再次观看Vue教程,重新总结
1. Vue的入门实例
工具:vscode 使用node安装插件 包括vue
// 创建项目
// 初始化node npm init -y
// 安装vue npm i vue
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>2. 双向数据绑定 v-model
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
<br>
<input type="text" v-model="message">
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue'
}
})
</script>3. 字符串拼接js与vue操作对比
document
<div id="demo">
<input type="text" id="firstName" name="firstName" value="孙"><br>
<input type="text" id="lastName" name="lastName" value="悟空"><br>
结果:<p id="fullName">孙悟空</p>
</div>
<script>
var firstName = document.getElementById("firstName")
var lastName = document.getElementById("lastName")
var fullName = document.getElementById("fullName")
// 监听事件
firstName.addEventListener('input',handleTextInput)
lastName.addEventListener("input",handleTextInput)
function handleTextInput(){
fullName.innerHTML = firstName.value + lastName.value
}
</script>vue
<div id="app">
<input type="text" name="firstName" v-model="firstName"><br>
<input type="text" name="lastName" v-model="lastName"><br>
结果:{{ firstName+lastName }}
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: '孙',
lastName: '悟空'
}
})
</script>4. v-on注册事件 methods
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="number">
<button v-on:click="increment">增加</button>
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
number: 0
},
methods:{
increment: function(){
this.number++
}
}
})
</script>5. 商品价格小案例
<div id="app">
价格:<input type="text" v-model="price"><br>
<button v-on:click="count=count-1<0?0:count-1">-</button>
{{ count }}
<button v-on:click="increment">+</button><br>
总价:{{ price * count }}
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
price: 0,
count: 0
},
methods:{
increment: function(){
this.count++
}
}
})
</script>6. v-for、v-model、@keydown.enter、v-bind、@click指令的综合应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.done {
text-decoration: line-through;
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>Todo小案例</h1>
<p>{{ todos.filter(item => !item.done).length }} of {{ todos.length }} remaining [archive]</p>
<p v-for="(item,index) in todos">
<input type="checkbox" v-model="item.done" >
<span v-bind:class="{ done: item.done}">{{ item.title }}</span>
<input type="button" @click="removeTodo(index)" value="×">
</p>
<input type="text" @keydown.enter="inrementTodo" v-model="todoText">
<input type="button" @click="inrementTodo" value="添加">
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const todos = [
{
id: 1,
title: 'build an Angular JS app',
done: true
},
{
id: 2,
title: '吃饭',
done: true
},
{
id: 3,
title: '睡觉',
done: true
},
{
id: 4,
title: '打豆豆',
done: true
}
]
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
todos: todos,
todoText: ''
},
methods:{
inrementTodo(){
const todoText = this.todoText.trim()
if(!todoText.length){
return
}
this.todos.push({
id: this.todos[todos.length-1].id+1,
title: todoText
})
// 添加完后清空
this.todoText = ''
},
removeTodo(index){
const todos = this.todos
todos.splice(index,1)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>7. vue实例创建
new Vue({
// el: document.getElementById('app')
el: '#app'
})
==
// .$mount更像是动作意图
new Vue({
}).$mount('#app')8. v-once 一次性 以后不会改变它
<h1 v-once>{{ message }}</h1>9. v-html 脚本
<div>
{{ rawHtml }}
</div>
<!-- 渲染 -->
<div v-html="rawHtml">
</div>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
rawHtml: '<h1>Hello</h1>'
}
})10. v-bind 绑定参数
<div id="app">
<p v-for="item in todos">
<!-- item.id和{{ item.title }}取值方式一样的
v-bind:href="item.id": 标签属性标定
{{ item.title }}:标签文本绑定
-->
<!-- <a v-bind:href="item.id">{{ item.title }}</a> -->
<a v-bind:href="'/todos?id='+item.id">{{ item.title }}</a>
</p>
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const todos = [
{
id: 1,
title: '唐僧'
},
{
id: 2,
title: '孙悟空'
},
{
id: 3,
title: '八戒'
},
{
id: 4,
title: '沙僧'
}
]
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
todos: todos
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>11. v-if
<input type="checkbox" v-model="seen">
<div class="box" v-if="seen">
</div>12. 总结指令
- v-if 条件渲染
- v-for 列表渲染
- v-on 注册事件
- v-bind 属性绑定
- v-once 只绑定一次
- v-html 绑定输出html
- v-on:click.prevent 阻止默认事件的发生
- .filter过滤器
- .some()
- .every()
13. 官方综合案例TodoMVC
1) 插件
- node
- vue
- browser-sync npm install --save-dev browser-sync 将包装在项目中 (--save-dev)
2) 资源安装指令

