反射(查看api为class)
抽象所有类共有的class、field、construct、method
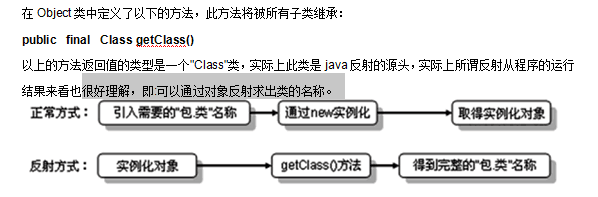
反射的简单介绍
"******************Student************************"
public class Student {
private int age;
private String name;
public String classname;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassname() {
return classname;
}
public void setClassname(String classname) {
this.classname = classname;
}
}
"*****************************************************"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Student> clazz=Student.class;
"*******************访问类中的属性*********************"
//另一种写法
//Class<? extends Student> clazz=
//访问所有公共的属性
//Field[] fileds=clazz.getFields();
//访问所有属性
Field[] fields=clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:fields){
System.out.println(field.getType().getName());
System.out.println(field.getName());
System.out.println(field.getModifiers());
}
"*********用反射修改对象private修饰的属性********"
Student xiao=new Student();
try {
//按属性名的到类中的一个属性
Field age=clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
//取消java访问修饰符检查
age.setAccessible(true);
//传入一个对象,修改对象的属性
age.set(xiao, 11);
//重新设置访问检查
age.setAccessible(false);
System.out.println(xiao.getAge());
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
反射的用途(工厂设计模式)
person类可用接口
在工程下创建文件 config.properties
在工程下创建文件 config.properties
文件内容:
person=com.agust4.factoydesign.Teacher
"************************Person类*********************"
package com.agust4.factoydesign;
public class Person {
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人睡觉");
}
}
"*************************Student类**********************"
package com.agust4.factoydesign;
public class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("学生睡觉");
}
}
"**********************Teacher类*************************"
package com.agust4.factoydesign;
import org.omg.Messaging.SyncScopeHelper;
public class Teacher extends Person {
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("老师睡觉");
}
}
"*********************Factory类***********************"
package com.agust4.factoydesign;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Factory {
public static Person creatPerson(){
Person person=null;
//propertise为性能,道具,内容,创建一个新对象
Properties p= new Properties();
try {
//加载配置文件,可以插入文件位置
p.load(new FileInputStream("config.properties"));
//文件中等号前面的值
String clazzName=p.getProperty("person");
//用路径名得到一个类
Class clazz =Class.forName(clazzName);
//用类名创建一个对象,强制转换类型
person =(Person) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return person;
}
}
"********************测试类***********************"
package com.agust4.factoydesign;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用方法的返回值得到一个对象
Person person=Factory.creatPerson();
person.sleep();
}
}
注解的用法
"*************************Clazz类******************************"
package com.agust4.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Clazz {
//用注释自动赋初值
@TeacherAnnotation(age=13,name="战三")
private Teacher javaTeacher;
//因为age有默认值,若不赋初值,默认为默认值
@TeacherAnnotation(name="李四")
private Teacher englishTeacher;
public Clazz(){
Class clazz=Clazz.class;
//得到clazz的所有属性
Field[] fields=clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:fields){
TeacherAnnotation ta=field.getAnnotation(TeacherAnnotation.class);
//得到注解类,如果没有则跳过
if(ta==null){
continue;
}else{
//创建临时的Teacher对象来完成值的传递
Teacher teacher=new Teacher();
//得到注解中的age
int age=ta.age();
//得到注解中的name
String name=ta.name();
teacher.setName(name);
teacher.setAge(age);
//设置不检查java的属性访问修饰符
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
//this为Teacher创建的当前对象
field.set(this, teacher);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//设置访问java的访问修饰符
field.setAccessible(false);
}
}
}
public Teacher getJavaTeacher() {
return javaTeacher;
}
public void setJavaTeacher(Teacher javaTeacher) {
this.javaTeacher = javaTeacher;
}
public Teacher getEnglishTeacher() {
return englishTeacher;
}
public void setEnglishTeacher(Teacher englishTeacher) {
this.englishTeacher = englishTeacher;
}
}
"**************************Teacher类****************************"
package com.agust4.annotation;
import org.omg.Messaging.SyncScopeHelper;
public class Teacher extends Person {
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int age;
private String name;
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("老师睡觉");
}
}
"************************TeacherAnnotation**********************"
package com.agust4.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// 表示此注释只能作用到属性上
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface TeacherAnnotation {
int age() default 19;
String name();
}
"****************************Test2测试类***********************"
package com.agust4.annotation;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clazz clazz=new Clazz();
System.out.println(clazz.getEnglishTeacher().getAge()+clazz.getEnglishTeacher().getName());
System.out.println(clazz.getJavaTeacher().getAge()+clazz.getJavaTeacher().getName());
