| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 16975 | Accepted: 6468 |
Description
Input
The input file is terminated by a line containing a single 0. Don't process it.
Output
Output a blank line after each test case.
Sample Input
2 10 10 20 20 15 15 25 25.5 0
Sample Output
Test case #1 Total explored area: 180.00
Source
扫描法就是用一根想象中的线扫过所有矩形,在写代码的过程中,这根线很重要。方向的话,可以左右扫,也可以上下扫。方法是一样的,这里我用的是由下向上的扫描法。

如上图所示,坐标系内有两个矩形。位置分别由左下角和右上角顶点的坐标来给出。上下扫描法是对x轴建立线段树,矩形与y平行的两条边是没有用的,在这里直接去掉。如下图。

现想象有一条线从最下面的边开始依次向上扫描。线段树用来维护当前覆盖在x轴上的线段的总长度,初始时总长度为0。用ret来保存矩形面积总和,初始时为0。
由下往上扫描,扫描到矩形的底边时将它插入线段树,扫描到矩形的顶边时将底边从线段树中删除。而在代码中实现的方法就是,每条边都有一个flag变量,底边为1,顶边为-1。
用cover数组(通过线段树维护)来表示某x轴坐标区间内是否有边覆盖,初始时全部为0。插入或删除操作直接让cover[] += flag。当cover[] > 0 时,该区间一定有边覆盖。
开始扫描到第一条线,将它压入线段树,此时覆盖在x轴上的线段的总长度L为10。计算一下它与下一条将被扫描到的边的距离S(即两条线段的纵坐标之差,该例子里此时为3)。
则 ret += L * S. (例子里增量为10*3=30)
结果如下图

橙色区域表示已经计算出的面积。
扫描到第二条边,将它压入线段树,计算出此时覆盖在x轴上的边的总长度。
例子里此时L=15。与下一条将被扫描到的边的距离S=2。 ret += 30。 如下图所示。

