目的:深入分析setContentView方法传入布局文件id,到底做了什么
setContentView方法内部:
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}调用了getWindow()的setContentView方法
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}getWindow返回一个Window 对象
/**
* Abstract base class for a top-level window look and behavior policy. An
* instance of this class should be used as the top-level view added to the
* window manager. It provides standard UI policies such as a background, title
* area, default key processing, etc.
*
* <p>The only existing implementation of this abstract class is
* android.view.PhoneWindow, which you should instantiate when needing a
* Window.
*/
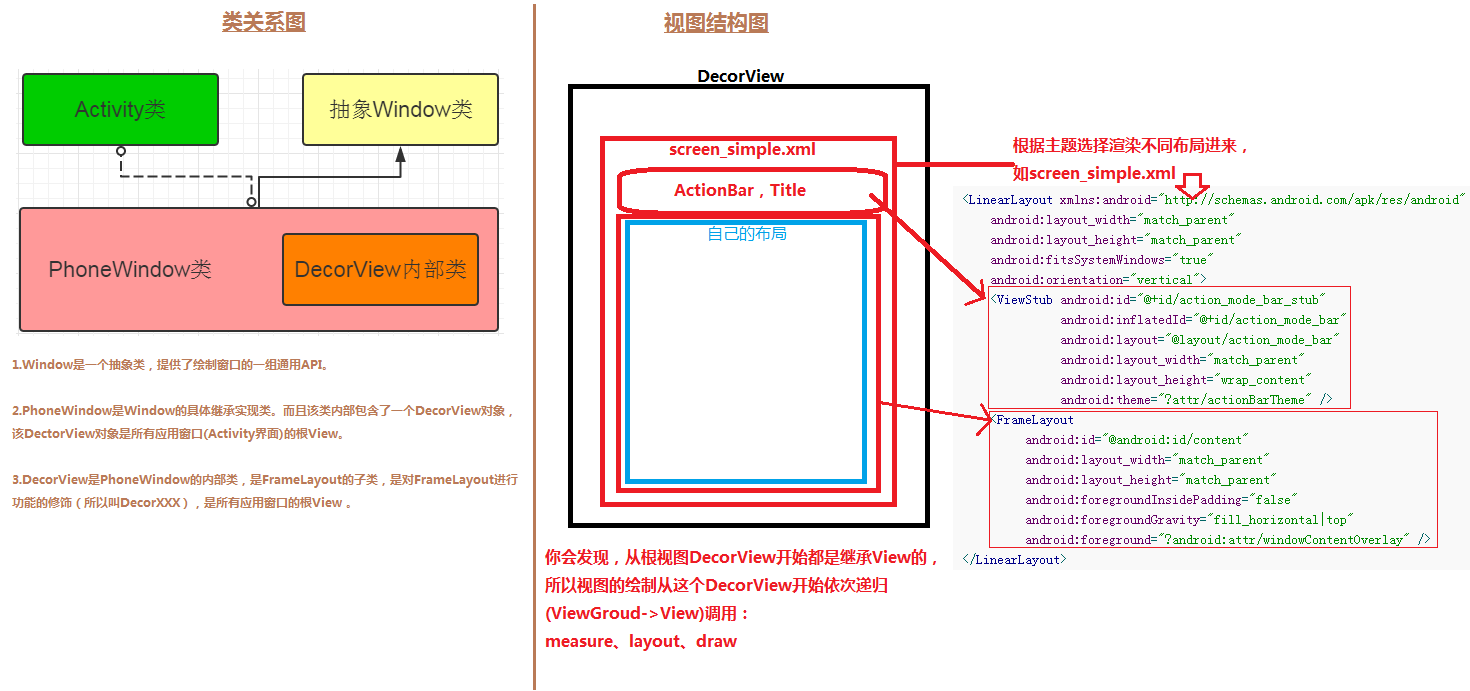
public abstract class Window {Window 对象的注释:The only existing implementation of this abstract class is android.view.PhoneWindow。只有一个实现类,就是PhoneWindow,所以就是调用了PhoneWindow的setContentView方法
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor.
private DecorView mDecor;
// This is the view in which the window contents are placed. It is either
// mDecor itself, or a child of mDecor where the contents go.
