PAT 1020. Tree Traversals (25)
题目地址
https://www.patest.cn/contests/pat-a-practise/1020
题目描述
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the postorder and inorder traversal sequences, you are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (<=30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the postorder sequence and the third line gives the inorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding binary tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Output:
4 1 6 3 5 7 2
ac
已知二叉树的后序 和 中序 遍历 求层次遍历
基本上 熟练的话 15分钟-20分钟AC这类问题
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 31
int n;
int post[N]; // 后
int in[N]; // 中
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
node(int _data = -1) :data(_data), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
}Bnode;
Bnode* root;
Bnode* createTree(int postL, int postR, int inL, int inR)
{
if (postL > postR)
{
return NULL;
}
int data = post[postR];
int pos = 0;
while (in[pos] != data)
{
pos++;
}
Bnode* bt = new Bnode(data);
bt->left = createTree(postL, postL + pos - inL - 1, inL, pos-1);
bt->right = createTree(postL + pos - inL, postR - 1, pos + 1, inR);
return bt;
}
void levelorder(Bnode* root)
{
queue<Bnode*> que;
while (!que.empty())
{
que.pop();
}
que.push(root);
bool flag = true;
while (!que.empty())
{
Bnode* bt = que.front();
que.pop();
if (flag)
{
printf("%d", bt->data);
flag = false;
}
else{
printf(" %d", bt->data);
}
if (bt->left != NULL)
{
que.push(bt->left);
}
if (bt->right != NULL)
{
que.push(bt->right);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in", "r", stdin);
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &post[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
}
root = NULL;
root = createTree(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
levelorder(root);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
4 1 6 3 5 7 2
*/总结: 先序和中序 ; 后序和中序 ; 可以求出二叉树,就是个递归建树的过程 要注意递归参数,调试时可以一步步看。
已知前序和中序求出树(C++ 解决)剑指offer
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
输入
8
1 2 4 7 3 5 6 8
4 7 2 1 5 3 8 6
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
struct TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int> pre, vector<int> in) {
int n = pre.size();
if (n == 0)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
int pos = 0;
while (in[pos] != pre[0])
pos++;
vector<int> preLeft, preRight, inLeft, inRight;
// 得到左子树 和 右子树
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= pos; i++){
preLeft.push_back(pre[i]);
}
for (i = pos + 1; i < n; i++){
preRight.push_back(pre[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < pos; i++){
inLeft.push_back(in[i]);
}
for (i = pos + 1; i < n; i++){
inRight.push_back(in[i]);
}
// 递归调用
root->left = reConstructBinaryTree(preLeft, inLeft);
root->right = reConstructBinaryTree(preRight, inRight);
return root;
}
};
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
vector<int> pre, in;
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
int i;
pre.resize(n);
in.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &pre[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
}
Solution sol;
struct TreeNode* root = sol.reConstructBinaryTree(pre, in);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}leetcode 原题,注意
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
题目地址
https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
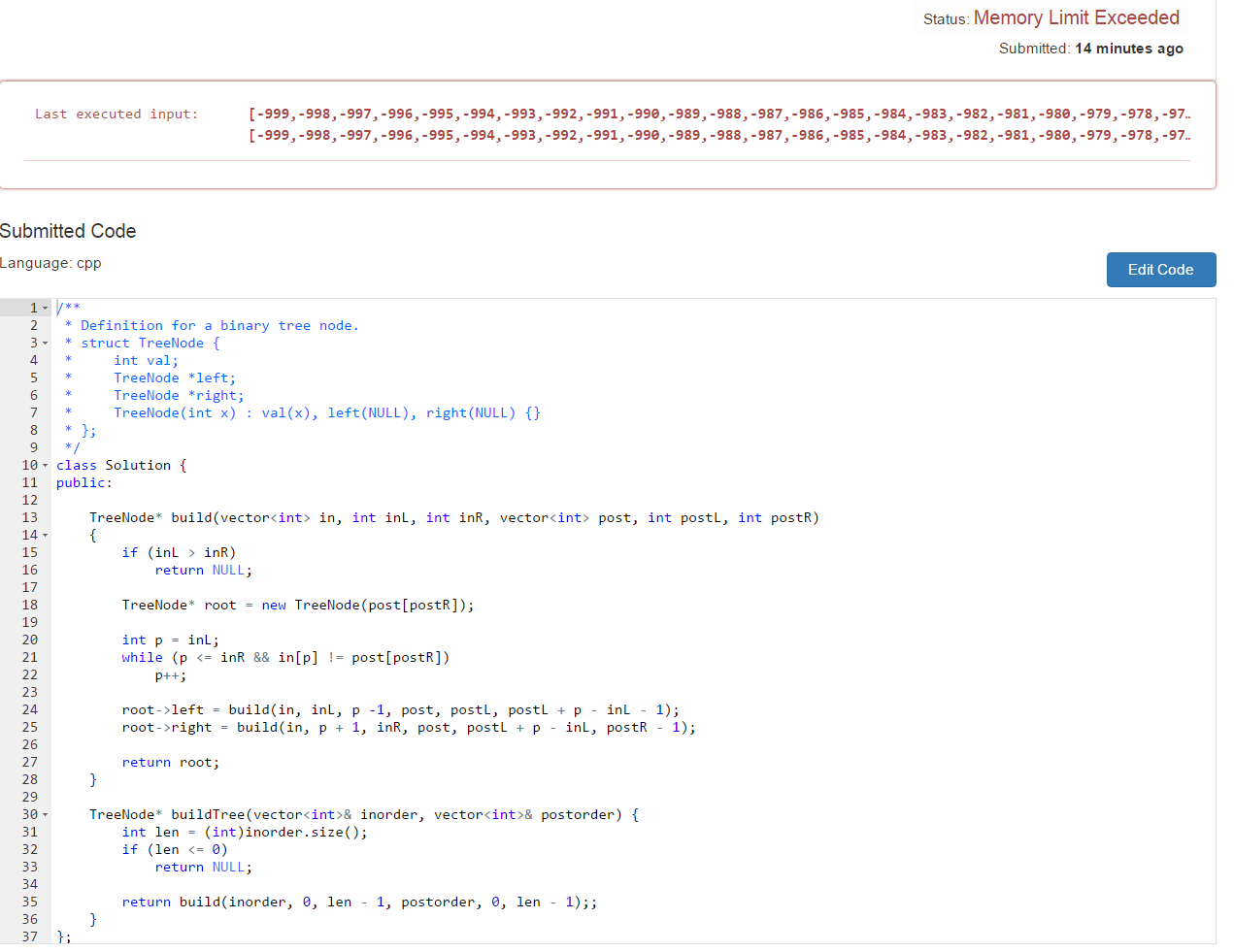
由于采用了递归做法,所以会消耗栈,当递归函数得形参太多时,就会造成内存超限错误,解决办法:
- 自定义全局变量处理