绿色区域为第二次面积的增量。
接下来扫描到了下方矩形的顶边,从线段树中删除该矩形的底边,并计算接下来面积的增量。如下图。

蓝色区域为面积的增量。
此时矩形覆盖的总面积已经计算完成。 可以看到,当共有n条底边和顶边时,只需要从下往上扫描n-1条边即可计算出总面积。
============ ================= 分割线 ==============================
此题因为横坐标包含浮点数,因此先离散化。另外,因为用线段树维护的是覆盖在x轴上的边,而边是连续的,并非是一个个断点,因此线段树的每一个叶子结点实际存储的是该点与下一点之间的距离。
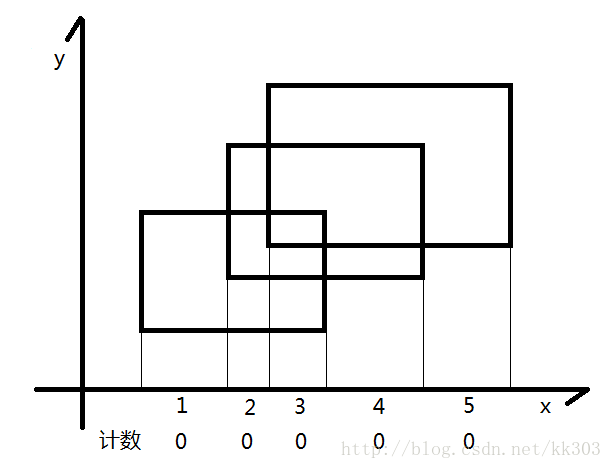
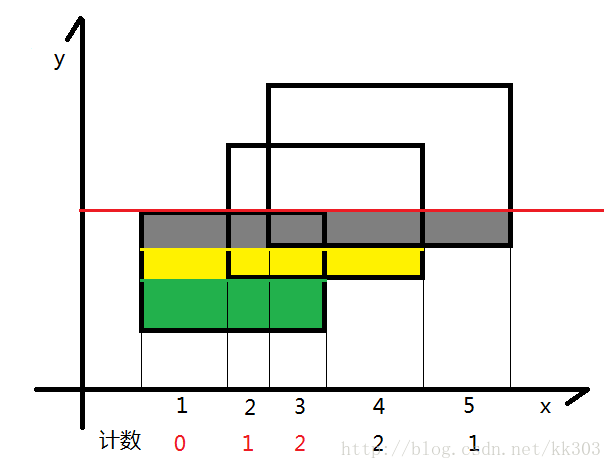
几个图说明扫描线扫描..线段树维护的过程..:
初始状态
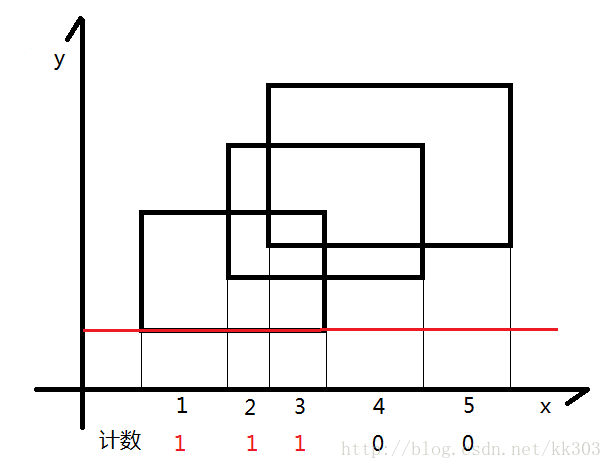
扫到最下边的线,点更新1~3为1
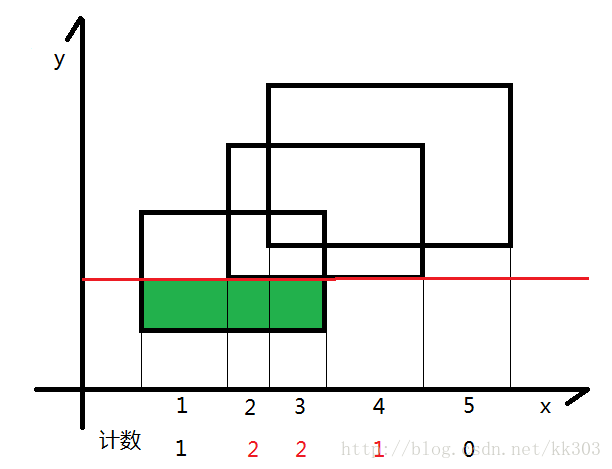
扫到第二根线,此时将计数器不为0的长度*上线两根线的长度,得到绿色的面积,加到答案中去.随后更新计数
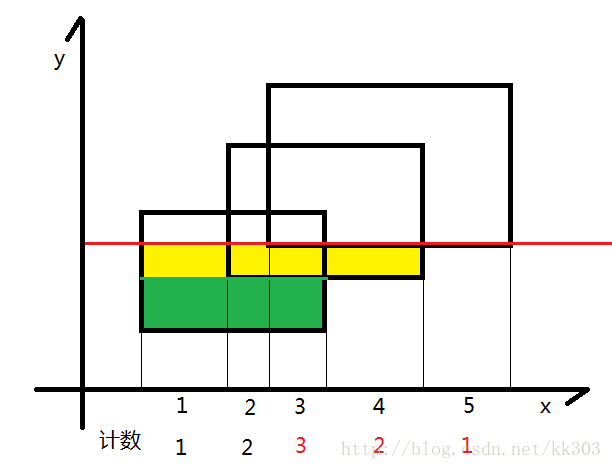
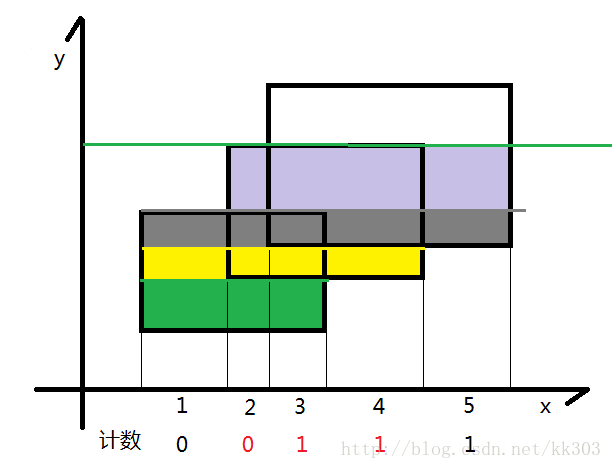
同上,将黄色的面积加到答案中去
同上,将灰色的面积加到答案中去
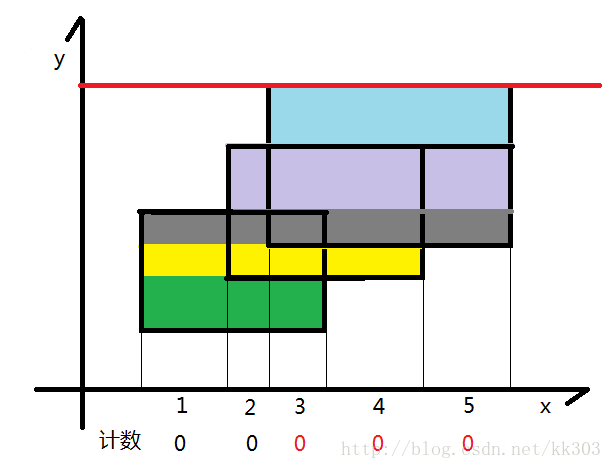
同上,将紫色的面积加到答案中去
同上,将蓝色的面积加到答案中去
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#define N 1000
#define eps 1e-6
using namespace std;
double x[N];
struct line
{
double l,r,h;
int flag;
line(){};
line(double ll,double rr,double hh,int fflag)
{
l=ll; r=rr; h=hh; flag=fflag;
}
}bian[N];
struct node
{
int x,y,p;
double sum;
}a[N*3];
bool cmp(line a,line b)
{
return a.h<b.h;
}
int binary(double k,int l,int r)
{
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(fabs(x[mid]-k)<=eps)
return mid;
else if(x[mid]>k)
r=mid-1;
else
l=mid+1;
}
return l;
}
void build(int t,int x,int y)
{
a[t].x=x;
a[t].y=y;
a[t].sum=0;
a[t].p=0;
if(x==y) return;
int mid=(x+y)>>1,temp=t<<1;
build(temp,x,mid);