3) 别名
4) 所要实现的功能
- No todos
- New todo
- Mark all as complete
- Item
- Editing
- Counter
- Clear completed button
- Persistence
- Routing
5) 基本入口

6) 渲染列表以及隐藏footer
<li v-for="item in todos">
<div class="view">
<input class="toggle" type="checkbox">
<label>{{ item.name }}</label>
<button class="destroy"></button>
</div>
<input class="edit" value="Rule the web">
</li>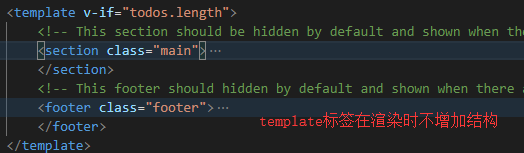
7) 添加、清除、自动聚焦
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Template • TodoMVC</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./node_modules/todomvc-common/base.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./node_modules/todomvc-app-css/index.css">
<!-- CSS overrides - remove if you don't need it -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/app.css">
</head>
<body>
<section class="todoapp" id="app">
<header class="header">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
<input class="new-todo" @keydown.enter="handleTodoAdd" placeholder="What needs to be done?" autofocus>
</header>
<template v-if="todos.length">
<!-- This section should be hidden by default and shown when there are todos -->
<section class="main">
<input @change="handleToggleAll" id="toggle-all" class="toggle-all" type="checkbox">
<label for="toggle-all">Mark all as complete</label>
<ul class="todo-list">
<li v-for="(item,index) in todos"
v-bind:class="{completed: item.completed,editing: currentEditing === item}">
<div class="view">
<input class="toggle" type="checkbox" v-model="item.completed">
<label @dblclick="handleGetEditingDblclick(item)">{{ item.name }}</label>
<button class="destroy" @click="remove(index)"></button>
</div>
<input class="edit"
@keydown.enter="handleSaveTodo(item,index,$event)"
@blur="handleSaveTodo(item,index,$event)"
@keydown.esc="handleESC"
:value="item.name">
</li>
</ul>
</section>
<!-- This footer should hidden by default and shown when there are todos -->
<footer class="footer">
<!-- This should be `0 items left` by default -->
<span class="todo-count"><strong>{{ todos.filter(item => !item.completed).length }}</strong> item left</span>
<!-- Remove this if you don't implement routing -->
<ul class="filters">
<li>
<a class="selected" href="#/">All</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#/active">Active</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#/completed">Completed</a>
</li>
</ul>
<!-- Hidden if no completed items are left ↓ -->
<button
class="clear-completed"
v-if="todos.some(item => item.completed)"
@click="handleClearAllDone">
Clear completed</button>
</footer>
</template>
</section>
<footer class="info">
<p>Double-click to edit a todo</p>
<!-- Remove the below line ↓ -->
<p>Template by <a href="http://sindresorhus.com">Sindre Sorhus</a></p>
<!-- Change this out with your name and url ↓ -->
<p>Created by <a href="http://todomvc.com">you</a></p>
<p>Part of <a href="http://todomvc.com">TodoMVC</a></p>
</footer>
<!-- Scripts here. Don't remove ↓ -->
<script src="./node_modules/todomvc-common/base.js"></script>
<!-- 引入vue -->
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./js/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
;(function(){
const todos = [
{
id: 1,
name: '唐僧',
