这篇论文是International Symposium on Non-Photorealistic Animation and Rendering (NPAR 2012) 的Best Paper Award,作者是(当时)港中文的Cewu Lu, Li Xu和Jiaya Jia。正好最近在做风格迁移的相关内容,尝试阅读这篇文章,并(尝试)复现一下。
文章的主页:Combining Sketch and Tone for Pencil Drawing Production (cuhk.edu.hk)

效果图
如上图所示,作者提出的居于图像的铅笔素描方法主要有两个步骤,即轮廓绘制和色调纹理绘制。其框架如图所示

flow chart
1 轮廓绘制
作者首先提出了一个observation,说现实中的画家在素描的时候不会画出很长的不间断的线条,并且艺术家倾向于用多跟线条表现同一个意向,这就导致在弯曲和顶点处常常会出现一些线条的交汇。如图3

因此,不能用连续函数来生成轮廓。这里作者采用多组较短的线条叠加的方式来近似逼近整体的轮廓。如图4

当绘制某一处的轮廓时,在“基于统一卷积框架的像素分类和链接过程中”确定该处轮廓的方向、长度和宽度(when drawing strokes at a point, we determine the direction, length,and width in a pixel classification and link process based on a uni-fied convolution framework.)
这里可以理解为,在绘制轮廓时,可以把一个轮廓看作许多个不同方向和形式的短的小的轮廓的叠加。
1.1 分类
这里的分类指的是根据梯度方向将轮廓分为不同的方向类别。
首先图像的灰度图上计算梯度,
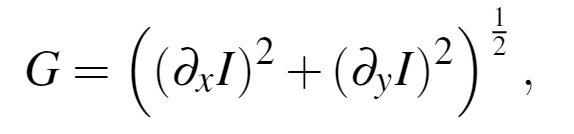
这里I是灰度图像的输入,∂x和∂ya是两个方向的梯度算子,由前向差分实现。
用上面的方法可以估计得到每个像素的梯度方向。但是这个梯度方向的估计对噪声非常敏感,因此非常不稳定。作者提出了一种使用局部信息的梯度方向估计策略。
首先把梯度方向分为8个类,0°,45°,90°...一直到315°,对于某一个类别的响应图,用下面的式子计算:
![]()
其中i代表第i个方向。Li被看作一个“卷积核”,其长度设置为图像的高度或宽度的1/30。
通过上面的式子,对整个图像用8个卷积核分别做卷积,可以得到图像在8个方向上的响应。对每个像素,选择其响应最大的那个方向,作为其梯度的方向。
1.2 轮廓整形
有了整个图像的梯度map,就可以通过下式在每个像素上通过卷积生成线条:
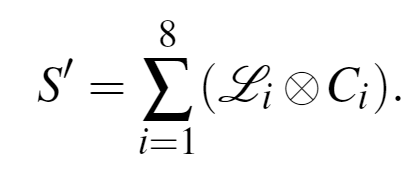
其中
![]()
再其中,p指的是像素。
通过这种方法,可以将各个方向的梯度线条连接起来。
将得到的S'映射到[0,1],就可以得到最终的轮廓图,如图6

1.3 讨论
这一节作者说了一下他们的方法的优点:
- 使用线条来模拟草图是非常有效的。卷积步骤在交点处延伸两条线的末端。请注意,只有原始边缘图中的长直线会显着扩展,因为方向卷积仅沿严格的直线聚合像素。
- 长线中心的像素将从两侧接收像素值,这使得线中心比两端暗,这在铅笔画中是理想的。
- 我们的策略帮助链接原始边缘图中不一定连接的像素,当附近的像素大多沿直线对齐时,模仿人类画线过程并抗噪。
这里作者对比了另一种边缘生成的方法,我觉得还挺好看的,这里Mark一下

提出的轮廓绘制方法的另一个优点是,对于纹理并不敏感,不会把例如草坪或者其他的粗糙的平面都提取出来。
2 色调生成
在素描中,人类会使用密集的笔触来强调阴影和神色物体。对这部分物体,作者也提出了拟合方法。
2.1 色调映射图生成 (Tone Map Generation)
需要注意的是,如图8所示,素描画的图像的色调值分布和真实图像是很不一样的,所以不可以直接用灰度图的像素值映射每个像素的颜色。

作者提出了一个参数模型来你和铅笔素描的色调分布。这个模型也是observation-based的,observation说,与自然图像中高度可变的色调不同,草图直方图通常遵循某些模式。对于非常明亮的区域,艺术家不会画任何东西来显示白纸。相反,重笔画用于强调边界和突出暗区。
结合这个observation,作者用以下模型来表示色调的分布:
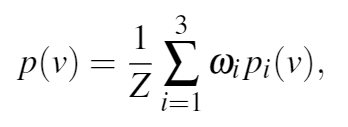
其中v是色调值,p(v)是铅笔画中的像素值具有v的概率,Z是一个归一化系数,使得
![]()
三个pi表示图像的三个tone layer,ωi和每个tone layer中的像素数粗略相关。(这里tone layer后面会说到)
v应该通过缩放在[0,1]的范围内,以抵消计算分布时的光照差异。
下图给出了一幅图像和他的色调分布

