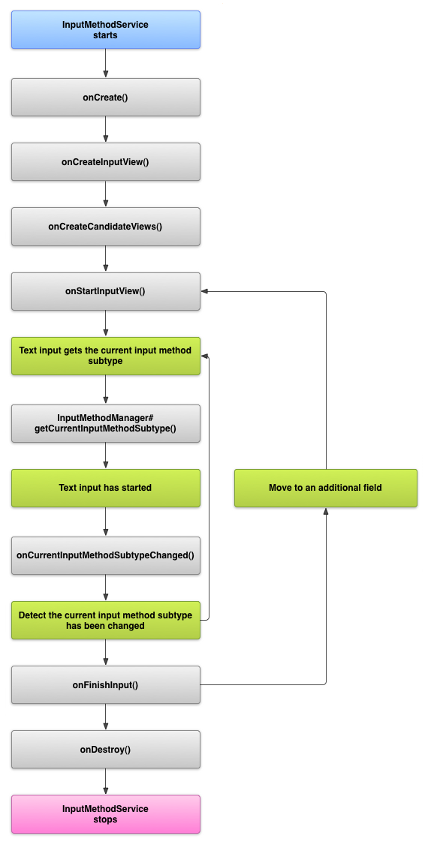
一、输入法的生命周期
二、写一个类继承InputMethodService
package com.input.application;
import android.inputmethodservice.InputMethodService;
import android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
public class MyImeService extends InputMethodService{
@Override
public View onCreateInputView() {
View mkeyView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(
R.layout.keyboardview, null);
new KeyboardUtil(this, (KeyboardView) mkeyView.findViewById(R.id.keyboardView));
return mkeyView;
}
@Override
public View onCreateCandidatesView() {
return null;
}
public void commitText(String data) {
getCurrentInputConnection().commitText(data, 0); // 往输入框输出内容
setCandidatesViewShown(false); // 隐藏 CandidatesView
}
public void deleteText(){
getCurrentInputConnection().deleteSurroundingText(1, 0);
}
public void hideInputMethod() {
hideWindow();
}
}
key_priview.xml的布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff8888ff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/tips"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textSize="40sp" />
keyboardview.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/keyboardView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:keyBackground="@drawable/btn_keyboard_key"
android:keyPreviewLayout="@layout/key_preview"
android:keyTextColor="@android:color/white" />
package com.input.application;
import android.inputmethodservice.Keyboard;
import android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView;
import android.inputmethodservice.KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.inputmethod.InputConnection;
public class KeyboardUtil {
private KeyboardView keyboardView;
private MyImeService myImeService;
private Keyboard k1;// 字母键盘
public KeyboardUtil(MyImeService myImeService1, KeyboardView keyboardView1) {
super();
keyboardView = keyboardView1;
keyboardView.setOnKeyboardActionListener(listener);
myImeService = myImeService1;
k1 = new Keyboard(myImeService.getApplicationContext(), R.xml.qwerty);
keyboardView.setKeyboard(k1);
keyboardView.setEnabled(true);
keyboardView.setPreviewEnabled(true);
}
