1. 振幅的基本概念
振幅是描述音频信号强度的一个重要参数。它通常表示为信号的幅度值,幅度越大,声音听起来就越响。为了更好地理解和处理音频信号,通常会将振幅转换为分贝(dB)单位。分贝是一个对数单位,能够更好地反映人耳对声音强度变化的感知。
人耳对声音的感知是非线性的,通常对响度变化的感知与实际的物理振幅变化不成正比。使用 RMS 和分贝单位进行计算,可以更好地模拟人耳的感知特性。以下是不同计算方法与听觉结果的一致性分析:
- 总 RMS:提供了整体响度的良好估计,通常与听觉感知一致。
- 最大 RMS:能够捕捉到音频信号中的最强响度部分,适合用于动态范围分析。
- 最小 RMS:有助于识别音频信号中的弱响度部分,适合用于音频修复和增强。
- 平均 RMS:提供了稳定的响度水平,适合用于音频混音和母带处理。
- 峰值幅度:虽然能够快速反映瞬时响度,但由于其瞬时特性,可能与人耳的感知不完全一致。
2. 振幅计算方法
2.1 总 RMS(Total RMS)
总 RMS 是一种常用的振幅计算方法,表示整个音频信号的平均能量。其计算公式为:
RMS
=
20
⋅
log
10
(
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
x
i
2
+
1.0
×
1
0
−
9
)
\text{RMS} = 20 \cdot \log_{10}(\sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} x_i^2} + 1.0 \times 10^{-9})
RMS=20⋅log10(N1i=1∑Nxi2+1.0×10−9)
其中, x i x_i xi是音频信号的样本值, N N N 是样本总数。总 RMS 提供了音频信号的整体响度感知。
2.2 最大 RMS(Max RMS)
最大 RMS 是通过将音频信号分成多个窗口,计算每个窗口的 RMS 值,并返回这些值中的最大值。其计算公式为:
Max RMS
=
max
(
20
⋅
log
10
(
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
x
i
2
+
1.0
×
1
0
−
9
)
)
\text{Max RMS} = \max \left( 20 \cdot \log_{10} \left( \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} x_i^2} + 1.0 \times 10^{-9} \right) \right)
Max RMS=max
20⋅log10
N1i=1∑Nxi2+1.0×10−9
其中:
- x i x_i xi 是窗口内的音频样本值。
- N N N是窗口内样本的总数。
2.3 最小 RMS(Min RMS)
最小 RMS 与最大 RMS 类似,但它返回的是每个窗口中计算出的最小 RMS 值。其计算公式为:
Min RMS
=
min
(
20
⋅
log
10
(
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
x
i
2
+
1.0
×
1
0
−
9
)
)
\text{Min RMS} = \min \left( 20 \cdot \log_{10} \left( \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} x_i^2} + 1.0 \times 10^{-9} \right) \right)
Min RMS=min
20⋅log10
N1i=1∑Nxi2+1.0×10−9
其中:
- x i x_i xi 是窗口内的音频样本值。
- N N N 是窗口内样本的总数。
2.4 平均 RMS(Avg RMS)
平均 RMS 是所有窗口 RMS 值的平均值,提供了音频信号的整体响度水平。其计算公式为:
Avg RMS
=
1
M
∑
j
=
1
M
(
20
⋅
log
10
(
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
x
i
j
2
+
1.0
×
1
0
−
9
)
)
\text{Avg RMS} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_{j=1}^{M} \left( 20 \cdot \log_{10} \left( \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} x_{ij}^2} + 1.0 \times 10^{-9} \right) \right)
Avg RMS=M1j=1∑M
20⋅log10
N1i=1∑Nxij2+1.0×10−9
其中:
- x i j x_{ij} xij 是第 j j j 个窗口内的音频样本值。
- N N N 是每个窗口内样本的总数。
- M M M 是窗口的总数。
2.5 峰值幅度(Peak Amplitude)
峰值幅度是音频信号中最大绝对值的幅度,通常用于表示信号的瞬时强度。其计算公式为:
Peak
=
20
⋅
log
10
(
max
(
∣
x
∣
)
+
1.0
×
1
0
−
9
)
\text{Peak} = 20 \cdot \log_{10}(\max(|x|) + 1.0 \times 10^{-9})
Peak=20⋅log10(max(∣x∣)+1.0×10−9)
峰值幅度能够快速反映音频信号的瞬时响度,但不一定能准确表示人耳的感知。
3. 程序实现
该程序实现了音频分析与音量调整功能,能够计算音频文件的总、最大、最小、平均 RMS 和峰值幅度,并根据用户指定的不同类型目标 dBFS 值自动调整音频的音量。
import os
import numpy as np
import librosa
import soundfile as sf
def calculate_total_rms_dbfs(audio_data):
rms_level = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(audio_data ** 2)) + 1.0e-9) # 计算总 RMS 并转换为 dBFS
return rms_level
def calculate_max_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.max(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf # 返回 -inf 如果没有 RMS 值
def calculate_min_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.min(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf # 返回 -inf 如果没有 RMS 值
def calculate_avg_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.mean(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf # 返回 -inf 如果没有 RMS 值
def calculate_peak_amplitude(audio_data):
return 20 * np.log10(np.max(np.abs(audio_data)) + 1.0e-9)
def adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs):
"""调整音频的音量到目标 RMS 值"""
current_rms = 10 ** (current_rms_dbfs / 20) # 将 dBFS 转换为线性幅度
target_rms = 10 ** (target_rms_dbfs / 20) # 将目标 dBFS 转换为线性幅度
# 计算调整因子
adjustment_factor = target_rms / current_rms if current_rms > 0 else 1.0
adjusted_audio = audio_data * adjustment_factor
return adjusted_audio
def adjust_volume_to_total_rms(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs):
current_rms_dbfs = calculate_total_rms_dbfs(audio_data)
return adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs)
def adjust_volume_to_max_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs):
