1 简介
Vibration signal analysis has become one of the important methods for machinery fault diagnosis. Extraction of weak fault features from vibration signals with heavy background noise remains a challenging problem. In this paper, we first introduce the idea of algorithm-aware sparsity-assisted methods for fault feature enhancement, which extends model-aware sparsity-assisted fault diagnosis and allows a more flexible and convenient algorithm design. In the framework of algorithm-aware methods, we define the generalized structured shrinkage operators and construct the generalized structured shrinkage algorithm (GSSA) to overcome the disadvantages of l1-norm regularization based fault feature enhancement methods. We then perform a series of simulation studies and two experimental cases to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. Additionally, comparisons with model-aware methods, including basis pursuit denoising and windowed-group-lasso, and fast kurtogram further verify the advantages of GSSA for weak fault feature enhancement.
2 部分代码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%clcclear allclose alladdpath(genpath(fileparts(mfilename('fullpath'))));rng('default')rng(19)%% Figure initializationglobal FontSize FontName;Tstring = 'Time (s)';Fstring = 'Frequency (Hz)';Astring = 'Amp (m/s^2)';FontSize = 11; FontName = 'Times New Roman';MarkerSize = 4; LineWidth = 1;%%FlagFigureAutoSave = 1;currentFolder = pwd;%% SimulationFs = 20480;N = 4096;mode = 'outer';% [Sig_Impulse , t] = MakeSignalBearing( Fs, N, 'outer');Sig_Impulse = QuasiPeiodicImpulseResponse_AM(N, Fs);t = (0 : N-1) / Fs;Sig_Cos = 0.5 * cos(2*pi*160*t') + 0.3 * cos(2*pi*320*t');Sigma = 0.6;Noise = Sigma * randn(N , 1);Sig_Combine = Sig_Cos + Sig_Impulse' + Noise;% Sig_Combine = Sig_Cos + Sig_Impulse + Noise;[ yf2, f2 ] = Dofft( Sig_Combine , Fs , 0);K = 10 : 10 : 1000;for i = 1 : length(K)%% Setting the parametersiQ = 2;r = 5;J =10;now = ComputeNow(N,Q,r,J,'radix2');AH = @(Sig) tqwt_radix2(Sig, Q, r, J);A = @(w) itqwt_radix2(w, Q, r , N);lam = 1.0 * now;rho = 1;%% method1 : Generalized Structured ShrinkageK1 = K(i);Method1.Name = 'WGL';Method1.Initial_Size = 5;Method1.SubName = 'MC';Method1.gamma = 2;Method1.window = 'gausswin';z1 = IterGSS(Sig_Combine, A, AH, lam, rho, K1, Method1);%% method2 : TQWT-L1 basedMethod2.Name = 'L1';K2 = K(i);z2 = IterGSS(Sig_Combine, A, AH, lam, rho, K2, Method2);%% method3 : Neighbor thresholdingparams.Q = 2;params.r = 5;params.J =10;K3 = K(i);z3 = TQWTDe( Sig_Combine, params , 'nc', K3);%% method4 : Structured ShrinkageMethod3.Name = 'WGL';Method3.Initial_Size = 5;Method3.SubName = 'L1';Method3.window = 'gausswin';K4 = K(i);z4 = IterGSS(Sig_Combine, A, AH, lam, rho, K4, Method3);z1 = real(A(z1));z2 = real(A(z2));% z3 = real(A(z3));z4 = real(A(z4));%% Calculate RMSEGST_RMSE(i) = RMSE(z1, Sig_Impulse);L1_RMSE(i) = RMSE(z2, Sig_Impulse);NC_RMSE(i) = RMSE(z3', Sig_Impulse);ST_RMSE(i) = RMSE(z4, Sig_Impulse);endsave('Harmonic_Inference_Best_K.mat', 'K', 'GST_RMSE', 'L1_RMSE', 'NC_RMSE', 'ST_RMSE')
3 仿真结果
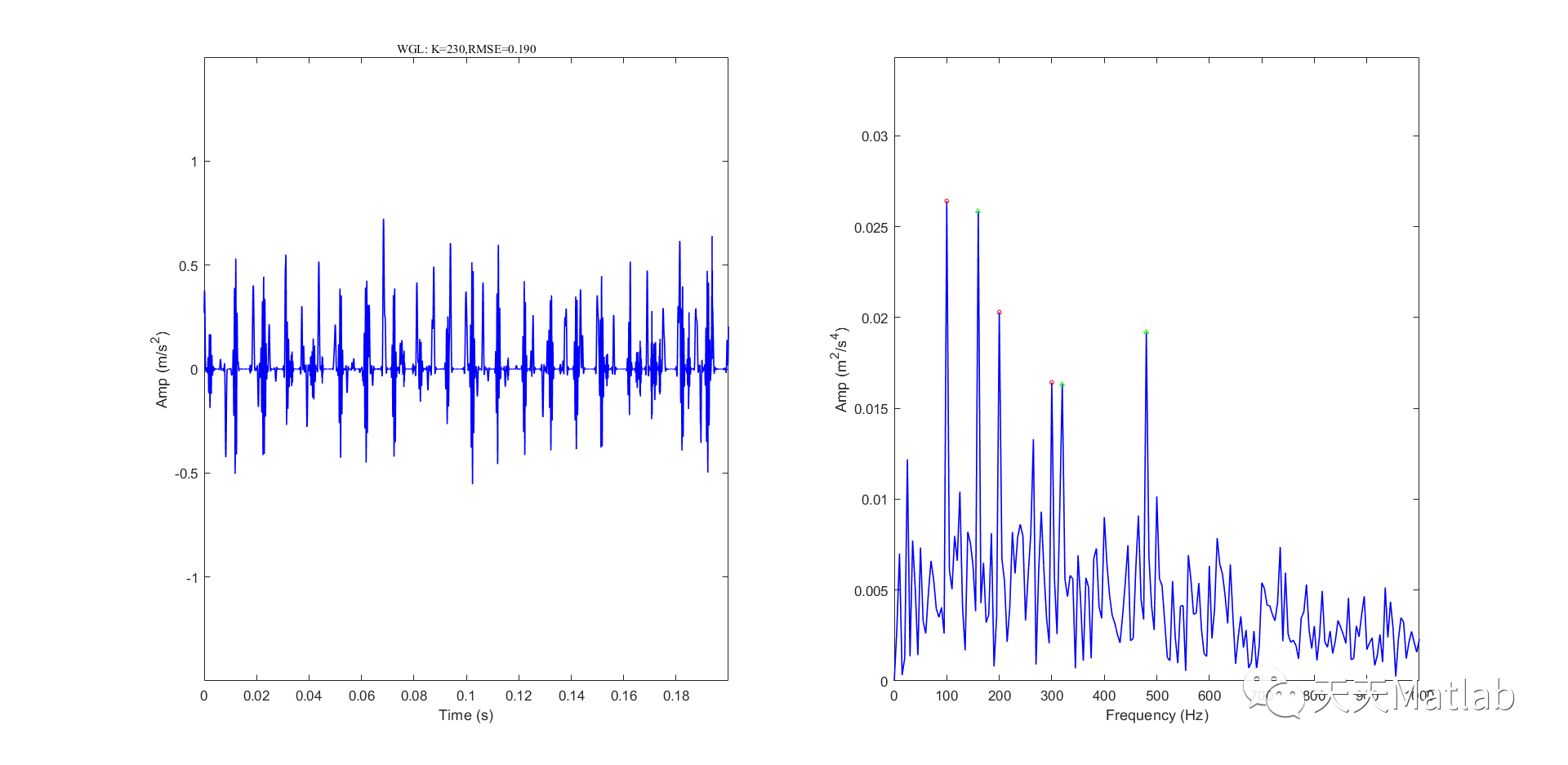


4 参考文献
[1] Zhao Z , Wang S , Xu W , et al. Sparsity-Assisted Fault Feature Enhancement: Algorithm-Aware Versus Model-Aware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, PP(99):1-1.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