completed: false
},
{
id: 2,
name: '悟空',
completed: false
},
{
id: 3,
name: '八戒',
completed: false
},
{
id: 4,
name: '沙僧',
completed: false
}
]
const app = new Vue({
data: {
message: 'yan',
todos: todos,
currentEditing: null
},
methods: {
// 这是添加todo方法
handleTodoAdd(e) {
const target = e.target
// .trim() 去除空格的方法
const value = target.value.trim()
// 首先判断是否值是否为空
if(!value.length){
return
}
// 判断collection中是否还有数据 如果使用const 此为常量的意思,下面就无法改变,因此在这使用let
let id = 0
if(!this.todos.length){
id = 0
}else{
id = this.todos[this.todos.length-1].id+1
}
// push到集合中
this.todos.push({
id: id,
name: value,
completed: false
})
// 然后清空
target.value = ''
},
// 当还想要event事件时,参数里可以添加 $event
remove(index){
if(!this.todos.length){
return
}
// 删除
this.todos.splice(index,1)
},
// 全选方法
handleToggleAll(e){
const checked = e.target.checked
this.todos.forEach(item => {
item.completed = checked
});
},
// 双击方法
handleGetEditingDblclick(item){
this.currentEditing = item
},
// 双击后改变方法
handleSaveTodo(item,index,e){
const target = e.target
const value = target.value.trim()
if(!value.length){
this.todos.splice(index,1)
}else{
item.name = value
this.currentEditing = null
}
},
// esc取消方法
handleESC(){
this.currentEditing = null
},
// 清除所有已完成方法
handleClearAllDone(){
// 不要使用foreach去删除,会导致索引混乱,因此使用for循环
for(let i=0;i<this.todos.length;i++){
if(todos[i].completed){
this.todos.splice(i,1)
i--
}
}
}
}
}).$mount('#app')
})()
13. v-text和v-cloak
<h1 v-text="message"></h1>正常情况下使用{{ message }},浏览器在渲染的时候首先出现{{ message }},在引入vue后,才渲染出数据
但是这样的话,显示比较麻烦,因此又有v-cloak指令 先不显示{{ message }},渲染之后才显示
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display: none;
}
</style>
<div id="app" v-cloak>
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
</div>14. v-if和v-show
- v-if:根据条件渲染不渲染
- v-show:根据条件显示不显示
15. v-pre
<span v-pre>{{ this will not be compiled }}</span>
// 显示的是{{ this will not be compiled }}
<span v-pre>{{msg}}</span>
// 即使data里面定义了msg这里仍然是显示的{{msg}}
16. 计算属性 避免重复调用
计算属性不是方法,只能当作属性使用
computed: {
remianingCounts() {
return this.todos.filter(item => !item.completed).length
}
// 该完整的写法 会自动调用其中的get方法
remianingCounts() {
get(){
return this.todos.filter(item => !item.completed).length
},
set(){
console.log('123')
}
}
}17. 本地数据持久化localstorage
todos: JSON.parse(window.localStorage.getItem(todos) || '[]'),windows.localStorage.setItem('todos',JSON.stringify(todos))18. watch
watch: {
// 监视todos的改变,当todos发生改变的时候做业务定制处理
// 引用类型只能监视一层,无法监视内部成员的子成员的改变
todos: {
// 党建是todos发生改变的时候,深度监视
handler() {
window.localStorage.setItem('todos',JSON.stringify(this.todos))
},
deep: true
}
},19. 路由切换
// 计算属性
filterTodos(){
// all return todas
// active todos.filter(item => !item.completed)
// completed todos.filter(item => item.completed)
switch (this.filterText) {
case 'active':
return this.todos.filter(item => !item.completed)
break;
case 'completed':
return this.todos.filter(item => item.completed)
break;
default:
return this.todos
break;
}
}20. 高亮
<ul class="filters">
<li>
<a :class="{selected: filterText === ''}" href="#/">All</a>
</li>
<li>
<a :class="{selected: filterText === 'active'}" href="#/active">Active</a>
</li>
<li>
<a :class="{selected: filterText === 'completed'}" href="#/completed">Completed</a>
</li>
