff ff callq 1149 <func_int>
func_str(loc_str);
1209: 48 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax
120d: 48 89 c7 mov %rax,%rdi
1210: e8 73 ff ff ff callq 1188 <func_str>
printf("main 结束 - 全局 g_int = %d, 全局 g_str = %s.\n", g_int, g_str);
1215: 48 8b 15 fc 2d 00 00 mov 0x2dfc(%rip),%rdx # 4018 <g_str>
121c: 8b 05 ee 2d 00 00 mov 0x2dee(%rip),%eax # 4010 <g_int>
1222: 89 c6 mov %eax,%esi
1224: 48 8d 3d 6d 0e 00 00 lea 0xe6d(%rip),%rdi # 2098 <_IO_stdin_used+0x98>
122b: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1230: e8 1b fe ff ff callq 1050 <printf@plt>
return 0;
1235: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
123a: c9 leaveq
123b: c3 retq
123c: 0f 1f 40 00 nopl 0x0(%rax)
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -s ./bin/weharmony
...省略部分
Contents of section .plt.got:
1040 f30f1efa f2ff25ad 2f00000f 1f440000 ......%./....D..
Contents of section .plt.sec:
1050 f30f1efa f2ff2575 2f00000f 1f440000 ......%u/....D..
Contents of section .data:
4000 00000000 00000000 08400000 00000000 .........@......
4010 33000000 00000000 08200000 00000000 3........ ......
Contents of section .rodata:
2000 01000200 00000000 68656c6c 6f20776f ........hello wo
2010 726c6400 00000000 66756e63 5f696e74 rld.....func_int
2020 20675f69 6e74203d 2025642c 746d7020 g_int = %d,tmp
2030 3d202564 2e0a0066 756e635f 73747220 = %d...func_str
2040 675f7374 72203d20 25732e0a 00000000 g_str = %s......
2050 6861726d 6f6e7920 6f730000 00000000 harmony os......
2060 6d61696e 20e5bc80 e5a78b20 2d20e585 main ...... - ..
2070 a8e5b180 20675f69 6e74203d 2025642c .... g_int = %d,
2080 20e585a8 e5b18020 675f7374 72203d20 ...... g_str =
2090 25732e0a 00000000 6d61696e 20e7bb93 %s......main ...
20a0 e69d9f20 2d20e585 a8e5b180 20675f69 ... - ...... g_i
20b0 6e74203d 2025642c 20e585a8 e5b18020 nt = %d, ......
20c0 675f7374 72203d20 25732e0a 00 g_str = %s...
解读
- main.o中被重定位的部分不再是00 00 00 00都已经有了实际的数据,例如:
char *loc_str = "harmony os";
11d4: 48 8d 05 75 0e 00 00 lea 0xe75(%rip),%rax # 2050 <_IO_stdin_used+0x50>
对应的# 2050 <_IO_stdin_used+0x50>地址数据正是.rodata 2050位置的 harmony os
- 看main()中的
void func_str(char *str) {
1188: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
- callq 1188 1188正是 func_str的入口地址
void func_str(char *str) {
1188: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
- 看全局变量 g_str``g_int对应的链接地址 0x4018和 0x4010
1215: 48 8b 15 fc 2d 00 00 mov 0x2dfc(%rip),%rdx # 4018 <g_str>
121c: 8b 05 ee 2d 00 00 mov 0x2dee(%rip),%eax # 4010 <g_int>
由.data区提供
4000 00000000 00000000 08400000 00000000 .........@......
