DCGAN是在GAN上进行的扩展,唯一的区别就是生成器和判别器分别使用转置卷积层和卷积层。在论文Unsupervised Representation Learning With Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks中提出。¶
from __future__ import print_function
#%matplotlib inline
import argparse
import os
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision.datasets as dset
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.utils as vutils
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
from IPython.display import HTML
# Set random seed for reproducibility
manualSeed = 999
#manualSeed = random.randint(1, 10000) # use if you want new results
print("Random Seed: ", manualSeed)
random.seed(manualSeed)
torch.manual_seed(manualSeed)
m = nn.ConvTranspose2d(100, 1024, (4,4), stride=(1,1),bias=False)
input = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 100, 1, 1))
output = m(input)
print(output.size())
print(output[0][0])
# Root directory for dataset
dataroot = "/home/kesci/input/dongman9005"
# Number of workers for dataloader
workers = 2
# Batch size during training
batch_size = 128
# Spatial size of training images. All images will be resized to this
# size using a transformer.
image_size = 64
# Number of channels in the training images. For color images this is 3
nc = 3
# Size of z latent vector (i.e. size of generator input)
nz = 100
# Size of feature maps in generator
ngf = 128
# Size of feature maps in discriminator
ndf = 128
# Number of training epochs
num_epochs = 1
# Learning rate for optimizers
lr = 0.0002
# Beta1 hyperparam for Adam optimizers
beta1 = 0.5
# Number of GPUs available. Use 0 for CPU mode.
ngpu = 0
# We can use an image folder dataset the way we have it setup.
# Create the dataset
dataset = dset.ImageFolder(root=dataroot,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(image_size),
transforms.CenterCrop(image_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]))
# creat the dataloader
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, num_workers=workers)
# device which device we want to run on
divice = torch.device("cuda:0" if (torch.cuda.is_available() and ngpu > 0) else "cpu")
# Plot some training images
real_batch = next(iter(dataloader))
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Training Images")
#print("real_batch:",type(real_batch),len(real_batch),type(real_batch[0]),real_batch[0].size())
#print(type(real_batch[0][0:64]),real_batch[0][0:64].size())
#print(type(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0][:64],padding=2, normalize=True)),vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0][:64],padding=2, normalize=True).size())
#print(type(np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0][:64],padding=2, normalize=True).cpu(),(1,2,0))),np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0][:64],padding=2, normalize=True).cpu(),(1,2,0)).size())
plt.imshow(np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0][:64],
padding=2, normalize=True).cpu(),(1,2,0)))