private OnKeyboardActionListener listener = new OnKeyboardActionListener() {
@Override
public void swipeUp() {
}
@Override
public void swipeRight() {
}
@Override
public void swipeLeft() {
}
@Override
public void swipeDown() {
}
@Override
public void onText(CharSequence text) {
}
@Override
public void onRelease(int primaryCode) {
}
@Override
public void onPress(int primaryCode) {
}
@Override
public void onKey(int primaryCode, int[] keyCodes) {
InputConnection ic = myImeService.getCurrentInputConnection();
switch (primaryCode) {
case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DELETE:
// myImeService.deleteText();
ic.deleteSurroundingText(1,0);
break;
case Keyboard.KEYCODE_CANCEL:
// myImeService.hideInputMethod();
break;
case Keyboard.KEYCODE_DONE:
ic.sendKeyEvent(new KeyEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN,KeyEvent.KEYCODE_NUMPAD_ENTER));
break;
default:
// myImeService.commitText(Character.toString((char) primaryCode));
ic.commitText(String.valueOf((char)primaryCode),1);
break;
}
}
};
}
method.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<input-method xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<subtype
android:label="@string/subtype_en_US"
android:imeSubtypeLocale="en_US"
android:imeSubtypeMode="keyboard" />
</input-method>qwerty.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Keyboard android:keyWidth="10.000002%p"
android:keyHeight="@dimen/key_height"
android:horizontalGap="0.0px"
android:verticalGap="0.0px"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<Row>
<Key android:codes="113" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"
android:keyLabel="q" />
<Key android:codes="119" android:keyLabel="ww" />
<Key android:codes="101" android:keyLabel="e" />
<Key android:codes="114" android:keyLabel="r" />
<Key android:codes="116" android:keyLabel="t" />
<Key android:codes="121" android:keyLabel="y" />
<Key android:codes="117" android:keyLabel="u" />
<Key android:codes="105" android:keyLabel="i" />
<Key android:codes="111" android:keyLabel="o" />
<Key android:codes="112" android:keyEdgeFlags="right"
