Introduction to Formal Verification
Requirements
- Assertion/Cover
- Assume(Constraint)
- Synthesizable RTL
Formal Results
- Proof
- Falsification
- Bounded Proof
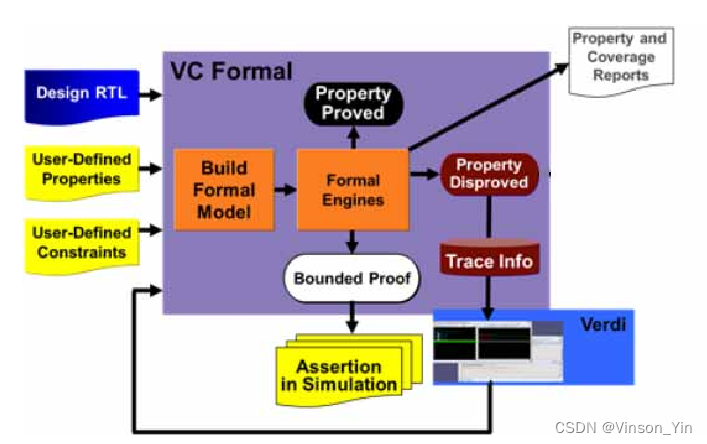
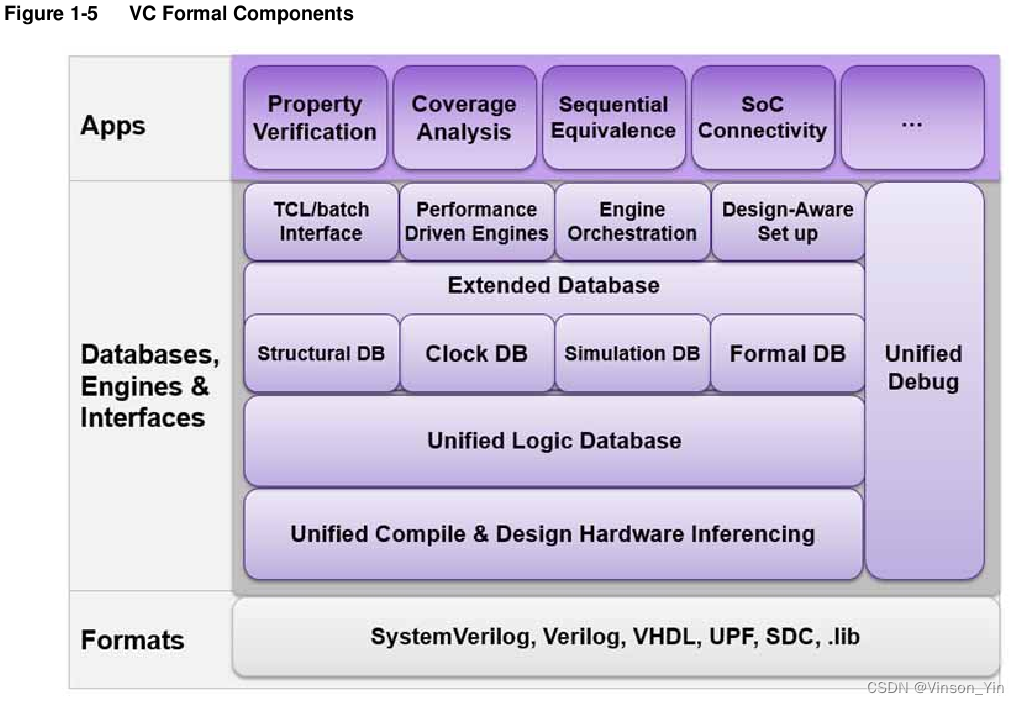
VC Formal
Flow
Components
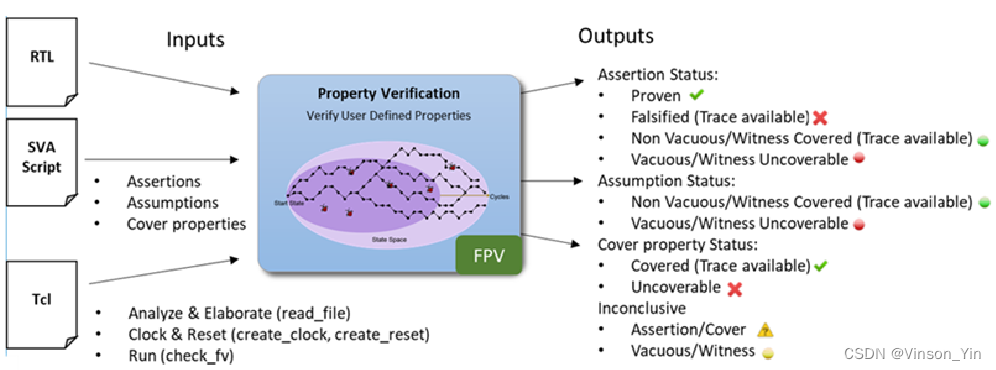
FPV
Methodology
Inputs for FPV
Analyze and elaborate commands (example, read_file )
Clock and reset commands (example, create_clock, create_reset )
Execute commands (example, check_fv )
Report commands (example, report_fv )
Onputs for FPV
Property Status
- Assertion status: Proven, Falsified, Vacuous(先决条件没有cover到), Witness-Coverable, Uncoverable and Inconclusive(没有得到证明)
- Assume status: Non-Vacuous, Vacuous(assume无效),Uncoverable and Inconclusive
- Cover status: Coverable and Uncoverable
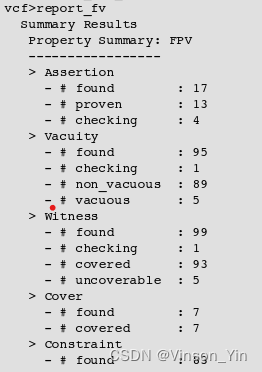
Execue FPV
vcf -f run.tcl
vcf -f run.tcl -verdi
Analyzing Results
report_fv
Property Control
Formal Runtime Control
控制time/memory/engine
- set_fml_var fml_max_time <time, ex. 24H>
- set_fml_var fml_progress_time_limit <time, ex. 100M>
- set_fml_var fml_max_mem <Maximum memory size>
Controlling Engine Effort
- set_engine [-on|-off] <engine id>
- set_fml_var fml_effort <effort level, ex. high>
Controlling Resume
- set_fml_var fml_enable_resume true
- set_fml_var fml_enable_resume_depth true
Controlling Grid Usage
- set_grid_usage -type [LSF|SGE|RTDA]=<#_of_workers> ...
- report_grid_usage
Convergence Improvement
- snip_driver
- set_blackbox
- set_abstractions
- get_abstractions
- report_abstraction
snip_driver
example:
packages/formal_sva_lib/fml_abstracted_models/ram_and_fifo/example/xxx
usage:
snip_driver spec.reg
snip_driver impl.reg
fvassume -expr { spec.reg == impl.reg }
And if we add the following assertions:
fvassert -expr { $driver(spec.reg) == $driver(impl.reg) }
Verdi Debug Command
生成proven的波形的
set_fml_var fml_witness_on true
Setting up Enviroment
Session
%vcf -session my_path/my_session
%vcf> save_session -session <session_name>
Application mods
vcf -fmode FPV|CC
set_fml_appmode FPV|CC
Compiling Designs
read_file
analyze
elaborate
Verilog + SVA example
read_file –format verilog –sva –top arb –vcs “-sverilog arb.v arb.sva arb_bind.v”
or
analyze –format verilog –vcs “-sverilog arb.v arb.sva arb_bind.v”