可以看出,绿色和蓝色代表的亮区和暗区有着一个唯一的峰,但是中间调的橙色区没有一个唯一的峰。为了拟合这三个tone layer的分布,作者用了三套模型。
在最亮的部分(蓝色区域),作者用拉普拉斯分布拟合了像素分布,其峰值设置为255
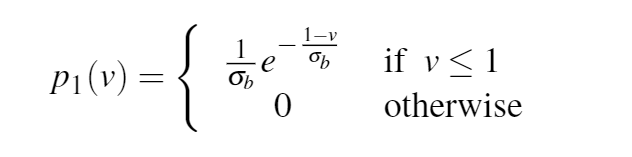
在中间调的区域(橙色区域),作者则使用均匀分布来拟合像素分布
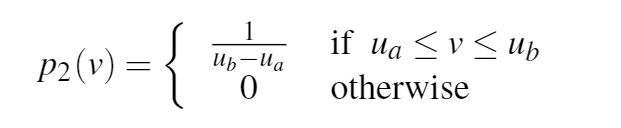
在暗区(绿色区域),作者用高斯分布拟合

其中,μd是暗区的均值,σ是范围参数。
2.2 参数确定
上述p1~p3中的参数都需要讨论。
其中明暗色调层的阈值需要人工确定。
每个tone layer中的像素数可以确定权重ω。
此外,在每一层tone layer中,用极大似然估计来确定参数。
以m和s来表示每个layer的均值和标准差的话,参数具有“封闭形式”的表示(the parameters have the closed-form represen-tation):
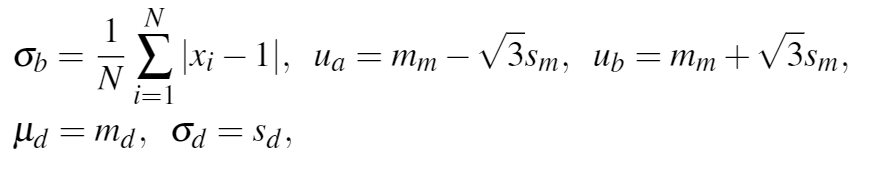
其中xi是像素值,N是这个layer中的像素数。
然后是ω的值,注意ω的值只是和像素数大致正相关的,并不是严格相关的,而使用不同的比例可以产生不同的效果。

2.3 铅笔纹理渲染
铅笔的笔划是有纹理的,所以要为整个图像生成合适的纹理。
铅笔画中大概有两种纹理,一种是有方向的纹理,一种叫做“色调纹理(Tonal texture)”,如图:
 这里作者选择的是没有方向的色调纹理。
这里作者选择的是没有方向的色调纹理。
在人类的绘画中,这种纹理是通过在一个位置重复地“下笔”形成的。作者用笔划的“相乘”来模拟这种过程。
Q:为什么用相乘,不用相加?
同一个笔划不断地相乘得到图案,用式子表示为
![]()
意思是,同一个笔划H,画了β次,得到了J。在对数域则可以表示为
![]()
β越大,则色调越深。并且,β在局部应该是平滑的。
在提出以上约束后,可以用解方程的方法求得β:
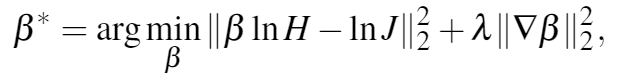
最小化右边的方程得到的β值应该就是最优值。
式子中的λ是一个经验值0.2,这样的话这个方程可以变成一个线性方程。可以用共轭梯度求解。
最终的纹理可以用下面的式子计算
![]()
3 整体框架
3.1 最终图像生成
在上面的两部分,轮廓S和纹理T都得到之后,最终将他们相乘得到铅笔画
![]()
3.2 彩色图像处理
将原本的图像转换到YUV空间,然后将Y通道提取出来,处理之后的Y'替换原来的Y通道,并将整个图像映射回RGB空间,可以得到最终的色调。
4 其它
在本文的对比图像中,有一些方法看上去还挺有意思的,结果看起来也不错。这里标注一下,立下flag,以后尝试去实现。
[1] SON,M.,KANG,H.,LEE,Y.,ANDLEE, S. 2007. Abstract linedrawings from 2d images. InPacific Conference on ComputerGraphics and Applications, 333–342.

[2] YAMAMOTO,S.,MAO,X.,ANDIMAMIYA, A. 2004. Enhancedlic pencil filter. InCGIV, 251–256.

[3] SOUSA,M.C.,ANDBUCHANAN, J. W. 1999. Computer-generated graphite pencil rendering of 3d polygonal models.Comput. Graph. Forum 18, 3, 195–208.

[4] LI,N.,ANDHUANG, Z. 2003. A feature-based pencil drawingmethod. InGRAPHITE, 135–140.

[5] LEE,H.,KWON,S.,ANDLEE, S. 2006. Real-time pencil render-ing. InNPAR, 37–45.

5 实现
Matlab的实现在项目的主页就有 这里就不赘述了






















 818
818











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