}
}
Thread
- setPriority()设置线程的优先级,只是优先考虑,并不保证会按优先级执行
- sleep()方法,使线程休眠一段时间
- yield()方法会使线程暂停1-2毫秒
继承Thread方法
package com.agust4.thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int ticket = 10;
public MyThread() {
}
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("卖出了" + ticket-- + "piao");
}
}
}
}
"*************************Test方法***********************"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread thread=new MyThread("1");
MyThread thread1=new MyThread("2");
MyThread thread2=new MyThread("3");
MyThread thread3=new MyThread("4");
MyThread thread4=new MyThread("5");
thread.start();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
}
}
Runnable()方法
"*************************Test方法**************************"
package com.agust4.thread;
public class RunnableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunable runnable=new MyRunable();
Thread thread=new Thread(runnable,"1");
Thread thread1=new Thread(runnable,"2");
Thread thread2=new Thread(runnable,"3");
Thread thread3=new Thread(runnable,"4");
Thread thread4=new Thread(runnable,"5");
thread.start();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
}
}
"****************************扩展的接口***************************"
package com.agust4.thread;
public class MyRunable implements Runnable {
private int i = 100;
@Override
public void run() {
while (i > 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized ("h") {
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖得票是" + i);
i--;
}
}
}
}
}
Jion()方法
"*************************扩展的接口***************************"
package com.agust4.thread;
public class MyRunable implements Runnable {
private int i = 100;
@Override
public void run() {
while (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized ("h") {
if (i > 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖得票是" + i);
i--;
}
}
}
}
}
"***************************Test方法**************************"
public class Jion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunable runnable=new MyRunable();
Thread thread=new Thread(runnable,"1");
thread.start();
try {
//thread.join();//不加参数时,先让加入的线程执行完,在执行其他线程
thread.join(1000);//加入参数,是让加入的线程先运行多长时间,然后并行
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}
}线程争用造成死锁
"*************************线程1**************************"
public class Myrun1 implements Runnable{
String lock1="1";
String lock2="2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等log2");
synchronized (lock2) {
}
}
}
}
"*************************线程2**************************"
public class Myrun2 implements Runnable {
String lock1 = "1";
String lock2 = "2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等log1");
synchronized (lock1) {
}
}
}
}
"*************************Test类***************************"
public class MyrunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myrun2 run2=new Myrun2();
Myrun1 run1=new Myrun1();
Thread thread1=new Thread(run1,"小明");
Thread thread2=new Thread(run2,"小红");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}解决死锁,(wait()和notify() api为object) 产生原因是因为锁中套锁,当一个锁用完后自动释放
"*************************线程1**************************"
public class Myrun1 implements Runnable{
String lock1="1";
String lock2="2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("run1已经启动");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等log2");
try {
System.out.println("run1释放lock1");
//释放lock1给其他线程
lock1.wait();
System.out.println("run1等待结束并运行");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("run1已经等到了lock2");
}
}
}
}
"*************************线程2**************************"
public class Myrun2 implements Runnable {
String lock1 = "1";
String lock2 = "2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("run2已经启动");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等log1");
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("等到了lock1");
System.out.println("唤醒等待的lock1");
//用完lock1后唤醒其他等待的线程,唤醒后的线程不会立即执行,必须等正在
//执行的线程运行完
lock1.notify();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("run2已经运行完");
}
}
}
}
"*************************Test类***************************"
public class MyrunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myrun2 run2=new Myrun2();
Myrun1 run1=new Myrun1();
Thread thread1=new Thread(run1,"小明");
Thread thread2=new Thread(run2,"小红");
thread1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread2.start();
}
}生产、消费产品问题
public class Coustom implements Runnable {
private Product pro;
public Coustom(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (pro) {
System.out.println("消费者抢到");
if (pro.getNum() != 0) {
System.out.println("消费者消费");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
pro.setNum(0);
pro.notify();
}
}
}
}
}
"*****************************************************"
public class Producer implements Runnable {
private Product pro;
public Producer(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (pro) {
System.out.println("生产者抢到仓库");