elaborate arb -sva
SystemVerilog+SVA example
read_file –format sverilog –sva –top arb –vcs “arb.sv arb.sva arb_bind.v”
or
analyze –format sverilog –vcs “arb.v arb.sva arb_bind.v”
elaborate arb -sva
Support for Multiple-Edge-Assignment and the Multiple-Process-Assignment
set_fml_var fml_enable_ndmerge true
Changing Severity of VC Static Error Messages
%vcf> set_message_severity -names message_names <error|warning|info>
eg: %vcf> set_message_severity -name CC_UID017 error #severity of CC_UID017 should be error
%vcf> set_message_error_action [-stop_at_error_count error_count] <stop | continue>
eg: set_message_error_action stop ##stop on CC_UID017 error
Block Boxing Modules in a Design
set_blackbox 必须再read_file 或者elaborate 之前
set_blackbox -help
set_blackbox [-level N] [-exclude <design>] [-cells <cell>] [-designs <design>]
eg:
set_blackbox -designs {moduleA}
read_file -format verilog -top top top.v
Specifying User-defined Clocks
create_clock -help
create_clock -period <period_value> (Specifies clock period value)
[-name <clock_name>] (Specifies clock name)
[-waveform <edge_list>] (Specifies edge list)
[-add] (Add new options to the original clock)
[-comment <string>] (Specifies comment)
[-refclk] (Use clock as reference clock [formal])
[-initial <value>] (Specify clock initial value (0/1 - default 1) at time 0
create_clock clk -waveform {10 90} -period 100
Specifying Reference Clock
create_clock clk -period 100 [-refclk]
Specifying User-defined Resets
create_reset -help
create_reset
[-sync] (If signal drives synchronous reset)
[-async] (If signal drives asynchronous reset)
[-type reset|set|load] (specifies the type of reset signal, default is reset)
[-name <rst_name>] (specifies the name of reset signal)
[-sense low|high|any] (specifies active value for reset)
[-clock <clk_name>] (specifies list of clock name)
[-synchronized] (specifies whether reset de assertion is syncronized or not)
Specifying Single Resets
create_reset rst_n -sense low
(same: sim_force rst -apply 1’b0, set_constant rst -apply 1’b1)
Constraints and Properties for Formal Analysis
Constraint
Constraints for formal analysis can be added as properties in the RTL source file, checker files, or script properties using the fvassume command.