- 采用引用&处理,因为引用不会copy形参,参考c++经典书,学习引用
本题的ac代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> in;
vector<int> post;
public:
TreeNode* build(int inL, int inR, int postL, int postR)
{
if (inL > inR)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(post[postR]);
int p = inL;
while (p <= inR && in[p] != post[postR])
p++;
root->left = build( inL, p -1, postL, postL + p - inL - 1);
root->right = build( p + 1, inR, postL + p - inL, postR-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
in = inorder;
post = postorder;
int len = inorder.size();
return build( 0, len - 1, 0, len - 1);;
}
};或者
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* build(vector<int> &in, int inL, int inR, vector<int> &post, int postL, int postR)
{
if (inL > inR)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(post[postR]);
int p = inL;
while (p <= inR && in[p] != post[postR])
p++;
root->left = build(in, inL, p -1, post, postL, postL + p - inL - 1);
root->right = build(in, p + 1, inR, post, postL + p - inL, postR - 1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int len = (int)inorder.size();
if (len <= 0)
return NULL;
return build(inorder, 0, len - 1, postorder, 0, len - 1);;
}
};而不是
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
同上
ac代码如下
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR)
{
if (inL > inR)
return NULL;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(preorder[preL]);
int pos = inL;
while (inorder[pos] != preorder[preL])
pos++;
root->left = build(preorder, inorder, preL + 1, preL + pos - inL, inL, pos - 1);
root->right = build(preorder, inorder, preL + pos - inL + 1, preR, pos + 1, inR);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int len1 = preorder.size();
int len2 = inorder.size();
if (len1 != len2)
return NULL;
TreeNode* root = build(preorder, inorder, 0, len1 - 1, 0, len1 - 1);
return root;
}
};PAT 1086. Tree Traversals Again (25)
题目地址
https://www.patest.cn/contests/pat-a-practise/1086
ac代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
const int MIN_INF = - INF -1;
typedef long long int LL;
const int N = 100005;
int n;
typedef struct node{
int val;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
node(int _val =-1)
{
val = _val;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
}Bnode;
vector<int> pre;
vector<int> in;
Bnode* buildTree(int preL, int preR, int inL , int inR)
{
if(preL > preR)
return NULL;
Bnode* root = new Bnode(pre[preL]);
int pos = inL;
while(pos < inR && in[pos] != pre[preL])
pos ++;
root->left = buildTree(preL + 1, preL + 1 + pos - inL - 1, inL , pos - 1);
root->right = buildTree(preL + 1 + pos - inL, preR, pos + 1 , inR);
return root;
}
vector<int> post;
void postOrder(Bnode* root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
post.push_back(root->val);
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
pre.clear();
in.clear();
stack<int> sta;
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++)
{
char s[10];
int tmp;
scanf("%s", s);
if(s[1] == 'u')
{
scanf("%d",&tmp);
sta.push(tmp);
pre.push_back(tmp);
}else{
int val = sta.top();
in.push_back(val);
sta.pop();
}
}
Bnode * root = NULL;
root = buildTree(0, n - 1, 0, n -1);
post.clear();
postOrder(root);
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
printf("%d ",post[i]);
}
printf("%d",post[n-1]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}




















 897
897











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








