
1.概述
转载:异步请求知识点与使用姿势小结 这是一个感觉有用,但是又没有用的知识点。
本篇博文作为异步请求的扫盲和使用教程,将包含以下知识点
什么是异步请求,有什么特点,适用场景
四种使用姿势:
AsyncContext方式
Callable
WebAsyncTask
DeferredResult
2. 异步请求
异步对于我们而言,应该属于经常可以听到的词汇了,在实际的开发中多多少少都会用到,那么什么是异步请求呢
2.1. 异步请求描述
先介绍一下同步与异步:
一个正常调用,吭哧吭哧执行完毕之后直接返回,这个叫同步;
接收到调用,自己不干,新开一个线程来做,主线程自己则去干其他的事情,等后台线程吭哧吭哧的跑完之后,主线程再返回结果,这个就叫异步
异步请求:
我们这里讲到的异步请求,主要是针对web请求而言,后端响应请求的一种手段,同步/异步对于前端而言是无感知、无区别的
同步请求,后端接收到请求之后,直接在处理请求线程中,执行业务逻辑,并返回
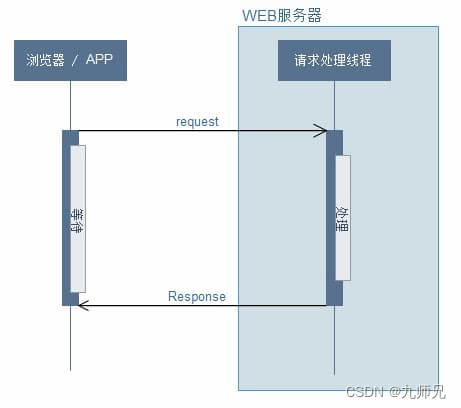
异步请求,后端接收到请求之后,新开一个线程,来执行业务逻辑,释放请求线程,避免请求线程被大量耗时的请求沾满,导致服务不可用
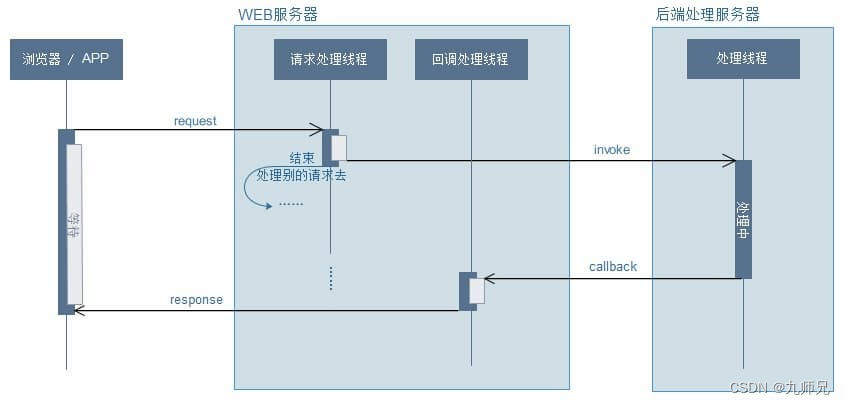
2.2. 特点
通过上面两张图,可以知道异步请求的最主要特点
业务线程,处理请求逻辑
请求处理线程立即释放,通过回调处理线程返回结果
2.3. 场景分析
从特点出发,也可以很容易看出异步请求,更适用于耗时的请求,快速的释放请求处理线程,避免web容器的请求线程被打满,导致服务不可用
举一个稍微极端一点的例子,比如我以前做过的一个多媒体服务,提供图片、音视频的编辑,这些服务接口有同步返回结果的也有异步返回结果的;同步返回结果的接口有快有慢,大部分耗时可能<10ms,而有部分接口耗时则在几十甚至上百
3.使用姿势
接下来介绍四种异步请求的使用姿势,原理一致,只是使用的场景稍有不同
3.1. AsyncContext
在Servlet3.0+之后就支持了异步请求,第一种方式比较原始,相当于直接借助Servlet的规范来实现,当然下面的case并不是直接创建一个servlet,而是借助AsyncContext来实现
package com.spring.async;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.AsyncContext;
import javax.servlet.AsyncEvent;
import javax.servlet.AsyncListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "servlet")
public class ServletRest {
/**
*todo: 2023/4/25 22:39 九师兄
* 界面执行:http://localhost:8082/servlet/get?sleep=10000
* 可以看到后端先打印
*
* 主线程over!!! http-nio-8082-exec-4
* 超时返回!!!
*
* 然后界面如下
* Whitelabel Error Page
* This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
*
* Tue Apr 25 22:39:52 CST 2023
* There was an unexpected error (type=Internal Server Error, status=500).
*
* 然后后端日志打印
*
* 操作完成:http-nio-8082-exec-6
* 内部线程:http-nio-8082-exec-5
* java.lang.IllegalStateException: The request associated with the AsyncContext has already completed processing.