</ul>21. 自定义语法
<script>
// 注册一个全局自定义指令 v-focus
Vue.directive('focus',{
// 当绑定的元素插入到Dom中时
// el参数就是作用该指令的DOM元素
inserted: function(el){
// 聚焦元素
el.focus()
}
})
</script>当需要操作底层的dom元素时需要使用自定义指令
- 全局
- 局部
起名规则:
- 指令的名字前面避免上 v-
- 如果是驼峰起名,在使用时需要转换为小写并用 - 连接 例:autoFocus => v-auto-focus
指令的钩子函数
// 只调用一次,指令第一次绑定到元素时调用。在这里可以进行一次性的初始化设置
// bind钩子函数中拿不到父节点
bind(){
},
// 被绑定元素插入父节点时调用 (仅保证父节点存在,但不一定已被插入文档中)。
inserted(){
},
// 所在组件的 VNode 更新时调用
update(){
},
// 指令所在组件的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用
componentUpdated(){
},
// 只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用
unbind() {
}
例子: my-show
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>自定义指令</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div id="box" class="box" v-my-show="seen">
</div>
</div>
<script src="/node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.directive('my-show',{
bind(el,binding){
if(binding.value){
el.style.display = 'block'
}else{
el.style.display = 'none'
}
},
inserted(){
},
update(){
if(binding.value){
el.style.display = 'block'
}else{
el.style.display = 'none'
}
},
componentUpdated(){
if(binding.value){
el.style.display = 'block'
}else{
el.style.display = 'none'
}
},
unbind(){
}
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
date: {
seen: true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>当需要同时使用bind和update钩子函数时,可简写
Vue.directive('color-swatch', function (el, binding) {
el.style.backgroundColor = binding.value
})22. 组件
组件化思想 封装视图
Element-ui npm i element-ui
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./node_modules/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<el-rate v-model="value3" show-text></el-rate>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/element-ui/lib/index.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Element',
value3: null
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>1) component基本使用
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/element-ui/lib/index.js"></script>
<script>
// 1. 先定义(注册)组件
// 2. 使用
Vue.component('my-component',{
template: '<div>My Component</div>'
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
})
</script>2) template
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./node_modules/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/element-ui/lib/index.js"></script>
<script>
// 1. 先定义(注册)组件
// 2. 使用
// 3. template
// 4. 组件是独立的作用域,就像node中的javascript
// 5. 组件其实是一个特殊的Vue实例,可以有自己的data、methods、computed、watch
// 6. 组件的实例必须是方法
Vue.component('my-component',{
template: `
<div>
<div>My Component</div>
<h2>{{ message }}</h2>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
message: '我是内部组件'
}
}
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>3) 全局组件与局部组件
全局组件
Vue.component('global-1',{
template: `
<div>
<h2>全局组件1</h2>
<global-2></global-2>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
message: '我是内部组件'
}
}
})
Vue.component('global-2',{
template: `
<h3>全局组件2</h3>
`,
})局部组件
Vue.component('global-1',{
template: `
<div>
<h2>全局组件1</h2>
<global-2></global-2>
<hello></hello>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
message: '我是内部组件'
}
},
components: {
// 组件名
hello: {
template: `
<div>hello 局部组件</div>
`
}
}
})4) 组件的管理


