#include <CGAL/Nef_polyhedron_S2.h>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Nef_polyhedron_S2.h>
//#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel.h>
//#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Lazy_exact_nt.h>
#include <CGAL/Exact_rational.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <iomanip>
//遇到浮点数精度问题,会导致Nef_polyhedron构造失败
//typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<doublet> LazyFloat;
//typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<CGAL::MP_Float> LazyFloat;
//typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<LazyFloat> Kernel;
//typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
//找了很久得到的解决方法!!!
typedef CGAL::Quotient<CGAL::MP_Float> Exact_NT; // doesn't do exact sqrt()
typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<Exact_NT> LazyFloat;
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<LazyFloat> Kernel;
typedef CGAL::Nef_polyhedron_S2<Kernel> Nef_polyhedron;
typedef Nef_polyhedron::Sphere_point Nef_Sphere_point;
typedef Nef_polyhedron::Sphere_segment Nef_Sphere_segment;
typedef Nef_polyhedron::SVertex_const_handle SVertex_const_handle;
typedef Nef_polyhedron::SVertex_const_iterator SVertex_const_iterator;
typedef Nef_polyhedron::SHalfedge_const_iterator SHalfedge_const_iterator;
#ifndef M_PI
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
#endif
const static double Rad2Deg = 180.0 / M_PI;
const static double Deg2Rad = M_PI / 180.0;
//通过经纬度创建球面的点,归一化的,输入单位:角度制
Nef_Sphere_point createPoint(double lon0, double lat0)
{
//假定:X轴为经纬度为<0,0>的方向,Z轴指北
double lon = lon0 * Deg2Rad;
double lat = lat0 * Deg2Rad;
LazyFloat x = std::cos(lat) * std::cos(lon);
LazyFloat y = std::cos(lat) * std::sin(lon);
LazyFloat z = std::sin(lat);
Nef_Sphere_point pt(x, y, z);
std::cout << std::setprecision(14) << std::setiosflags(std::ios::fixed)
<< "Sphere_point \t" << lon0 << ", \t" << lat0 << ": \t" << pt << "\n";
return pt;
}
//从归一化的三维点得到经纬高,alt期望为0(TODO 1: 但是没有符合期望,暂不理解)