def weights_init(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0)
# Generator Code
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is Z, going into a convolution
nn.ConvTranspose2d( nz, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf, nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# state size. (nc) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
# Create the generator
netG = Generator(ngpu)
# Handle multi-gpu if desired
if (ngpu > 1):
netG = nn.DataParallel(netG, list(range(ngpu)))
# Apply the weights_init function to randomly initialize all weights
# to mean=0, stdev=0.2.
netG.apply(weights_init)
# Print the model
print(netG)
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is (nc) x 64 x 64
nn.Conv2d(nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
实例化判别器并输出网络结构
# Create the Discriminator
netD = Discriminator(ngpu)
# Handle multi-gpu if desired
if (ngpu > 1):
netD = nn.DataParallel(netD, list(range(ngpu)))
# Apply the weights_init function to randomly initialize all weights
# to mean=0, stdev=0.2.
netD.apply(weights_init)
# Print the model
# print(netG)
print(netD)
Discriminator(
(main): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 128, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace)
(2): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(3): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(4): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace)
(5): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(6): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(7): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace)
(8): Conv2d(512, 1024, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(9): BatchNorm2d(1024, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(10): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace)
(11): Conv2d(1024, 1, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(12): Sigmoid()
)
)
损失函数及优化器
# Initialize BCELoss function
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
# Create batch of latent vectors that we will use to visualize
# the progression of the generator
fixed_noise = torch.randn(128, nz, 1, 1)
#print(type(fixed_noise),fixed_noise.size())
#print(fixed_noise[0].size(),"\n",fixed_noise[0])
#print(torch.randn(100))
# fixed_z_ = torch.randn((5 * 5, 100)).view(-1, 100, 1, 1) # fixed noise
# print(type(fixed_z_),"\n",fixed_z_.size())
# Establish convention for real and fake labels during training
real_label = 1
fake_label = 0
# Setup Adam optimizers for both G and D
optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
训练
第一部分—更新判别器
第二部分—更新生成器
# Training Loop
# Lists to keep track of progress
img_list = []
G_losses = []
D_losses = []
iters = 0
print("Starting Training Loop...")
# For each epoch
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# For each batch in the dataloader
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
############################
# (1) Update D network: maximize log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z)))
###########################
## Train with all-real batch
netD.zero_grad()
# Format batch
real_cpu = data[0]
# print(type(data[0]),data[0].size(0),"\n",type(data[1]),data[1].size(),data[1])
b_size = real_cpu.size(0)
label = torch.full((b_size,), real_label)
# print(type(label),label.size(),label)
# Forward pass real batch through D
# print(type(real_cpu),real_cpu.size())
output = netD(real_cpu).view(-1)
# print(output)
# Calculate loss on all-real batch
errD_real = criterion(output, label)
# print(errD_real)
# Calculate gradients for D in backward pass
errD_real.backward()
D_x = output.mean().item()
# print(type(output),type(output.mean()),output.mean())
## Train with all-fake batch
# Generate batch of latent vectors
noise = torch.randn(b_size, nz, 1, 1)
# Generate fake image batch with G
fake = netG(noise)
# print(type(fake),fake.size())
label.fill_(fake_label)
# print(type(label),label)
# Classify all fake batch with D
# print(type(fake.detach),fake.detach().size())
output = netD(fake.detach()).view(-1)
# print(output)
# Calculate D's loss on the all-fake batch
errD_fake = criterion(output, label)
# Calculate the gradients for this batch
errD_fake.backward()
# print(errD_fake)
D_G_z1 = output.mean().item()
# Add the gradients from the all-real and all-fake batches
errD = errD_real + errD_fake
# Update D
optimizerD.step()
############################
# (2) Update G network: maximize log(D(G(z)))
###########################
netG.zero_grad()
label.fill_(real_label) # fake labels are real for generator cost
# Since we just updated D, perform another forward pass of all-fake batch through D
output = netD(fake).view(-1)
# Calculate G's loss based on this output
errG = criterion(output, label)
# Calculate gradients for G
errG.backward()
D_G_z2 = output.mean().item()
# Update G
optimizerG.step()
# Output training stats
if i % 50 == 0:
print('[%d/%d][%d/%d]\tLoss_D: %.4f\tLoss_G: %.4f\tD(x): %.4f\tD(G(z)): %.4f / %.4f'
% (epoch, num_epochs, i, len(dataloader),
errD.item(), errG.item(), D_x, D_G_z1, D_G_z2))
# Save Losses for plotting later
G_losses.append(errG.item())
D_losses.append(errD.item())
# Check how the generator is doing by saving G's output on fixed_noise
if (iters % 500 == 0) or ((epoch == num_epochs-1) and (i == len(dataloader)-1)):
with torch.no_grad():
fake = netG(fixed_noise).detach().cpu()
img_list.append(vutils.make_grid(fake, padding=2, normalize=True))
iters += 1
break
# Training Loop
# Lists to keep track of progress
img_list = []
G_losses = []
D_losses = []
iters = 0
print("loading model...")
netG = Generator(ngpu)
netD = Discriminator(ngpu)
optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
checkpoint = torch.load("/home/kesci/input/animation_203680/model_animation-20.pth",map_location = 'cpu')
start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
netG.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net_G'])
netD.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net_D'])
optimizerG.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_G'])
optimizerD.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_D'])
print("loaded!")
# For each batch in the dataloader
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
noise = torch.randn(64, nz, 1, 1)
with torch.no_grad():
fake = netG(noise).detach().cpu()
img_list.append(vutils.make_grid(fake, padding=2, normalize=True))
iters += 1
if(iters == 8):
break
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.title("Generator and Discriminator Loss During Training")
plt.plot(G_losses,label="G")
plt.plot(D_losses,label="D")
plt.xlabel("iterations")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#%%capture
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.axis("off")
ims = [[plt.imshow(np.transpose(i,(1,2,0)), animated=True)] for i in img_list]
ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, ims, interval=1000, repeat_delay=1000, blit=True)
HTML(ani.to_jshtml())
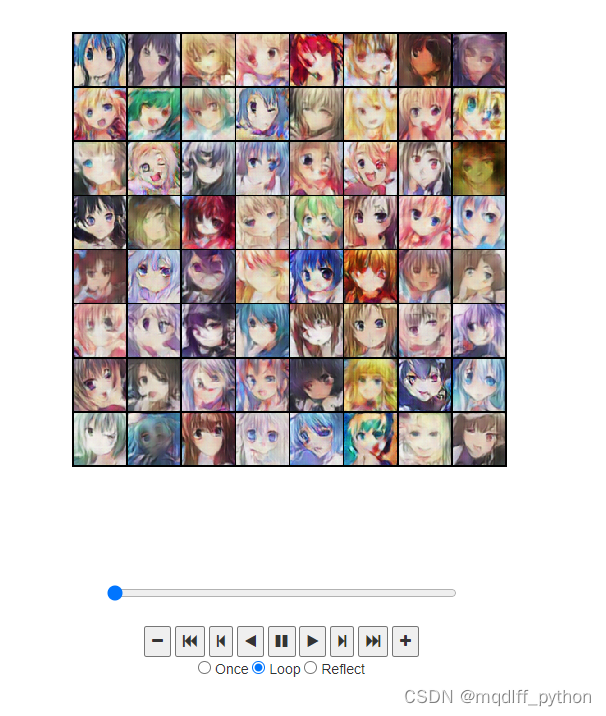
生成器输出 前面我们保存了生成器的输出,现在我们用动画的形式来观察结果,按下播放键开始动画。

























 220
220











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