build(temp+1,mid+1,y);
}
void pushdown(int t)
{
int temp=t<<1;
if(a[t].p)//如果当前区间存在,不用看儿子的,直接计算区间和
a[t].sum=x[a[t].y]-x[a[t].x-1];
else if(a[t].x==a[t].y)//如果区间没有儿子了,而且不存在了,区间和为0
a[t].sum=0;
else//如果当前区间不存在了,但是有儿子,它的区间和由儿子决定
a[t].sum=a[temp].sum+a[temp+1].sum;
}
void update(int xx,int yy,int c,int t)
{
if(a[t].x==xx&&a[t].y==yy)
{
a[t].p+=c;
pushdown(t);
return;
}
int mid=(a[t].x+a[t].y)>>1,temp=t<<1;
if(yy<=mid)
update(xx,yy,c,temp);
else if(xx>mid)
update(xx,yy,c,temp+1);
else
{
update(xx,mid,c,temp);
update(mid+1,yy,c,temp+1);
}
pushdown(t);
}
int main()
{
int t,cnt=1,i,k,j,xx,yy,n;
double x1,y1,x2,y2,ans;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n!=0)
{
k=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
bian[k]=line(x1,x2,y1,1);
x[k++]=x1;
bian[k]=line(x1,x2,y2,-1);
x[k++]=x2;
}
sort(bian,bian+k,cmp);
sort(x,x+k); j=1;
for(i=1;i<k;i++)//去重点
{
if(x[i]!=x[i-1])
x[j++]=x[i];
}
ans=0;
build(1,1,j-1);
for(i=0;i<k-1;i++)
{
xx=binary(bian[i].l,0,j-1)+1;
yy=binary(bian[i].r,0,j-1);
//printf("%d %d %d\n",xx,yy,bian[i].flag);
if(xx<=yy)
update(xx,yy,bian[i].flag,1);
//printf("%lf\n",a[1].sum);
ans+=(bian[i+1].h-bian[i].h)*a[1].sum;
}
printf("Test case #%d\n",cnt++);
printf("Total explored area: %.2lf\n\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}






















 415
415

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