if (pro.getNum() == 0) {
System.out.println("生产产品");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
pro.setNum(1);
try {
pro.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
"*****************************************************"
public class Product {
private int num=0;
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
"*****************************************************"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product product=new Product();
Coustom cus=new Coustom(product);
Producer pro=new Producer(product);
Thread c=new Thread(cus);
Thread p=new Thread(pro);
p.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
c.start();
}
}同步代码块可写为同步方法,调用方法的对象为锁
public class Producer implements Runnable {
private Product pro;
public Producer(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
pro.producer();
}
}
}
"************************************************"
public class Coustom implements Runnable {
private Product pro;
public Coustom(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
pro.custom();
}
}
}
"************************************************"
public class Product {
private int num=0;
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public synchronized void custom(){
System.out.println("消费者抢到");
if (getNum() != 0) {
System.out.println("消费者消费");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
setNum(0);
notify();
}
}
public synchronized void producer(){
System.out.println("生产者抢到仓库");
if (getNum() == 0) {
System.out.println("生产产品");
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
setNum(1);
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
"************************************************"
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product product=new Product();
Coustom cus=new Coustom(product);
Producer pro=new Producer(product);
Thread c=new Thread(cus);
Thread p=new Thread(pro);
p.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
c.start();
}
}
"************************************************"守护线程
守护线程并非虚拟机内部可以提供,用户也可以自行的设定守护线程,方法:public final void setDaemon(boolean on) ;但是有几点需要注意:
1)、thread.setDaemon(true)必须在thread.start()之前设置,否则会跑出一个IllegalThreadStateException异常。你不能把正在运行的常规线程设置为守护线程。 (备注:这点与守护进程有着明显的区别,守护进程是创建后,让进程摆脱原会话的控制+让进程摆脱原进程组的控制+让进程摆脱原控制终端的控制;所以说寄托于虚拟机的语言机制跟系统级语言有着本质上面的区别)
2)、 在Daemon线程中产生的新线程也是Daemon的。 (这一点又是有着本质的区别了:守护进程fork()出来的子进程不再是守护进程,尽管它把父进程的进程相关信息复制过去了,但是子进程的进程的父进程不是init进程,所谓的守护进程本质上说就是“父进程挂掉,init收养,然后文件0,1,2都是/dev/null,当前目录到/”)
3)、不是所有的应用都可以分配给Daemon线程来进行服务,比如读写操作或者计算逻辑。因为在Daemon Thread还没来的及进行操作时,虚拟机可能已经退出了。
例子:
mport java.io.*;
class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);//守护线程阻塞1秒后运行
File f=new File("daemon.txt");
FileOutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(f,true);
os.write("daemon".getBytes());
}
catch(IOException e1){
e1.printStackTrace();
}
catch(InterruptedException e2){
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
Runnable tr=new TestRunnable();
Thread thread=new Thread(tr);
thread.setDaemon(true); //设置守护线程
thread.start(); //开始执行分进程
}
}
运行结果:文件daemon.txt中没有"daemon"字符串。
但是如果把thread.setDaemon(true); //设置守护线程注释掉,文件daemon.txt是可以被写入daemon字符串的守护线程的实际用途
JRE判断程序是否执行结束的标准是所有的前台执线程行完毕了,而不管后台线程的状态,因此,在使用后台线程候一定要注意这个问题。
但是daemon Thread实际应用在那里呢?举个例子,web服务器中的Servlet,容器启动时后台初始化一个服务线程,即调度线程,负责处理http请求,然后每个请求过来调度线程从线程池中取出一个工作者线程来处理该请求,从而实现并发控制的目的。
Thread和Runnable的用法(查看 api)
基于多线程的Server通信
"*******************************************************"
public class MyReader implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public MyReader(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (true) {
try {
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("说了" + str);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} // 等待客户端
}
}
}
"*******************************************************"
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("服务器运转");
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = server.accept();
Thread write = new Thread(new MyWriter(socket));
Thread read = new Thread(new MyReader(socket));
read.start();
write.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
"*******************************************************"
public class Mysoceket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("192.168.0.31", 8080);
System.out.println("客户端启动");
Thread write = new Thread(new MyWriter(socket));
Thread read = new Thread(new MyReader(socket));
read.start();
write.start();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
"*******************************************************"
public class MyWriter implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public MyWriter(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (true) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = input.next();
try {
bw.write(s + "\n");
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
























 467
467

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