void getLLA(double x, double y, double z, double &lon, double &lat, double &alt)
{
lon = 0;
lat = 0;
alt = 0;
double rr = x*x + y*y +z*z;
//assert(std::fabs(rr-1.0) < 0.001);
double r = std::sqrt(rr);
alt = r - 1.0;
double z_r = z / r;
lon = Rad2Deg * atan2(y, x);
lat = Rad2Deg * asin(z_r);
}
int main()
{
//注意:先不考虑扁率,仅考虑正球面上的布尔运算
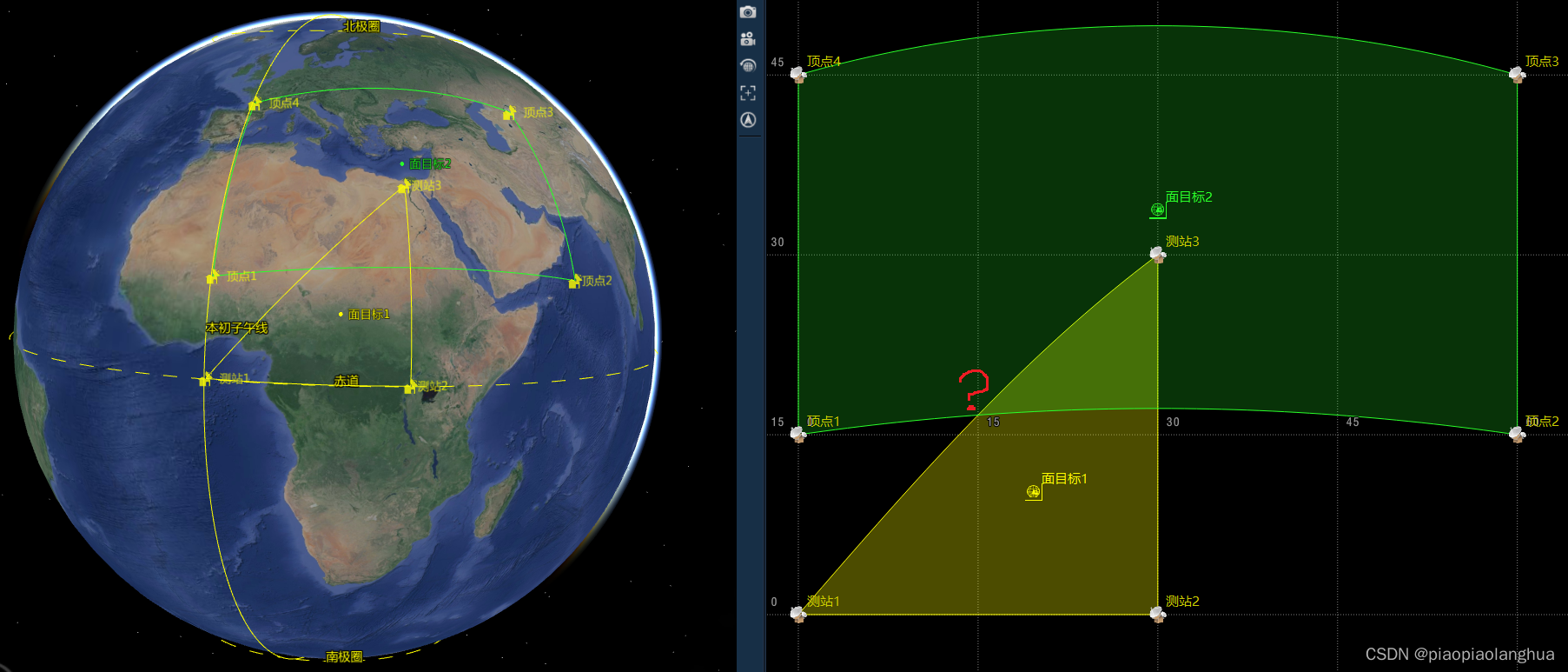
//面目标1 经、纬度:<0,0> <30,0> <30,30>
//面目标2 经、纬度:<0,15> <60,15> <60,45> <0,45>
//LazyFloat::set_relative_precision_of_to_double(1e-3); //1e-30, TODO 2: 好像没毛影响,暂不理解
Nef_Sphere_point cz1 = createPoint(0, 0);
Nef_Sphere_point cz2 = createPoint(30,0);
Nef_Sphere_point cz3 = createPoint(30,30);
Nef_Sphere_point dd1 = createPoint(0, 15);
Nef_Sphere_point dd2 = createPoint(60,15);
Nef_Sphere_point dd3 = createPoint(60,45);
Nef_Sphere_point dd4 = createPoint(0, 45);
//Nef_polyhedron构造方法参考官方:Nef_S2/nef_s2_construction.cpp
Nef_Sphere_segment cz_s1(cz1,cz2);
Nef_Sphere_segment cz_s2(cz2,cz3);
Nef_Sphere_segment cz_s3(cz3,cz1);
Nef_Sphere_segment dd_s1(dd1,dd2);
Nef_Sphere_segment dd_s2(dd2,dd3);
Nef_Sphere_segment dd_s3(dd3,dd4);
Nef_Sphere_segment dd_s4(dd4,dd1);
//std::cout << "cz_s2: " << cz_s1.source() << "," << cz_s1.target() << "," << cz_s1.is_short() << std::endl;
Nef_Sphere_segment triangle[] = { cz_s1, cz_s2, cz_s3 };
Nef_Sphere_segment rectangle[] = { dd_s1, dd_s2, dd_s3, dd_s4 };
const Nef_polyhedron N1(triangle, triangle+3, Nef_polyhedron::INCLUDED);
const Nef_polyhedron N2(rectangle, rectangle+4, Nef_polyhedron::INCLUDED);
const Nef_polyhedron N3 = N1 * N2;
//---- 以下是Nef_polyhedron_S2遍历相关的代码 ----
//std::cout << N3.is_empty() << "\n" << N3 << "\n\n";
const Nef_polyhedron::Sphere_map &m = N3.sphere_map();
Nef_polyhedron::Const_decorator D(&m);
std::cout << "vert count: " << D.number_of_svertices()<< "\n";
std::cout << "edge count: " << D.number_of_sedges() << "\n";
std::cout << "loop count: " << D.number_of_sloops() << "\n";
std::cout << "face count: " << D.number_of_sfaces() << "\n";
std::cout << "\n\n ------------------------\n";
