在讲解这个之前,我们首先讲一下tf.range(),因为这两个一般都是在一起用的
tf.range()
其和python中的range()的用法基本一样,只不过这里返回的是一个1-D的tensor
tf.range(limit, delta=1, dtype=None, name=‘range’)
tf.range(start, limit, delta=1, dtype=None, name=‘range’)
'''
Args:
start: A 0-D Tensor (scalar). Acts as first entry in the range if limit is not None; otherwise, acts as range limit and first entry defaults to 0.
limit: A 0-D Tensor (scalar). Upper limit of sequence, exclusive. If None, defaults to the value of start while the first entry of the range defaults to 0.
delta: A 0-D Tensor (scalar). Number that increments start. Defaults to 1.
dtype: The type of the elements of the resulting tensor.
name: A name for the operation. Defaults to "range".
Returns:
An 1-D Tensor of type dtype.
'''
tf.gather
该接口的作用:就是抽取出params的第axis维度上在indices里面所有的index(看后面的例子,就会懂)
tf.gather(
params,
indices,
validate_indices=None,
name=None,
axis=0
)
'''
Args:
params: A Tensor. The tensor from which to gather values. Must be at least rank axis + 1.
indices: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: int32, int64. Index tensor. Must be in range [0, params.shape[axis]).
axis: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: int32, int64. The axis in params to gather indices from. Defaults to the first dimension. Supports negative indexes.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A Tensor. Has the same type as params.
'''
说明
参数
- params: A Tensor.
- indices: A Tensor. types必须是: int32, int64. 里面的每一个元素大小必须在 [0, params.shape[axis])范围内.
- axis: 维度。沿着params的哪一个维度进行抽取indices
返回
返回的是一个tensor
帮助理解图
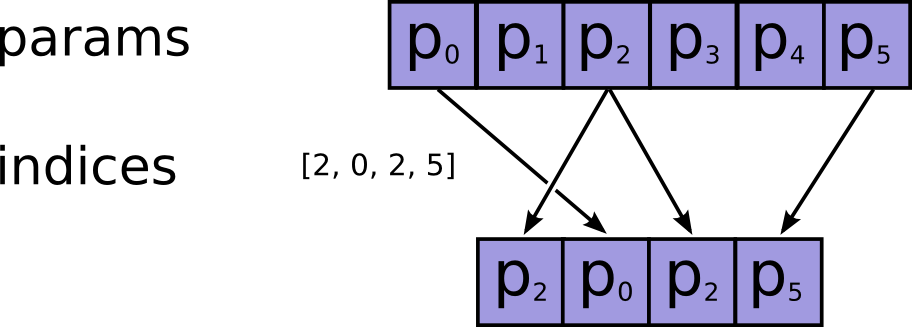
例子1
代码
import tensorflow as tf
Params = tf.range(0,10)*10
a = tf.gather(Params,[0,5,9])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print("Params: \n",sess.run(Params))
print("抽取的结果: \n",sess.run(a))
输出
Params:
[ 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90]
抽取的结果:
[ 0 50 90]
例子2
代码
import tensorflow as tf
Params=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,3,4]))
indicxs_0=[0,1]
indicxs_1=[0,2]
indicxs_2=[2,3]
gather_0=tf.gather(params=Params,indices=indicxs_0,axis=0)
gather_1=tf.gather(params=Params,indices=indicxs_1,axis=1)
gather_2=tf.gather(params=Params,indices=indicxs_2,axis=2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print("Params :\n ",sess.run(Params))
print("沿着第O维度抽取第0,1个: \n",sess.run(gather_0))
print("沿着第1维度抽取第0,3个: \n",sess.run(gather_1))
print("沿着第2维度抽取第3,4个: \n",sess.run(gather_2))
输出
Params :
[
[[ 0.78150964 2.09648061 2.37558031 1.20743346]
[-1.12413085 -0.66349769 1.15486336 -1.17151475]
[ 0.0476133 -0.09292984 -0.29620713 0.70557141]]
[[-1.34968698 -0.2931003 -1.94950449 -0.27036974]
[ 0.27591622 -0.19094539 -0.56113148 0.55863774]
[-0.48273012 -0.7819376 0.3261987 -0.97833097]]
]
沿着第O维度抽取第0,1个:
[[[ 0.78150964 2.09648061 2.37558031 1.20743346]
[-1.12413085 -0.66349769 1.15486336 -1.17151475]
[ 0.0476133 -0.09292984 -0.29620713 0.70557141]]
[[-1.34968698 -0.2931003 -1.94950449 -0.27036974]
[ 0.27591622 -0.19094539 -0.56113148 0.55863774]
[-0.48273012 -0.7819376 0.3261987 -0.97833097]]]
沿着第1维度抽取第0,3个:
[[[ 0.78150964 2.09648061 2.37558031 1.20743346]
[ 0.0476133 -0.09292984 -0.29620713 0.70557141]]
[[-1.34968698 -0.2931003 -1.94950449 -0.27036974]
[-0.48273012 -0.7819376 0.3261987 -0.97833097]]]
沿着第2维度抽取第3,4个:
[[[ 2.37558031 1.20743346]
[ 1.15486336 -1.17151475]
[-0.29620713 0.70557141]]
[[-1.94950449 -0.27036974]
[-0.56113148 0.55863774]
[ 0.3261987 -0.97833097]]]





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