ViewGroup mContentParent;
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}一开始mContentParent 为空,PhoneWindow会调用installDecor方法
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
...
}mDecor 为空,调用generateDecor方法
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
// System process doesn't have application context and in that case we need to directly use
// the context we have. Otherwise we want the application context, so we don't cling to the
// activity.
Context context;
if (mUseDecorContext) {
Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext == null) {
context = getContext();
} else {
context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, getContext());
if (mTheme != -1) {
context.setTheme(mTheme);
}
}
} else {
context = getContext();
}
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}其中实例化了一个DecorView对象
DecorView(Context context, int featureId, PhoneWindow window,
WindowManager.LayoutParams params) {
super(context);
mFeatureId = featureId;
mShowInterpolator = AnimationUtils.loadInterpolator(context,
android.R.interpolator.linear_out_slow_in);
mHideInterpolator = AnimationUtils.loadInterpolator(context,
android.R.interpolator.fast_out_linear_in);
mBarEnterExitDuration = context.getResources().getInteger(
R.integer.dock_enter_exit_duration);
mForceWindowDrawsStatusBarBackground = context.getResources().getBoolean(
R.bool.config_forceWindowDrawsStatusBarBackground)
&& context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion >= N;
mSemiTransparentStatusBarColor = context.getResources().getColor(
R.color.system_bar_background_semi_transparent, null /* theme */);
updateAvailableWidth();
setWindow(window);
updateLogTag(params);
mResizeShadowSize = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(
R.dimen.resize_shadow_size);
initResizingPaints();
}通过setWindow(window)将DecorView与PhoneWindow绑定。之后继续回到PhoneWindow的installDecor方法,对mContentParent进行了判空
private void installDecor() {
...
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
// Set up decor part of UI to ignore fitsSystemWindows if appropriate.
mDecor.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows();
final DecorContentParent decorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) mDecor.findViewById(
R.id.decor_content_parent);
...
}
}调用generateLayout方法并复制给mContentParent
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
...
// Inflate the window decor.
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
// System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features));
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_swipe_dismiss;
setCloseOnSwipeEnabled(true);
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
// System.out.println("Title Icons!");
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0
&& (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) {
// Special case for a window with only a progress bar (and title).
// XXX Need to have a no-title version of embedded windows.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress;
// System.out.println("Progress!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) {
// Special case for a window with a custom title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) {
// If no other features and not embedded, only need a title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) {
layoutResource = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout,
R.layout.screen_action_bar);
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title;
}
// System.out.println("Title!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode;
} else {
// Embedded, so no decoration is needed.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
// System.out.println("Simple!");
}
mDecor.startChanging();
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
...
}调用getLocalFeatures来判断加载什么样的基础布局,我们看一个最简单的布局里是怎么写的
R.layout.screen_simple
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</LinearLayout>然后调用mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource)方法加载基础布局,加载xml生成控件的方法(inflater.inflate)以后会介绍
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) {
...
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) {
addView(mDecorCaptionView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
} else {
// Put it below the color views.
addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root;
...
}回到generateLayout方法
/**
* The ID that the main layout in the XML layout file should have.
*/
public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
...
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
...
return contentParent;
}发现findViewById了一个ViewGroup,并返回了出去,ID_ANDROID_CONTENT 就是基础布局中的FrameLayout的id,所以installDecor方法中的mContentParent接受的就是这个FrameLayout
DecorView的初始化过程就先介绍到这,总结来说,PhoneWindow的setContentView方法中先对DecorView初始化,并将mContentParent赋值为DecorView中id为com.android.internal.R.id.content的控件,也是requestFeature要在setContentView之前调用的原因,因为setContentView方法会调用getLocalFeatures来判断加载什么样的基础布局,setContentView方法之后调用requestFeature将没有效果
1_Activity加载UI-类图关系和视图结构.png






















 169
169











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








