Description for 22.4-2

Solutions for 22.4-2
-
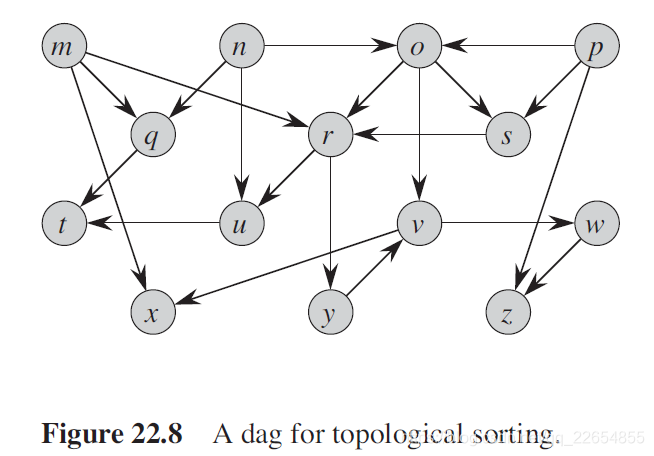
第22章第4节讲述了拓扑排序的应用,最直观的做法是先利用拓扑排序对图22.8进行DFS从而获得一个拓扑序列T,之后从t开始依次向前扫描处理直到s (利用了有向无环图中无环即无反向边的性质)
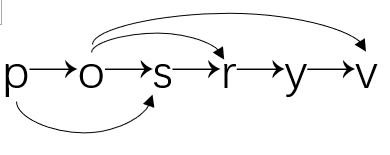
下图为其中一个拓扑排序:
算法一 (求p到v的简单路径数):
1)将所有节点赋值num=0,v赋值num=1
2)从v开始向前依次遍历,对于当前节点y:
3)若y之前存在节点x,并且在此拓扑序列中存在边(x,y)
4)x.num += y.num
5)如果v==p,输出p.num
2.下面的例子方便理解,算法正确性参考DFS以及拓扑排序(有向无环图)的相关性质。考虑到时间复杂度,我们可以直接修改DFS,在拓扑序列生成前,完成对s到t的简单路径数的计算:
算法二 (DFS修改): 调用DFS(G,s)
DFS(G,s,t)
1) for each vertex u ∈ G.V
2) u.color = WHITE
3) u.sum = 0
3) num = DFS-VISIT(G,s,t)
4) return num
DFS-VISIT(G,u,t)
1)u.color = Gray
2) if u == t
3) return 1
4)for each v ∈ G:adj[u]
5) if u.color == WHITE
6) sum += DFS(G,v,t)
7) u.Color == BLACK
8)return u.sum























 372
372











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








