1、首先要掌握
链表包括单链表、双链表和环形链表,环形链表可以解决约瑟夫问题。
链表的入口称为头节点head。
| 插入/删除时间复杂度 | 查询时间复杂度 | 适用场景 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数组 | O(n) | O(1) | 数据量固定,频繁查询,较少增删 |
| 链表 | O(1) | O(n) | 数据量不固定,频繁增删,较少查询 |
2、21题合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4] 输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
这里的技巧是使用了一个虚拟头节点dummyHead,然后设置一个移动指针cur,指向这个虚拟头节点,然后通过循环体中不断给cur.next赋值,最后输出dummyHead.next。
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 类似归并排序中的合并过程
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);//虚拟头节点
ListNode cur = dummyHead;//临时指针,指向当前变量
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;//给cur.next赋值
cur = cur.next;//继续移动
l1 = l1.next;//继续移动
} else {
cur.next = l2;
cur = cur.next;//继续移动
l2 = l2.next;//继续移动
}
}
// 任一为空,直接连接另一条链表
if (l1 == null) {
cur.next = l2;
} else {
cur.next = l1;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
3、83题删除链表中的重复元素
存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点
head,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 。返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
//虚拟头节点
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;//指向链表的头
ListNode cur = head;
if (head == null){
return head;
}
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == cur.val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;//删除cur的下一个节点
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
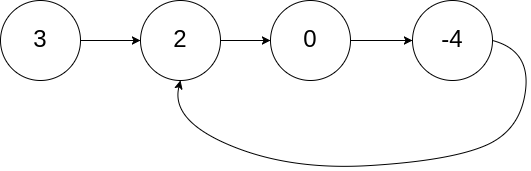
4、141题环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
快慢指针法:
给定两个指针,一个一次移动一步叫做慢指针,一个一次移动两步叫做快指针。
如果存在环,则两个指针一定在环中相遇
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode low = head;//慢指针
ListNode fast = head.next;//快指针
while(low != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;//快指针走到头,说明没有环
}
low = low.next;//移动慢指针
fast = fast.next.next;//移动快指针
}
if(low == fast){
return true;//两个指针相遇了
}else{
return false;
}
}
5、203题移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0);
temp.next = head;
ListNode cur = temp;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.val == val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return temp.next;
}
6、206题反转链表
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
递归法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur) {
if(cur == null) {
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
双指针法
没有额外的链表,而规定了一个pre节点,将每一个当前节点cur都指向pre
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode temp = null;
while(cur!=null){
temp = cur;
cur = cur.next;
temp.next = pre;
pre = temp;
}
return pre;
}
算法要画图!








 本文详细解析了力扣中关于链表的六个经典问题,包括合并两个有序链表、删除重复元素、判断环形链表、移除指定元素、反转链表等,提供了不同的解题思路和算法实现,强调了画图在理解链表问题中的重要性。
本文详细解析了力扣中关于链表的六个经典问题,包括合并两个有序链表、删除重复元素、判断环形链表、移除指定元素、反转链表等,提供了不同的解题思路和算法实现,强调了画图在理解链表问题中的重要性。















 173
173

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