//遍历Nef_polyhedron_S2的顶点
int i = 1;
for (SVertex_const_iterator it = D.svertices_begin(); it != D.svertices_end(); i++, ++it)
{
double lon = 0, lat = 0, alt = 0;
double x = CGAL::to_double(it->point().x());
double y = CGAL::to_double(it->point().y());
double z = CGAL::to_double(it->point().z());
getLLA(x, y, z, lon, lat, alt);
std::cout << std::setprecision(14) << std::setiosflags(std::ios::fixed)
<< i << ":"
//<< it->point() //Sphere_point SM_items::SVertex::point();
<< "| " << it->point().x()
<< ", " << it->point().y()
<< ", " << it->point().z()
<< "| " << lon
<< "; " << lat
<< "; " << alt
<< std::endl;
}
//TODO 3: 先遍历面,再获取面相关的点,参考https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Manual/devman_iterators_and_circulators.html (Iterators, Circulators and Handles)
//TODO 4: 暂不理解为什么会有多个面number_of_sfaces,按照理解应该只有一个,随后从特征上排除非真正的结果
return 0;
}
/*
输出:
=====================================================================================
Sphere_point 0.00000000000000, 0.00000000000000: 1.00000000000000 0.00000000000000 0.00000000000000
Sphere_point 30.00000000000000, 0.00000000000000: 0.86602540378444 0.50000000000000 0.00000000000000
Sphere_point 30.00000000000000, 30.00000000000000: 0.75000000000000 0.43301270189222 0.50000000000000
Sphere_point 0.00000000000000, 15.00000000000000: 0.96592582628907 0.00000000000000 0.25881904510252
Sphere_point 60.00000000000000, 15.00000000000000: 0.48296291314453 0.83651630373781 0.25881904510252
Sphere_point 60.00000000000000, 45.00000000000000: 0.35355339059327 0.61237243569579 0.70710678118655
Sphere_point 0.00000000000000, 45.00000000000000: 0.70710678118655 0.00000000000000 0.70710678118655
vert count: 7
edge count: 7
loop count: 0
face count: 2
------------------------
1:| 0.35355339059327, 0.61237243569579, 0.70710678118655| 59.99999999999999; 45.00000000000001; 0.00000000000000
2:| 0.70710678118655, 0.00000000000000, 0.70710678118655| 0.00000000000000; 45.00000000000001; 0.00000000000000