android:keyLabel="p" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key android:horizontalGap="4.999995%p" android:codes="97"
android:keyEdgeFlags="left" android:keyLabel="a" />
<Key android:codes="115" android:keyLabel="s" />
<Key android:codes="100" android:keyLabel="d" />
<Key android:codes="102" android:keyLabel="f" />
<Key android:codes="103" android:keyLabel="g" />
<Key android:codes="104" android:keyLabel="h" />
<Key android:codes="106" android:keyLabel="j" />
<Key android:codes="107" android:keyLabel="k" />
<Key android:codes="108" android:keyEdgeFlags="right"
android:keyLabel="l" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key android:keyWidth="14.999998%p" android:codes="-1"
android:keyEdgeFlags="left" android:isModifier="true"
android:isSticky="true" android:keyIcon="@drawable/sym_keyboard_shift" />
<Key android:codes="122" android:keyLabel="z" />
<Key android:codes="120" android:keyLabel="x" />
<Key android:codes="99" android:keyLabel="c" />
<Key android:codes="118" android:keyLabel="v" />
<Key android:codes="98" android:keyLabel="b" />
<Key android:codes="110" android:keyLabel="n" />
<Key android:codes="109" android:keyLabel="m" />
<Key android:keyWidth="14.999998%p" android:codes="-5"
android:keyEdgeFlags="right" android:isRepeatable="true"
android:keyIcon="@drawable/sym_keyboard_delete" />
</Row>
<Row android:rowEdgeFlags="bottom">
<Key android:keyWidth="20.000004%p" android:codes="-2"
android:keyLabel="12#" />
<Key android:keyWidth="14.999998%p" android:codes="44"
android:keyLabel="," />
<Key android:keyWidth="29.999996%p" android:codes="32"
android:isRepeatable="true" android:keyIcon="@drawable/sym_keyboard_space" />
<Key android:keyWidth="14.999998%p" android:codes="46"
android:keyLabel="." />
<Key android:keyWidth="20.000004%p" android:codes="-3"
android:keyEdgeFlags="right" android:keyLabel="完成" />
</Row>
</Keyboard>
三、在Mainfest中声明组件
在android系统中,输入法是包含特定的输入法服务的应用。应用的mainfest中必需声明该服务、所需要的权限、action.view.InputMethod、定义了输入法的metadata。总之,需要提供允许修改输入法行为的接口设置,也可以定义从系统设置中启动的“设置”界面。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.input.application" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<service
android:name=".MyImeService"
