#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class myString
{
private:
char *str;
int size;
public:
myString():size(10)
{
str = new char [size];
strcpy(str,"");
cout << this->str<<endl;
}
myString(const char *str)
{
size = strlen(str);
this->str = new char [size+1];
strcpy(this->str , str);
cout << this->str<<endl;
}
myString(const myString &other):str(new char[other.size+1]),size(other.size)
{
int i = 0 ;
while (*(other.str+i) != '\0' )
{
this->str[i] = *(other.str+i);
i++;
}
cout << this->str<<endl;
}
~myString()
{
delete []this->str;
cout << "析构成功" << endl;
}
void judge_empty()
{
if(!*(this->str))
{
cout << "空" <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "非空" <<endl;
}
}
int len_size ()
{
return this->size;
}
const char *c_str()
{
return this->str;
}
char at (int i)
{
return *(str+i);
}
};
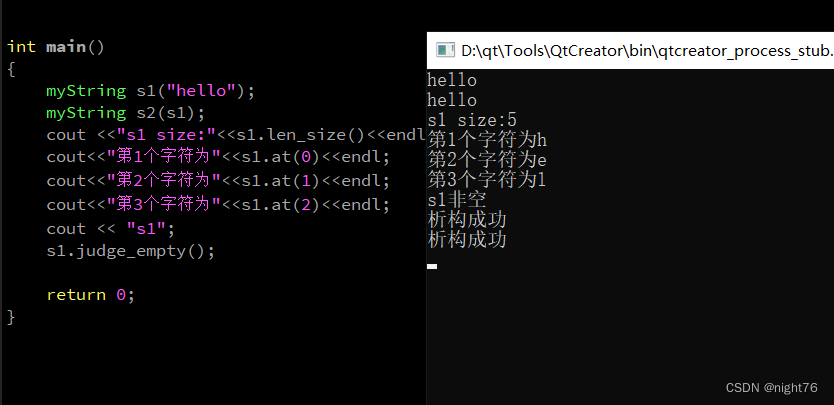
int main()
{
myString s1("hello");
myString s2(s1);
cout <<"s1 size:"<<s1.len_size()<<endl;
cout<<"第1个字符为"<<s1.at(0)<<endl;
cout<<"第2个字符为"<<s1.at(1)<<endl;
cout<<"第3个字符为"<<s1.at(2)<<endl;
cout << "s1";
s1.judge_empty();
return 0;
}






















 489
489











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