3:| 0.75000000000000, 0.43301270189222, 0.50000000000000| 30.00000000000000; 30.00000000000000; 0.00000000000000
4:| 0.48296291314453, 0.83651630373781, 0.25881904510252| 59.99999999999999; 15.00000000000000; 0.00000000000000
5:| 0.34987976320958, 0.20200317547305, 0.12500000000000| 30.00000000000000; 17.19212373402097; -0.57709796452986
6:| 0.34987976320958, 0.09375000000000, 0.10825317547305| 15.00000000000000; 16.63922203701361; -0.62194754173052
7:| 0.96592582628907, 0.00000000000000, 0.25881904510252| 0.00000000000000; 15.00000000000000; 0.00000000000000
=====================================================================================
*/
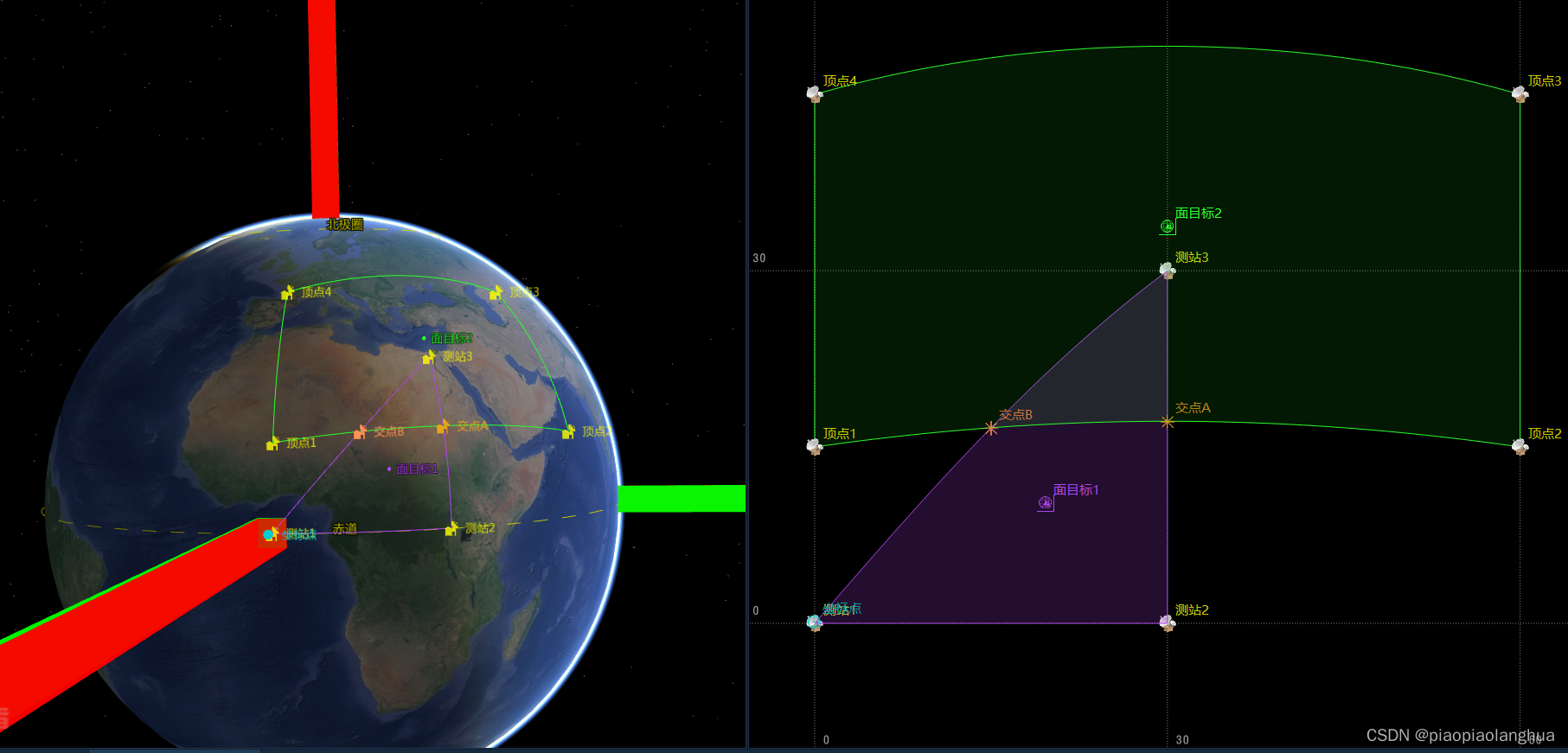
//新增的两个交点
//5:| 0.34987976320958, 0.20200317547305, 0.12500000000000| 30.00000000000000; 17.19212373402097; -0.57709796452986
//6:| 0.34987976320958, 0.09375000000000, 0.10825317547305| 15.00000000000000; 16.63922203701361; -0.62194754173052
PS/TODO:还有一些"土豆"没有挖。。。
尝试查看例子、文档找到的关键代码如下,尽管还未充分理解
//遇到浮点数精度问题,会导致Nef_polyhedron构造失败
//typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<doublet> LazyFloat;
//typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<CGAL::MP_Float> LazyFloat;
//typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<LazyFloat> Kernel;
//typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
//找了很久得到的解决方法!!!
typedef CGAL::Quotient<CGAL::MP_Float> Exact_NT; // doesn't do exact sqrt()
typedef CGAL::Lazy_exact_nt<Exact_NT> LazyFloat;
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<LazyFloat> Kernel;
【参考链接】
https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Nef_S2/index.html
https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Number_types/index.html
https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Manual/devman_iterators_and_circulators.html
https://www.cgal.org/FAQ.html#kernels
.../cgal-5.5.2/number_types/test/Number_types/Lazy_exact_nt.cpp
























 2588
2588











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