5) 父子组件之间的通信
父传子 props prop是单向传递,子组件不能更改父组件传来的数据
Vue.component('global-1',{
template: `
<div>
<h2>全局组件1</h2>
<hello :abc="message"></hello>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
message: {
id: 1,
title: 'Hello'
}
}
},
components: {
// 组件名
hello: {
template: `
<div>{{ abc.title }}</div>
`,
props: ['abc']
}
}
})子传父 $emit() 子组件将修改的数据传入到父组件,让父组件来进行修改,这样可以很好的管理,不会出现数据乱改出错而无法定位
Vue.component('global-1',{
template: `
<div>
<h2>全局组件1</h2>
<hello :abc="message"></hello>
</div>
`,
data() {
return {
message: {
id: 1,
title: 'Hello'
}
}
},
components: {
// 组件名
hello: {
template: `
<div>{{ abc.title }}</div>
`,
props: ['abc'],
methods: {
onChange(e){
const target = e.target
const value = target.value.trim()
this.$emit('abc',value)
}
}
}
}
})

案例:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="msgfromparents">
<input type="button" @click="sendToChildren" value="向子组件发送消息">
<children v-bind:message="tmpmsg" @func="getMsgFromSon"></children>
来自子组件的消息:<input type="text" :value="msgFromSon">
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./node_modules/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
const children = {
template: `
<div>
来自父组件的消息:<input type="text" :value="message"><br>
<input type="text" v-model="msgfromchildren">
<input type="button" value="向父组件传递消息" @click="sendMsg">
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
msgfromchildren: ''
}
},
props: ['message'],
methods:{
sendMsg(){
this.$emit('func',this.msgfromchildren)
}
}
}
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{
msgFromSon: '',
msgfromparents: '',
tmpmsg: ''
},
methods:{
sendToChildren(){
console.log(this.msgfromparents)
this.tmpmsg = this.msgfromparents
},
getMsgFromSon(data){
this.msgFromSon = data
// console.log(this.msgFromSon);
}
},
routes:[
],
components:{
children: children
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>23. router
前端路由是通过hash来进行跳转的
1) vue-router npm i vue-router
入门例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>路由的基本使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<a href="#/login">登录</a>
<a href="#/register">注册</a>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./node_modules/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// 路由中的组件是否必须是对象
const login = {
template: '<h1>登录组件</h1>'
}
// 而不能这样使用
// Vue.component('login',{
// template: '<h1>登录组件</h1>'
// })
const register = {
template: '<h1>注册组件</h1>'
}
const routerObj = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: login
},
{
path: '/register',
component: register
}
]
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
router: routerObj
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2) router-link使用
使用此标签是为了去掉hash中的#
<router-link to="/login">登录</router-link>3) redirect重定向解决路由不明确问题
const routerObj = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
// 页面重定向
redirect: '/login'
},
{
path: '/login',
component: login
},
{
path: '/register',
component: register
}
]
})4) 动画简单须知
<style>
.v-enter,
.v-leave-to{
opacity: 0;
transform: translateX(140px);
}
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active{
transition: all 0.5s ease;
}
</style>
<transition model="out-in">
<router-view></router-view>
</transition>5) 路由中的参数
方式一:字符串传参
<router-link to="/login?id=1&name=yan">登录</router-link>
// 路由中的组件是否必须是对象
const login = {
template: '<h1>登录组件 -- {{ $route.query.id }} -- {{ $route.query.name }}</h1>',
data(){
return{
}
},
// 生命周期钩子函数
created(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}方式二:restful规则
<router-link to="/login/12/yan">登录</router-link>
const login = {
template: '<h1>登录组件 -- {{ $route.params.id }} -- {{ $route.params.name }}</h1>',
data(){
return{
}
},
// 生命周期钩子函数
created(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
const register = {
template: '<h1>注册组件</h1>'
}
const routerObj = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
// 页面重定向
redirect: '/login'
},
{
path: '/login/:id/:name',
component: login
},
{
path: '/register',
component: register
}
]
})6) 路由的嵌套 children属性的使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>路由的基本使用</title>
<style>
.v-enter,
.v-leave-to{
opacity: 0;
transform: translateX(140px);
}
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active{
transition: all 0.5s ease;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-link to="/account">Account</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<!-- 主路由 -->
<template id="account">
<div>
<h1>Account</h1>
<router-link to="/account/login/12/yan">登录</router-link>
<router-link to="/account/register">注册</router-link>
<transition model="out-in">
<router-view></router-view>
</transition>
</div>
</template>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./node_modules/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
const account = {
template: '#account',
}
// 路由中的组件是否必须是对象
const login = {
template: '<h1>登录组件 -- {{ $route.params.id }} -- {{ $route.params.name }}</h1>',
data(){
return{
}
},
// 生命周期钩子函数
created(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}
const register = {
template: '<h1>注册组件</h1>'
}
const routerObj = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
// 页面重定向
redirect: '/account'
},
{
path: '/account',
component: account,
children: [
{
path: 'login/:id/:name',
component: login
},
{
path: 'register',
component: register
}
]
}
]
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
router: routerObj
})
</script>
</body>
</html>24. 视图布局