android:label="MyCustomIME"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_INPUT_METHOD" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.view.InputMethod" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.view.im"
android:resource="@xml/method" />
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
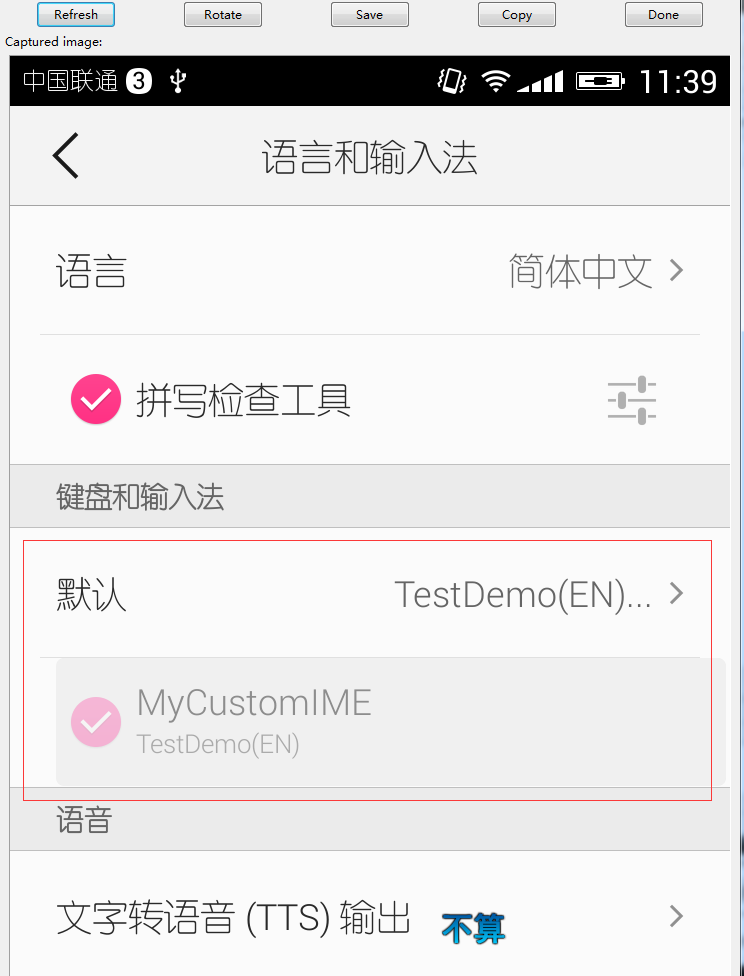
四、在设置中选中自定义的输入法
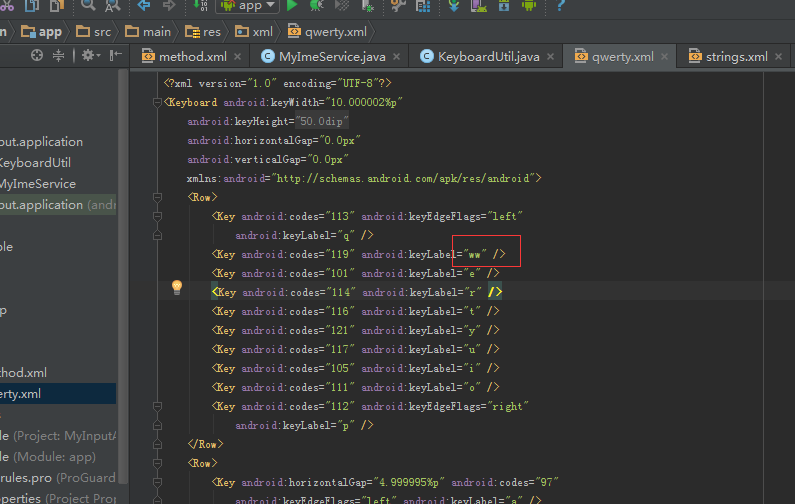
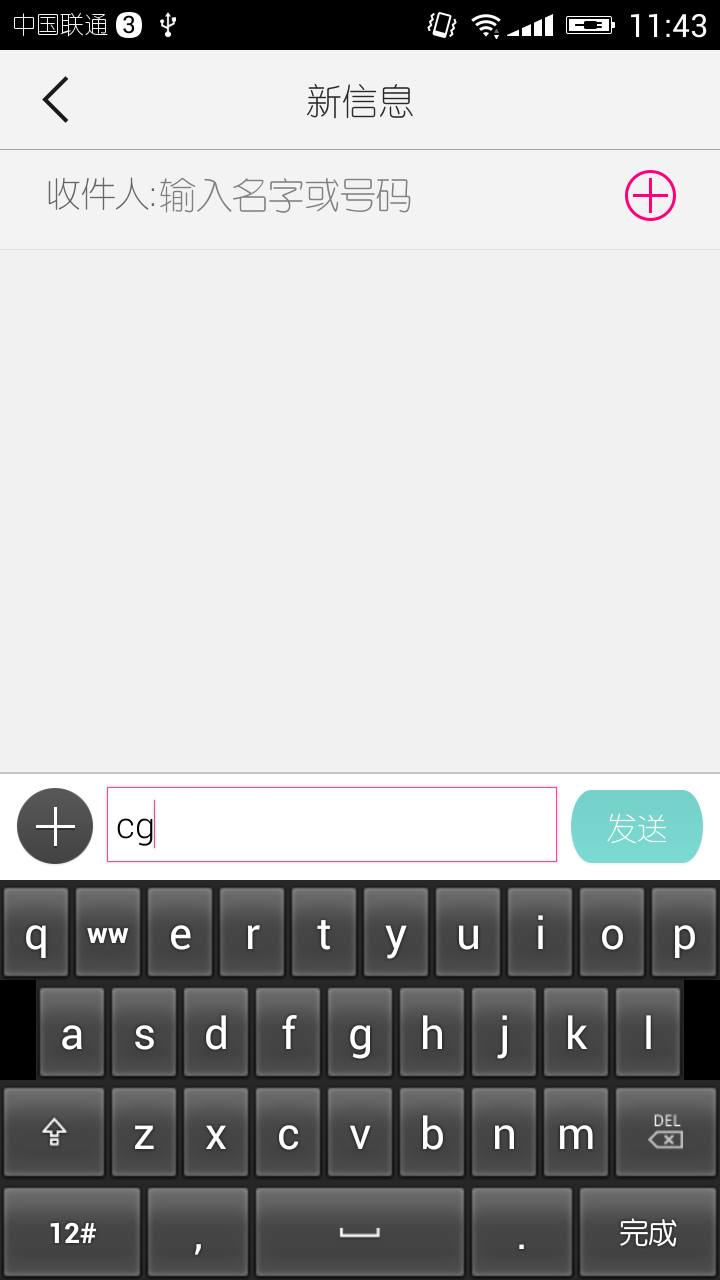
五、运行后可以看到自定义的输入法(显示的w建故意写成了两个ww,方便与其它的输入法区分)
注:
1.参考资料:
https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/text/creating-input-method.html
http://blog.csdn.net/dreamintheworld/article/details/50917804
http://blog.csdn.net/dreamintheworld/article/details/50917055
http://www.cnblogs.com/over140/archive/2011/01/12/1933468.html
https://notes.wanghao.work/2015-09-04-Create-a-Simple-Android-Keyboard.html
http://blog.csdn.net/aqi00/article/details/73199269
http://410063005.iteye.com/blog/1768313
http://mft.iteye.com/blog/2332291
2.输入法的API
输入法的类在包android.inputmethodservice和android.view.inputmethod下。KeyEvent是处理字母键盘字母的重要的类。
输入法的核心是继承InputMethodService的服务组件。总之,该服务的生命周期提供了输入法界面、处理用户输入、传递文字到当前聚焦区域的回调。
BaseInputConnection
读取文字、传递到文本框、将原始的键盘事件发送到应用。应用应该继承这个类而不是实现接口InputConnection
KeyboardView
渲染键盘并响应用户的输入事件。键盘的界面需要在xml文件夹中声明
3.声明设置界面(可选)
ACTION_MAIN声明了该界面是应用的主入口
<!-- Optional: an activity for controlling the IME settings --> <activity android:name="FastInputIMESettings" android:label="@string/fast_input_settings"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/> </intent-filter> </activity>4.Input View
Input View是用户点击输入文字的界面。当输入法第一次显示的时候,系统调用onCreateInputView()的回调。当实现这个方法的时候,创建一个像显示在输入法窗口的布局并将布局返回给系统。下面的片段是实现onCreateInputView()方法的例子:
@Override
public View onCreateInputView() {
MyKeyboardView inputView =
(MyKeyboardView) getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.input, null);
inputView.setOnKeyboardActionListener(this);
inputView.setKeyboard(mLatinKeyboard);
return mInputView;
}5.Candidates View
Candidates View是输入法显示可能或者建议的文字让用户选择的界面。在输入法的生命周期,当显示candidates view的时候会调用方法onCreateCandidatesView()。在实现这个方法的时候,可以返回一个布局用来显示,如果不想显示任何布局,可以返回null。返回null是默认的,如果不想提供候选界面,可以不实现。
