- 定义一个Person类,包含私有成员,int *age,string &name,一个Stu类,包含私有成员double *score,Person p1,写出Person类和Stu类的特殊成员函数,并写一个Stu的show函数,显示所有信息
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//1.定义一个Person类,包含私有成员,int *age,string &name,一个Stu类,
//包含私有成员double *score,Person p1,写出Person类和Stu类的特殊成员函数,
//并写一个Stu的show函数,显示所有信息。
class Person{
int *age;
string &name;
public:
Person(int age,string &name):age(new int(age)),name(name){
cout << "person 一个参构造函数" << endl;
}
int get_age();
string get_name();
//拷贝函数
Person(const Person &other):age(new int(*(other.age))),name(other.name){
cout << "person 拷贝函数 " << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Person &operator=(const Person &other){
*(this->age) = *(other.age);
name = other.name;
}
//析构函数,释放指针堆空间
~Person(){
cout << "---------------------------------Person delete----------------------" << endl;
cout << "age 地址信息 " << age << endl;
cout << "释放age堆空间" << endl;
delete age;
}
};
class Stu{
double *score;
Person p1;
public:
Stu(double score,int age,string name):score(new double(score)),p1(age,name){
cout << "Stu 一个参数构造函数" << endl;
}
void show();
//拷贝函数
Stu(const Stu &other):score(new double(*(other.score))),p1(other.p1){
cout << "Stu 拷贝函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Stu &operator=(const Stu &other){
*(this->score) = *(other.score);
this->p1 = other.p1;
}
//析构函数,释放指针堆空间
~Stu(){
cout << "---------------------------------Stu delete----------------------" << endl;
cout << "score 地址信息 " << score << endl;
cout << "释放score堆空间" << endl;
delete score;
}
};
int Person::get_age(){
return *age;
}
string Person::get_name(){
return name;
}
void Stu::show(){
cout << "score = " << *score << endl;
cout << "person age = " << p1.get_age() << endl;
cout << "person name = " << p1.get_name() << endl;
}
int main()
{
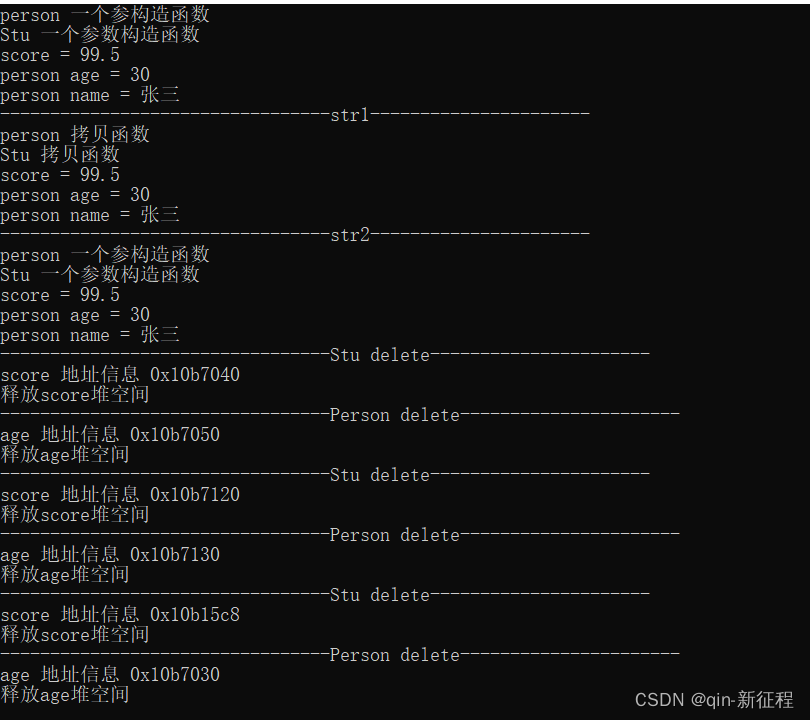
Stu str(99.5,30,"张三");
str.show();
cout << "---------------------------------str1----------------------" << endl;
Stu str1 = str; // 调用拷贝函数
str1.show();
cout << "---------------------------------str2----------------------" << endl;
Stu str2(0,0,"");
str2 = str;
str2.show();
return 0;
}
2.思维导图





















 346
346











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