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>路由的基本使用</title>
<style>
.header{
background-color: yellow;
height: 80px;
}
h1{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-size: 16px
}
.container{
display: flex;
height: 800px
}
.left{
background-color: red;
flex: 2;
}
.main{
background-color: green;
flex: 8
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
<div class="container">
<router-view name="left"></router-view>
<router-view name="main"></router-view>
</div>
</div>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./node_modules/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
// head组件 -- 头部
const header = {
template: '<h1 class="header">视图头部</h1>'
}
// left组件 -- 左边
const leftBox = {
template: '<h1 class="left">视图左部</h1>'
}
// main组件 -- 主题部分
const mainBox = {
template: '<h1 class="main">视图主体部分</h1>'
}
const routerObj = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
components: {
'default': header,
'left': leftBox,
'main': mainBox
}
}
]
})
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
router: routerObj
})
</script>
</body>
</html>25. nrm
解决npm下载慢的问题
npm i nrm -g 全局安装
nrm ls 查看
nrm use npm 或者 nrm use taobao
26. webpack
1) 网页常见静态资源
- JS:.js .jsx .coffee .ts(TypeScript)
- CSS:.css .less .scss
- Images: .jpg .png .gif .bmp .svg
- Fonts:.svg .ttf .eot .woff .woff2
- 模板文件:.ejs .jade
2) webpack npm i webpack webpack-cli
前端的一个项目构建工具,基于node.js开发
作用:
- 处理js文件的互相依赖关系
- 处理js的兼容问题,把高级的浏览器不识别的语法转换为低级的
1) 入门案例

结合es6语法管理资源头文件

webpack.config.js 使用npx webpack 或者 webpack构建项目
![]()
let path = require('path')
module.exports = {
// 模式 development和production
mode: 'development',
// 入口
entry: './src/main.js',
output: {
// 打包后的文件名
filename: 'bundle.js',
// 将路径变为绝对路径
path: path.resolve(__dirname,'dist'),
}
}2) webpack-dev-server工具使用自动打包
使用方式:
- node nodemon
- webpack webpack-dev-server
全局安装:可直接使用webpack
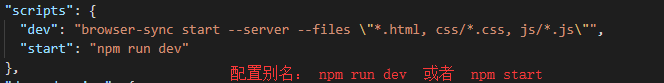
因此需要在package.json配置简化 npm run dev
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"dev": "webpack-dev-server"
},托管给服务器更改js出现页面无法更新的情况注意
<script src="/bundle.js"></script>webpack-dev-server常用命令参数:
方式一:推荐
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --open --port 3000 --contenBase src --hot"方式二:配置
const path = require('path')
const webpack = require('webpack') // 热更新-2
module.exports = {
// 模式 development和production
// mode: 'development',
// 入口
entry: './src/main.js',
output: {
// 打包后的文件名
filename: 'bundle.js',
// 将路径变为绝对路径
path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist'),
},
devServer:{
open: true, // 自动打开浏览器
port: 3000, // 设置启动端口
contentBase: 'src', // 指定托管项目的根目录
hot: true // 热更新-1
},
plugins:[
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin() // 热更新-3
]
}3) html-webpack-plugin
可以帮省去bundle.js的路径的引用
const path = require('path')
const webpack = require('webpack') // 热更新-2
const htmlWebPack = require('html-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
// 模式 development和production
// mode: 'development',
// 入口
entry: './src/main.js',
output: {
// 打包后的文件名
filename: 'bundle.js',
// 将路径变为绝对路径
path: path.resolve(__dirname,'./dist'),
},
devServer:{
open: true, // 自动打开浏览器
port: 3000, // 设置启动端口
contentBase: 'src', // 指定托管项目的根目录
hot: true // 热更新-1
},
plugins:[
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(), // 热更新-3
new htmlWebPack({ // 创建生成一个在内存中生成的html
// 指定模板页面, 以后会根据指定的页面路径去生成内存中的页面
template: path.join(__dirname,'./src/index.html'),
// 指定生成的页面的名称
filename: 'index123.html'
})
]
}4) loader管理第三方css
npm i style-loader css-loader :处理非js文件的引入问题
且在webpack.config.js中配置module节点加载第三方配置
module:{
rules: [
{ test: /\.css$/,use:['style-loader','css-loader'] },
]
}npm i less-loader less
npm i sass-loader sass
npm i url-loader file-loader
module:{
rules: [
{ test: /\.css$/,use:['style-loader','css-loader'] },
{ test: /\.less$/,use:['style-loader','css-loader','less-loader'] },
{ test: /\.scss$/,use:['style-loader','css-loader','less-loader','sass-loader'] },
// limit给定的值是图片的大小,若引用的图片大于或等于limit值,则不会转为base64格式
// name后面的参数是保持图片的名字不变 8为hash防止重命名
{ test: /\.(jpg|png|gif|bmp|jpeg)$/,use: 'url-loader?limit=7631&name=[hash:8]-[name].[ext]' },
// 字体文件
{ test: /\.(ttf|eot|svg|woff|woff2)$/,use: 'url-loader' }
]
}JSON中不能注释
5) babel配置
将高级语法转换为低级语法
注意:babel版本的对应
- babel-loader 8.x对应babel-core 7.x
- babel-loader 7.x对应babel-core 6.x

