设原图像大小为(scr_height,scr_width),新图像大小为(dst_height,dst_width),则图像的尺度(放大缩小尺度)scale=dst_height/scr_height=dst_width/scr_width(本文是对xy轴都使用同一scale,不同scale原理相同)
设新图像中的任意一个像素点(dst_x,dst_y),将(dst_x,dst_y)映射回原图像的坐标(x,y)
其中x=dst_x/scale,y=dst_y/scale,可以看到,x和y不可能正好是整数,因此可以将x和y分别整数部分(int_x,int_y)和小数部分(float_x,float_y),几种插值方法只是对于x和y使用不同的处理方法得到新图像的像素点
1、最近邻插值
最近邻插值就是简单的选择x和y的整数部分的坐标像素点赋值给新图像
def nearest_interpolation(img,scale):
dst_cols = (int)(img.shape[0] * scale)
dst_rows = (int)(img.shape[1] * scale)
img_dst = np.zeros([dst_cols, dst_rows])
for i in range(dst_cols-1):
for j in range(dst_rows-1):
#坐标转换
scr_x=(i+0.5)/scale-0.5
scr_y=(j+0.5)/scale-0.5
# 整数部分
int_x = int(scr_x)
int_y = int(scr_y)
img_dst[i][j]=img[int_x][int_y]
return img_dst
2、双线性插值
双线性插值就是使用int_x,int_y为左上角的坐标,取右、右下、下一共四个点进行线性插值得到dst的图像值
def bilinear_interpolation(img,scale):
dst_cols=(int)(img.shape[0]*scale)
dst_rows=(int)(img.shape[1]*scale)
img_dst=np.zeros([dst_cols,dst_rows])
for i in range(dst_cols-1):
for j in range(dst_rows-1):
#坐标转换
scr_x=(i+0.5)/scale-0.5
scr_y=(j+0.5)/scale-0.5
#整数部分
int_x=int(scr_x)
#小数部分
float_x=scr_x-int_x
int_y=int(scr_y)
float_y=scr_y-int_y
if int_x==img.shape[0]-1:
int_x_p=img.shape[0]-1
else:
int_x_p=int_x+1
if int_y==img.shape[1]-1:
int_y_p=img.shape[1]-1
else:
int_y_p=int_y+1
img_dst[i][j]=(1-float_x)*(1-float_y)*img[int_x][int_y]+(1-float_x)*float_y*img[int_x][int_y_p]+\
float_x*(1-float_y)*img[int_x_p][int_y]+float_x*float_y*img[int_x_p][int_y_p]
return img_dst
3、双立方插值
双立方插值就是使用int_x,int_y为左上角的坐标,取附近一共16个点进行线性插值得到dst的图像值
其中S为采样公式
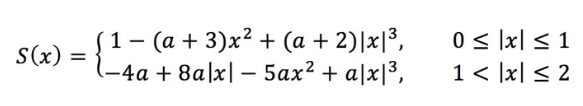
def bicubic_interpolation(img,scale):
def s(x,a=-1):
x_abs=math.fabs(x)
if x_abs>=0 and x_abs<=1:
return 1-(a+3)*math.pow(x_abs,2)+(a+2)*math.pow(x_abs,3)
elif x_abs>1 and x_abs<=2:
return -4*a+8*a*x_abs-5*a*math.pow(x_abs,2)+a*math.pow(x_abs,3)
else:
return 0
dst_cols = (int)(img.shape[0] * scale)
dst_rows = (int)(img.shape[1] * scale)
img_dst = np.zeros([dst_cols, dst_rows])
for i in range(dst_cols-1):
for j in range(dst_rows-1):
#坐标转换
scr_x=(i+0.5)/scale-0.5
scr_y=(j+0.5)/scale-0.5
# 整数部分
int_x = int(scr_x)
int_y = int(scr_y)
# 小数部分
float_x=scr_x-int_x
float_y=scr_y-int_y
sum=0
for r in range(-1,3):
for c in range(-1,3):
sum+=img[int_x+r][int_y+c]*s(r-float_x)*s(c-float_y)
img_dst[i][j]=sum
return img_dst






















 1948
1948











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