6.向应用发送文字
在输入法中,通过编辑光标附近的文字,通过发送单独的key事件,可以向应用发送文字,也可以通过实例InputConnection传递文字。通过调用
InputMethodService.getCurrentInputConnection()返回该实例
7.编辑光标附近的文字
在编辑光标附近的文字时,BaseInputConnection中的一些有用的方法是:
getTextBeforeCursor():返回光标之前的字符个数
getTextAfterCursor():返回光标之后的字符个数
deleteSurroundingText():删除光标之前和之后的特定个数的字符
commitText():将字符发送到文本框并重新设置光标位置
下面的代码片段显示了如何将光标左侧的四个字符替换为“hello”
InputConnection ic = getCurrentInputConnection();
ic.deleteSurroundingText(4, 0);
ic.commitText("Hello", 1);
ic.commitText("!", 1);8.与输入法进行交互
重写方法onKeyDown()和onKeyUp()可以实现交互。
如果不想自己处理,在方法中调用super()
9.创建输入法的类型
输入法类型允许输入法暴露多个输入模型和语言。输入法类型:
--本地语言例如en_US或者fr_FR
--输入模型例如语音(voice)、键盘(keyboard)、或者手写(handwriting)
--其它的输入类型,构词或者特殊的输入法属性,例如数字键盘或者传统的键盘
在xml文件中定义subtypes,使用<subtype>元素。下面的代码片段订阅了两个输入法类型:一个是本地语言---英语,另一个是法语:
<input-method xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.softkeyboard.Settings"
android:icon="@drawable/ime_icon">
<subtype android:name="@string/display_name_english_keyboard_ime"
android:icon="@drawable/subtype_icon_english_keyboard_ime"
android:imeSubtypeLanguage="en_US"
android:imeSubtypeMode="keyboard"
android:imeSubtypeExtraValue="somePrivateOption=true" />
<subtype android:name="@string/display_name_french_keyboard_ime"
android:icon="@drawable/subtype_icon_french_keyboard_ime"
android:imeSubtypeLanguage="fr_FR"
android:imeSubtypeMode="keyboard"
android:imeSubtypeExtraValue="foobar=30,someInternalOption=false" />
<subtype android:name="@string/display_name_german_keyboard_ime" ... />
</input-method>10.为了保证输入类型在界面中显示正确,使用s%来获取与本地label一致的subtype label。下面是两段示例代码。第一段是输入法xml文件中的一段:
<subtype
android:label="@string/label_subtype_generic"
android:imeSubtypeLocale="en_US"
android:icon="@drawable/icon_en_us"
android:imeSubtypeMode="keyboard" />下面的片段是string.xml文件中的一段。在输入法的界面中使用label_subtype_generic来定义subtype的标签,定义如下:
<string name="label_subtype_generic">%s</string>11.选择输入法类型
android系统管理着所有输入法暴露出来的输入法类型。在提示栏中,用户可以选择当前输入法的输入类型。
在提示栏栏中选择输入法类型
在系统设置中设置输入法偏好
在系统设置中选择输入法
Settings --> Language&input --> 选择包含实现了输入法类型的设置






















 1552
1552

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