27. Vue中render
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- 网页中不推荐此处引入静态资源 -->
<!-- <script src="../node_modules/jquery/dist/jquery.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="/bundle.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<login></login>
</div>
<template id="login">
<h1>这是登录组件</h1>
</template>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var login = {
template: '#login'
}
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data:{},
components:{
},
// createElements是一个方法,调用它能够把指定的组件模板渲染为html
render:function(createElements){
// 返回的结果会替换el指定的容器
return createElements(login)
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>28. vue与webpack
1) 包的查找规则:
import Vue from 'vue'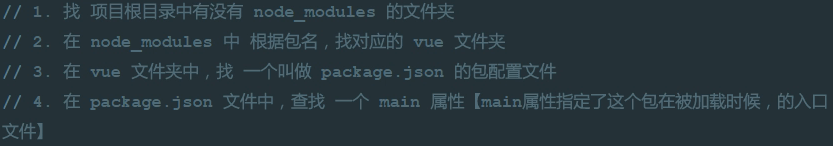
这样的功能不全(runtime-only)
因此import时候需要导入module里面的
import Vue from '../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js'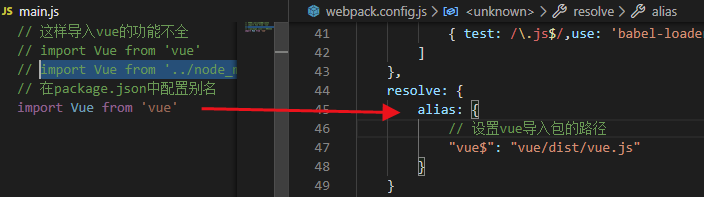
2) .vue第三方包且依赖插件
npm i vue-loader vue-template-compiler
// 依赖的插件 在webpack.config.js中存在
const vueLoaderPlugin = require('vue-loader/lib/plugin')匹配规则:
{ test: /\.vue$/,use: 'vue-loader' }
29. export default与export
暴露对象给外界
需要安装插件 npm i babel-register
30. webpack与vue-router
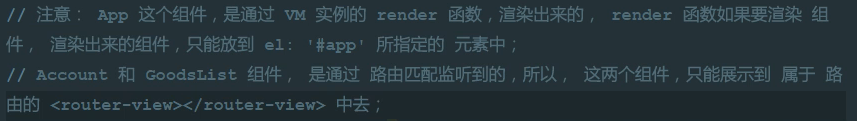
抽离路由模板:router.js
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
var router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
]
})
export default router31. style样式中的scope和lang
// 本组件中有效
<style scope>
</style>
// 指定样式格式
<style lang="scss">
</style>32. Mint-UI与Element-UI
-
mint-ui:移动端
-
element-ui: PC端
mint-ui
npm i mint-ui
// 引入全部组件
import Mint from 'mint-ui'
import Vue from 'vue'
vue.use(Mint)
// 按需导入组件
import {Cell,Checklist} from 'minu-ui'
Vue.use(Cell.name,Cell)
Vue.use(Checklist.name,Checklist)
按需导入需要注意安装插件
npm i babel-plugin-component
// 在babelrc配置
"plugins": ["transform-runtime",
"component", [
{
"libraryName": "mint-ui",
"style": true
}]
]1) 入门实例

2) mui与bootstrap一样,不依赖于vue等前端框架,不存在技术捆绑
主要需要引入:

33. 大型商场项目
1) 项目资源展示
2) 页面布局

3) git管理项目
.gitignore、README.md和开源协议
// 在PC端配置全局属性
git config --global user.email "邮箱"
git config --global user.name "用户名"
// git在本地
git init
git status 展示所有文件状态
git add . 添加
git commit -m "init my project"
// 将本地代码上传到git中
// 在你的git仓库中创建空项目
git remote add origin https://github.com/yanshiwu/Vue_Mall.git
git push -u origin mastervscode插件快速提交代码: 自带

