RTTI Run-Time Type Identification
RTTI也叫作运行时类型识别。
使用RTTI时需要
include< typeinfo>
实例:
class Fly
{
public:
virtual void takeoff()=0;
virtual void land()=0;
};
class Plane:public Fly
{
public:
void carry(){ cout<<"乘客"<<endl;}
virtual void takeoff(){cout<<"飞机起飞"<<endl;}
virtual void land(){cout<<"飞机降落"<<endl;}
};
class Bird:public Fly
{
public:
void eat(){ cout<<"吃东西"<<endl;}
virtual void takeoff(){cout<<"小鸟起飞"<<endl;}
virtual void land(){cout<<"小鸟落地"<<endl;}
};
void dosomething(Fly *obj)
{
//如果我们可以知道传入指针所指向实例化对象的类型的话(是Bird类还是Plane类),那么就可以通过RTTI来调用子类中的函数(carry() or eat())
obj->takeoff();
cout<<typeid(*obj).name()<<endl;//打印出指针所指向实例化对象的类型
if(typeid(*obj)==typeid(Bird))
{
Bird *bird=dynamic_cast<Bird *>(obj);//将指针类型转化为指针一开始所实例化对象的类型,此时即可调用实例化对象类型的成员函数。
bird->eat();
}
obj->land();
}
int main()
{
Fly *p1=new Bird;
Fly *p2=new Plane;
dosomething(p1);
cout<<endl;
dosomething(p2);
delete p1;
p1=NULL;
delete p2;
p2=NULL;
return 0;
}
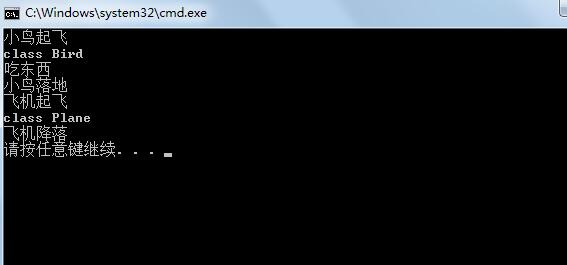
运行结果为:
dynamic_cast的使用注意事项
1.只能应用于指针或者引用的转换。
2.要转换的类型中必须要包含虚函数。
3.如果转换成功那么返回子类的地址,失败则返回NULL。
typeid的使用注意事项
1.typeid返回的是一个type_info对象的引用。
2.如果想通过基类的指针获得派生类的数据类型,基类中就必须有虚函数。
3.只能获取对象的实际类型。






















 838
838

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