4010 33000000 00000000 08200000 00000000 3........ ......
0x4010 = 0x33 = 51
- main函数中调用 printf代码为 callq 1050
1230: e8 1b fe ff ff callq 1050 <printf@plt>
内容由.plt.sec区提供,并反汇编该区为
Contents of section .plt.sec:
1050 f30f1efa f2ff2575 2f00000f 1f440000 ......%u/....D..
Disassembly of section .plt.sec:
0000000000001050 <printf@plt>:
1050: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
1054: f2 ff 25 75 2f 00 00 bnd jmpq *0x2f75(%rip) # 3fd0 <printf@GLIBC_2.2.5>
105b: 0f 1f 44 00 00 nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
注意3fd0,需要运行时环境提供,加载器动态重定位实现.
- 总结下来就是 weharmony 已完成了所有.o文件的静态重定位部分, 组合成一个新的可执行文件,其中只还有动态链接部分尚未完成,因为那需要运行时重定位地址.如下:
objdump -R ./bin/weharmony
root@5e3abe332c5a:/home/docker/test4harmony/54# objdump -R ./bin/weharmony
./bin/weharmony: file format elf64-x86-64
DYNAMIC RELOCATION RECORDS
OFFSET TYPE VALUE
0000000000003db8 R_X86_64_RELATIVE *ABS*+0x0000000000001140
0000000000003dc0 R_X86_64_RELATIVE *ABS*+0x0000000000001100
0000000000004008 R_X86_64_RELATIVE *ABS*+0x0000000000004008
0000000000004018 R_X86_64_RELATIVE *ABS*+0x0000000000002008
0000000000003fd8 R_X86_64_GLOB_DAT _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
0000000000003fe0 R_X86_64_GLOB_DAT __libc_start_main@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000003fe8 R_X86_64_GLOB_DAT __gmon_start__
0000000000003ff0 R_X86_64_GLOB_DAT _ITM_registerTMCloneTable
0000000000003ff8 R_X86_64_GLOB_DAT __cxa_finalize@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000003fd0 R_X86_64_JUMP_SLOT printf@GLIBC_2.2.5
解读
- 这是weharmony对运行时环境提交的一份外交说明,有了它就可以与国际接轨,入住地球村.
- 这份说明其他部分很陌生,看个熟悉的3fd0,其动态链接重定位类型为 R_X86_64_JUMP_SLOT,它在告诉动态加载器,在运行时环境中找到 printf并完成动
如果想更深入的学习 OpenHarmony (鸿蒙南向)全栈开发的内容,可以参考以下学习文档:
OpenHarmony 开发环境搭建:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
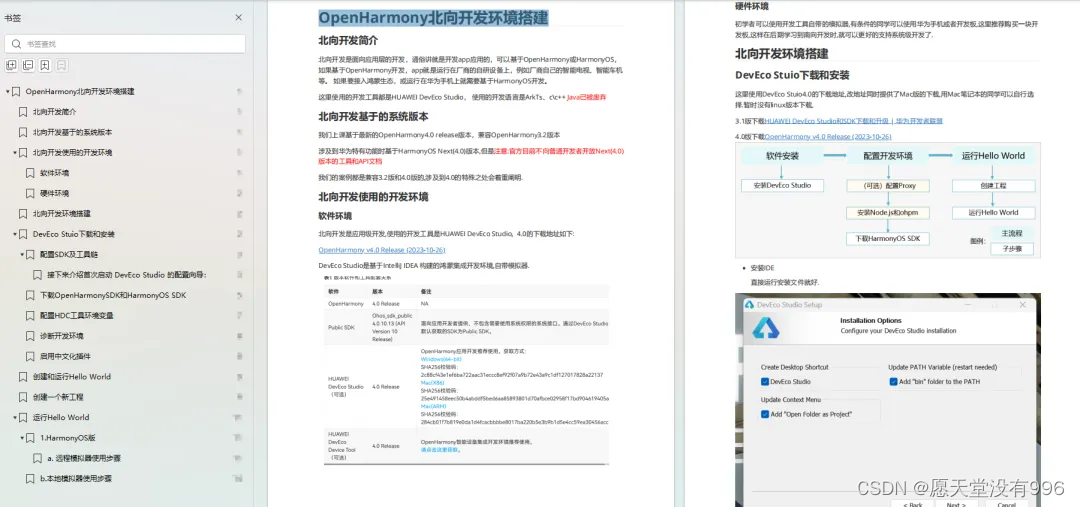
《OpenHarmony源码解析》:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
- 搭建开发环境
- Windows 开发环境的搭建
- Ubuntu 开发环境搭建
- Linux 与 Windows 之间的文件共享
- ……

系统架构分析:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
- 构建子系统
- 启动流程
- 子系统
- 分布式任务调度子系统
- 分布式通信子系统
- 驱动子系统
- ……

OpenHarmony 设备开发学习手册:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy

OpenHarmony面试题(内含参考答案):https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
写在最后
- 如果你觉得这篇内容对你还蛮有帮助,我想邀请你帮我三个小忙:
- 点赞,转发,有你们的 『点赞和评论』,才是我创造的动力。
- 关注小编,同时可以期待后续文章ing🚀,不定期分享原创知识。
- 想要获取更多完整鸿蒙最新学习资源,请移步前往小编:
https://gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH


























 3060
3060











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








