There are hundreds of
JVM parameters or
JVM Options exists inside sun JDK and its virtually impossible to keep track of every single
JVM option and based on my experience we don't even use most of JVM flags except couple of important JVM option related to java heap size, java options for printing garbage collection details and most likely JVM switches for setting up remote debugging in Java. but there are many other useful category of JVM parameters which you at least like to be familiar even if not intending to use it more frequently. In this article we will see examples of 10 different categories of
JVM parameter which I found useful and use more frequently than other. I would recommend to get a full knowledge of what does a particular JVM options does by referring official list of JVM options.
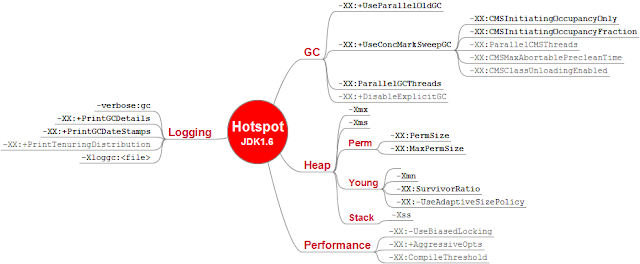
JVM parameters in Java
On the basis of how we specify
JVM option it can be divided into two parts, JVM Options which starts with –X and those which starts with -XX:
1)
JVM Options that begin with -X are non-standard (thy are not guaranteed to be supported on all JVM implementations), and are subject to change without notice in subsequent releases of the JDK.
2)
JVM Options or parameters which are specified with -XX are not stable and are not recommended for casual use. These options are subject to change without notice also.
I was thinking about writing post on JVM options when I completed my post on
Java Heap Size and
Java Garbage Collection because these are two main area where we see usages of various JVM flags. But it didn’t happened even after I covered OutOfMemoryError post which has some
JVM option to solve OutOfMemoryError in Java. Now I am happy that I have completed this piece of information and its ready to be published. As always I look for your feedback, suggestions and any other JVM flags which I have missed and you guys find useful to share.
Good knowledge of JVM options specially related to GC tuning is important for time critical application e.g. high volume low latency electronic trading platform where every micro seconds matter. though getting right combination requires lot of profiling and trial and error and depends heavily on nature of trading application.
Good knowledge of JVM options specially related to GC tuning is important for time critical application e.g. high volume low latency electronic trading platform where every micro seconds matter. though getting right combination requires lot of profiling and trial and error and depends heavily on nature of trading application.
Important Points about JVM Options:
1) Boolean JVM options can be turned on with -XX:+ and can be turned off with -XX:-.
2) Numeric JVM Options can be set with -XX:=. Numbers can include 'm' or 'M' for megabytes, 'k' or 'K' for kilobytes, and 'g' or 'G' for gigabytes (for example, 32k is the same as 32768).
3) String JVM options can be set by using -XX:=, and usually used to specify a file, a path, or a list of commands.
The command
java -help lists the standard options (standard across different JVM implementations) for the Java application launcher. The
command java -X can be used to see the Java application launcher's non-standard (X for extension specific to that JVM) arguments.The -X options are non-standard and subject to change without notice. If you wish to detect which JVM arguments your currently running Java application is using, you can use the ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getInputArguments()
Now here is my list of important JVM flags, switches, options or parameters which is most commonly used while running Java applications:
1) JVM memory options related to java heap size
Following three JVM options are used to specify initial and max heap size and thread stack size while running Java programs.
-Xms set initial Java heap size
-Xmx set maximum Java heap size
-Xss> set java thread stack size
2) JVM option to print gc details
-verbose:gc logs garbage collector runs and how long they're taking. I generally use this as my first tool to investigate if GC is a bottleneck for a given application.
-XX:+PrintGCDetails includes the data from -verbose:gc but also adds information about the size of the new generation and more accurate timings.
-XX:-PrintGCTimeStamps Print timestamps at garbage collection.
3) JVM parameters to specify Java Garbage collector
-XX:+UseParallelGC Use parallel garbage collection for scavenges
-XX:-UseConcMarkSweepGC Use concurrent mark-sweep collection for the old generation. (Introduced in 1.4.1)
-XX:-UseSerialGC Use serial garbage collection. (Introduced in 5.0.)
beware when you use GC Parameters if you are working on time critical application e.g. high frequency trading application. As GC is time consuming operation and its desired to create a balance.
beware when you use GC Parameters if you are working on time critical application e.g. high frequency trading application. As GC is time consuming operation and its desired to create a balance.
4) JVM debug options JVM options for remote debugging
-Xdebug -Xnoagent -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=8000
to read more about remote debugging check How to Setup Java remote debugging in Eclipse and 10 Java debugging tips in Eclipse
to read more about remote debugging check How to Setup Java remote debugging in Eclipse and 10 Java debugging tips in Eclipse
5) JVM options related to profiling
-Xprof
-Xrunhprof
6) JVM options related to java classpath
Xbootclasspath specifies classpath entries you want loaded without verification. The JVM verifies all classes it loads to ensure they don't try to dereference an object with an int, pop extra entries off the stack or push too many, and so on. This verification is part of the reason why the JVM is very stable, but it's also rather costly, and responsible for a large part of start up delay. Putting classes on the bootclasspath skips this cost, but should only be used when you know the classes have been verified many times before. In JRuby, this reduced startup time by half or more for a simple script. The -
Xbootclasspath option can be used to either prepend (/p) or append (/a) resources to the bootstrap classpath. You Can read more about Java Classpath in my articles
How Classpath Works in Java and
How to Solve ClassNotFoundException in Java
7) JVM options to change Perm Gen Size
These JVM optiosn are quite useful to solve
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError:Perm Gen Space.
-XX:PermSize and MaxPermSize
-XX:NewRatio=2 Ratio of new/old generation sizes.
-XX:MaxPermSize=64m Size of the Permanent Generation.
8) JVM parameters to trace classloading and unloading
-XX:+TraceClassLoading and
-XX:+TraceClassUnloading are two JVM options which we use to print logging information whenever classes loads into JVM or unloads from JVM. These JVM flags are extremely useful if you have any memory leak related to classloader and or suspecting that classes are not unloading or garbage collected.
9) JVM switches related to logging
-XX:+TraceClassLoading and -XX:+TraceClassUnloading print information class loads and unloads. Useful for investigating if you have a class leak or if old classes (like JITed Ruby methods in JRuby) are getting collected or not. You can read more about logging in Java on my post
10 Tips while logging in Java
-XX:+PrintCompilation prints out the name of each Java method Hotspot decides to JIT compile. The list will usually show a bunch of core Java class methods initially, and then turn to methods in your application. In JRuby, it eventually starts to show Ruby methods as well
10) JVM Switches for debugging purpose
-XX:HeapDumpPath=./java_pid.hprof Path to directory or file name for heap dump.
-XX:-PrintConcurrentLocks Print java.util.concurrent locks in Ctrl-Break thread dump.
-XX:-PrintCommandLineFlags Print flags that appeared on the command line.
That’s all on JVM Options, I understand its not possible to remember all JVM flags but at-least having an idea of what kind of JVM flags are available is good asset. Image for JVM parameters is from Java tuning and Nutshell. For full list of JVM options you can refer these link from Oracle Java site:
Java Hotspot VM Options
Read more: http://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2011/11/hotspot-jvm-options-java-examples.html#ixzz3fgKpvnDJ





















 98
98

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