* at org.apache.catalina.core.AsyncContextImpl.check(AsyncContextImpl.java:489)
*
**/
@GetMapping(path = "get")
public void get(HttpServletRequest request) {
AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
asyncContext.addListener(new AsyncListener() {
@Override
public void onComplete(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("操作完成:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Override
public void onTimeout(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("超时返回!!!");
asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("超时了!!!!");
}
@Override
public void onError(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("出现了m某些异常");
asyncEvent.getThrowable().printStackTrace();
asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("出现了某些异常哦!!!!");
}
@Override
public void onStartAsync(AsyncEvent asyncEvent) throws IOException {
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
});
asyncContext.setTimeout(3000L);
asyncContext.start(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(Long.parseLong(request.getParameter("sleep")));
System.out.println("内部线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
asyncContext.getResponse().setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().println("异步返回!");
asyncContext.getResponse().getWriter().flush();
// 异步完成,释放
asyncContext.complete();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
System.out.println("主线程over!!! " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
完整的实现如上,简单的来看一下一般步骤
javax.servlet.ServletRequest#startAsync()获取AsyncContext
添加监听器 asyncContext.addListener(AsyncListener)(这个是可选的)
用户请求开始、超时、异常、完成时回调
设置超时时间 asyncContext.setTimeout(3000L) (可选)
异步任务asyncContext.start(Runnable)
3.2. Callable
相比较于上面的复杂的示例,SpringMVC可以非常easy的实现,直接返回一个Callable即可
package com.spring.async;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "call")
public class CallableRest {
/**
*todo: 2023/4/25 22:42 九师兄
*
* 执行 http://localhost:8082/call/get
* 正常返回
* 打印如下
* do some thing
* 执行完毕,返回!!!
**/
@GetMapping(path = "get")
public Callable<String> get() {
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("do some thing");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("执行完毕,返回!!!");
return "over!";
}
};
return callable;
}
/**
*todo: 2023/4/25 22:42 九师兄
* 执行这个 http://localhost:8082/call/exception
* 前后端都报错
* 2023-04-25 22:42:31,622 [http-nio-8082-exec-6] ERROR o.a.c.c.C.[.[.[.[dispatcherServlet].log(DirectJDKLog.java:175) - Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcherServlet] threw exception
* java.lang.RuntimeException: some error!
* at com.spring.async.CallableRest$2.call(CallableRest.java:36)
**/
@GetMapping(path = "exception")
public Callable<String> exception() {
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("do some thing");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("出现异常,返回!!!");
throw new RuntimeException("some error!");
}
};
return callable;
}
}
请注意上面的两种case,一个正常返回,一个业务执行过程中,抛出来异常
3.3. WebAsyncTask
callable的方式,非常直观简单,但是我们经常关注的超时+异常的处理却不太好,这个时候我们可以用WebAsyncTask,实现姿势也很简单,包装一下callable,然后设置各种回调事件即可
package com.spring.async;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncTask;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "task")
public class WebAysncTaskRest {
/**
*todo: 2023/4/25 22:45 九师兄
*
* http://localhost:8082/task/get?sleep=10000
*
* Request URI: '/task/get'
* !!!
* do some thing
* over!!!
**/
@GetMapping(path = "get")
public WebAsyncTask<String> get(long sleep, boolean error) {
Callable<String> callable = () -> {
System.out.println("do some thing");
Thread.sleep(sleep);
if (error) {
System.out.println("出现异常,返回!!!");
throw new RuntimeException("异常了!!!");
}
return "hello world";
};
// 指定3s的超时
WebAsyncTask<String> webTask = new WebAsyncTask<>(3000, callable);
webTask.onCompletion(() -> System.out.println("over!!!"));
webTask.onTimeout(() -> {
System.out.println("超时了");
return "超时返回!!!";
});
webTask.onError(() -> {
System.out.println("出现异常了!!!");
return "异常返回";
});
System.out.println("返回");
return webTask;
}
}
3.4. DeferredResult
DeferredResult与WebAsyncTask最大的区别就是前者不确定什么时候会返回结果,
DeferredResult的这个特点,可以用来做实现很多有意思的东西,如后面将介绍的SseEmitter就用到了它
下面给出一个实例
package com.spring.async;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.DeferredResult;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "defer")
public class DeferredResultRest {
private Map<String, DeferredResult> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
*todo: 2023/4/25 22:51 九师兄
*
* 先执行 http://localhost:8082/defer/pub?id=10000&content=lcc
* 然后执行 http://localhost:8082/defer/get?id=10000
* 可以看到界面打印 lcc
* 否则会卡着
**/
@GetMapping(path = "get")
public DeferredResult<String> get(String id) {
DeferredResult<String> res = new DeferredResult<>();
cache.put(id, res);
res.onCompletion(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("over!");
}
});
return res;
}
@GetMapping(path = "pub")
public String publish(String id, String content) {
DeferredResult<String> res = cache.get(id);
if (res == null) {
return "no consumer!";
}
res.setResult(content);
return "over!";
}
}
那么这个可以设置超时么,如果一直把前端挂住,貌似也不太合适吧
在构造方法中指定超时时间: new DeferredResult<>(3000L)
设置全局的默认超时时间
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConf implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
// 超时时间设置为60s
configurer.setDefaultTimeout(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(10));
}
}























 1119
1119











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