%vcf> fvassume -help
fvassume const_pipeid –stable -expr {pipe_id} #pipe_id is either 0 or 1 in cycle 1, and remains
constant thereafter.一开始随机,后面stable
depth constraint
fvassume -expr <expr> -depth <n>
eg: fvassume -expr { state == 2'b0 } -depth 3 #reset之后前3个cycle 约束state == 0
Environment Global Constraints
Environment constraints 生效在reset和formal analysis期间,必须在sim_run command 之前,应用于primary inputs, undriven nets, snip points or black box outputs
eg: fvassume -env -expr {vld_status == 1 }
Constant Constraints
set_constant scan_en –value 0
If used together on the same signal, the value set by set_constant can be overridden by sim_force during the reset phase.
example: signal SCAN_EN should be set to 1 during reset and changed to 0 during formal analysis as the following code snippet shows:
set_constant SCAN_EN –apply 0
sim_force SCAN_EN –apply 1
...
sim_run
sim_save_reset
如果出现在进行重置和形式化分析时,可能会遇到由于不匹配而导致的造假初始状态,可以使用 fvassume
sim_force SSE –apply 1
...
sim_run
sim_save_reset
fvassume sse0 –expr {SSE == 0}
Property Attributes
Automatically Extracted Properties
AEPs 是tool 分析完design后自动提取出来的property,Use the read_file or elaborate command to enable AEPs.
read_file -aep arith_oflow+x_assign -sva -top $top -format verilog -vcs “-sverilog -f demo.files”
read_file -aep all -sva -top $top -format verilog -vcs “-sverilog -f demo.files”
Coverage Properties
read_file -cov line+cond -sva -top $top -format verilog -vcs “-sverilog -f demo.files”
read_file -cov all -sva -top $top -format verilog -vcs “-sverilog -f demo.files”
Source Properties
fvassume, fvassert, fvcover, fvenable and fvdisable等命令改变source property使用
Script Properties
- fvassert property_name –expr <expression>
- fvassume property_name –expr <“expression”>
- fvcover property_name –expr <“expression”>
Builtin functions
-
$onehot(<expr>):
-
$onehot0(<expr>):
-
$countbits(<expr>):
-
$countones(<expr>):
-
$isunknown(<expr>):
-
$signed(<expr>):
-
$unsigned(<expr>):
-
$stable(<stableExpr>):
-
$rose(<expr>):
-
$fell(<expr>):
-
$past(<expr>[, <#cycles>):
Performing and Configuring VC Formal Checks
Performing VC Formal Checks
vcf> check_fv -help
check_fv
[-block] (Makes command input block while this command is active.)
[-run_finish <cmds>] (Set of commands to run when this command finishes in non-
blocking mode.)
[-stop] (Stops execution)
[-break <#of falsification(s)>]
[-property <list-or-collection-of-properties>] (List or collection of properties)
[-subtype <list-of-subtypes>] (goal subtype selection: property, vacuity, witness)
[-assume] (Use proven assertions and uncoverable covers as constraints)
eg:
check_fv –run_finish {
report_fv –list –status falsified > falsification_list.txt
report_fv –list –status proven > proven_list.txt
report_fv –list –status unknown > unknown_list.txt
quit
}
Running on Compute Farm
Configuring Grids
vcf> set_grid_usage -help
Use the following command to configure an LSF farm for 10 Linux redhat 4 machines, where each machine has at least 8G memory:
set_grid_usage -type lsf=10 -control { bsub -q bnormal -R arch==glinux -R os_version==WS4_0 -R rusage[mem=8000] }
Report of Grid Configuration
vcf> report_grid_usage
Debugging the Grid Setup
vcf> report_fml_hosts
Controlling check_fv Runs
set_fml_var fml_max_time 10H
set_fml_var fml_max_mem 8GB
Restoring Session
set_app_var fml_auto_save true/false
vcf –session <session_name> –restore\
Viewing Progress of check_fv Runs
report_fml_engines
report_fml_jobs
Profiling bound Statistics for Goals
set_app_var fml_orc_bmc_depth_profile true
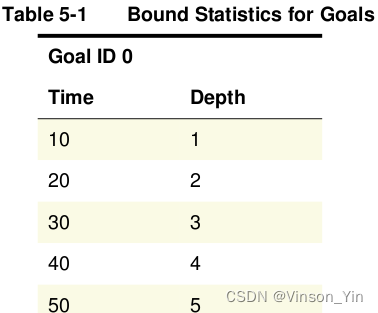
Supporting the Bug Hunting Feature
%vcf> bug_hunting_config [-mode 0-4] [-random <0|1>] [-saveDir dir]
%vcf> report_fml_bug_hunting [-jobId <id>] [-status <0|1>] [-nlines <n>] [-pos
<head|tail|all>]
Providing User-Defined Property Order to Improve Bug Hunting
The fvorder Command:
%vcf> fvorder [-clear] [-print]<list-of-names-ids-or-collections-of-properties>
Debugging Results of Formal Verification






















 1266
1266











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