4) 页面图标的修改icon,使用mui中的icon和icon-extra 导入样式 字体样式的导入
router-link-active
5) 路由高亮
webpack使用路由,加载vue-router且使用Vue(VueRouter)
6) tabbar切换
7) 轮播图
第一步:轮播图
第二步:加载数据
vue-resource
8) 九宫格
本地图片显示[object-module]问题
解决办法:转载 https://blog.csdn.net/simper_boy/article/details/103455444 作者:Smirky-boy
10) tabbar切换时的动画
11) ES6中的Promise



使用场景:
- 前面有失败了就终止执行 使用catch捕获异常
- 前面失败不影响后面的执行
使用.then(),前面失败了不影响后面的结果
11) NewsList路由及其页面
- 页面
- 数据获取
- 页面中时间的处理,需要定义全局过滤器 且使用moment插件
// 需要使用moment 时间格式插件
import moment from 'moment'
// 定义全局过滤器
Vue.filter('dateFormat',function(dataStr,pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"){
return moment(dataStr).format(pattern)
})
<span>发表时间:{{ item.add_time | dateFormat('YYYY-MM-DD') }}</span> - 新闻列表中的跳转
- 评论展示
- 加载更多
- 添加评论
12) 图片路由 来自复制文档
绘制 图片列表 组件页面结构并美化样
-
需要借助于 MUI 中的 tab-top-webview-main.html
-
需要把 slider 区域的 mui-fullscreen 类去掉
-
滑动条无法正常触发滑动,通过检查官方文档,发现这是JS组件,需要被初始化一下:
-
导入 mui.js
-
调用官方提供的 方式 去初始化:
mui('.mui-scroll-wrapper').scroll({
deceleration: 0.0005 //flick 减速系数,系数越大,滚动速度越慢,滚动距离越小,默认值0.0006
});-
我们在初始化 滑动条 的时候,导入的 mui.js ,但是,控制台报错:
Uncaught TypeError: 'caller', 'callee', and 'arguments' properties may not be accessed on strict mode
-
经过我们合理的推测,觉得,可能是 mui.js 中用到了 'caller', 'callee', and 'arguments' 东西,但是, webpack 打包好的 bundle.js 中,默认是启用严格模式的,所以,这两者冲突了;
-
解决方案: 1. 把 mui.js 中的 非严格 模式的代码改掉;但是不现实; 2. 把 webpack 打包时候的严格模式禁用掉;
-
最终,我们选择了 plan B 移除严格模式: 使用这个插件 babel-plugin-transform-remove-strict-mode
-
刚进入 图片分享页面的时候, 滑动条无法正常工作, 经过我们认真的分析,发现, 如果要初始化 滑动条,必须要等 DOM 元素加载完毕,所以,我们把 初始化 滑动条 的代码,搬到了 mounted 生命周期函数中;
-
当 滑动条 调试OK后,发现, tabbar 无法正常工作了,这时候,我们需要把 每个 tabbar 按钮的 样式中
mui-tab-item重新改一下名字; -
获取所有分类,并渲染 分类列表;
制作图片列表区域
-
图片列表需要使用懒加载技术,我们可以使用 Mint-UI 提供的现成的 组件
lazy-load -
根据
lazy-load的使用文档,尝试使用 -
渲染图片列表数据
实现了 图片列表的 懒加载改造和 样式美化
实现了 点击图片 跳转到 图片详情页面
-
在改造 li 成 router-link 的时候,需要使用 tag 属性指定要渲染为 哪种元素
实现 详情页面的布局和美化,同时获取数据渲染页面
实现 图片详情中 缩略图的功能
-
使用 插件 vue-preview 这个缩略图插件
-
获取到所有的图片列表,然后使用 v-for 指令渲染数据
-
注意: img标签上的class不能去掉
-
注意: 每个 图片数据对象中,必须有 w 和 h 属性
13) 商品列表
手机上调试
14) Vuex




剩下的差不多。。。





















 240
240











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