current_rms_dbfs = calculate_max_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
return adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs)
def adjust_volume_to_min_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs):
current_rms_dbfs = calculate_min_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
return adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs)
def adjust_volume_to_avg_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs):
current_rms_dbfs = calculate_avg_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
return adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs)
def adjust_volume_to_peak_amplitude(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs):
current_rms_dbfs = calculate_peak_amplitude(audio_data)
return adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs)
def analyze_audio_file(audio_path, target_rms_dbfs, window_duration=0.05):
audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=None)
window_size = int(window_duration * sr)
total_rms_dbfs = calculate_total_rms_dbfs(audio_data)
max_rms_dbfs = calculate_max_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
min_rms_dbfs = calculate_min_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
avg_rms_dbfs = calculate_avg_rms_dbfs(audio_data, window_size)
peak_amplitude = calculate_peak_amplitude(audio_data)
print(f"File: {audio_path}")
print(f"Total RMS (dBFS): {total_rms_dbfs:.2f}")
print(f"Max RMS (dBFS): {max_rms_dbfs:.2f}")
print(f"Min RMS (dBFS): {min_rms_dbfs:.2f}")
print(f"Avg RMS (dBFS): {avg_rms_dbfs:.2f}")
print(f"Peak Amplitude (dBFS): {peak_amplitude:.2f}")
# 调整音频到目标 RMS
adjusted_audio_total = adjust_volume_to_total_rms(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs)
adjusted_audio_max = adjust_volume_to_max_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs)
adjusted_audio_min = adjust_volume_to_min_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs)
adjusted_audio_avg = adjust_volume_to_avg_rms(audio_data, window_size, target_rms_dbfs)
adjusted_audio_peak = adjust_volume_to_peak_amplitude(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs)
# 保存调整后的音频
sf.write(os.path.splitext(audio_path)[0] + '_adjusted_total.wav', adjusted_audio_total, sr)
sf.write(os.path.splitext(audio_path)[0] + '_adjusted_max.wav', adjusted_audio_max, sr)
sf.write(os.path.splitext(audio_path)[0] + '_adjusted_min.wav', adjusted_audio_min, sr)
sf.write(os.path.splitext(audio_path)[0] + '_adjusted_avg.wav', adjusted_audio_avg, sr)
sf.write(os.path.splitext(audio_path)[0] + '_adjusted_peak.wav', adjusted_audio_peak, sr)
print(f"Adjusted audio files saved with target RMS: {target_rms_dbfs} dBFS")
if __name__ == "__main__":
audio_path = './test_volume.wav'
target_rms_dbfs = -20 # 目标 RMS 值 (dBFS)
analyze_audio_file(audio_path, target_rms_dbfs)

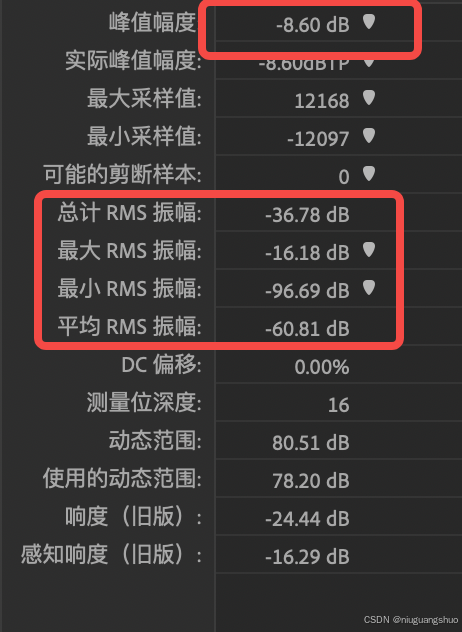 计算结果与Audition一致。
计算结果与Audition一致。
4. 基于策略模式的代码重构
import numpy as np
import librosa
import soundfile as sf
# 策略接口
class AudioProcessingStrategy:
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
pass
def adjust_volume(self, audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, window_size=None):
current_rms_dbfs = self.calculate_rms(audio_data, window_size)
return self._adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs, window_size)
@staticmethod
def _adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, current_rms_dbfs, window_size=None):
current_rms = 10 ** (current_rms_dbfs / 20)
target_rms = 10 ** (target_rms_dbfs / 20)
adjustment_factor = target_rms / current_rms if current_rms > 0 else 1.0
return audio_data * adjustment_factor
# 具体策略:总 RMS
class TotalRMSStrategy(AudioProcessingStrategy):
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
return 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(audio_data ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
# 具体策略:最大 RMS
class MaxRMSStrategy(AudioProcessingStrategy):
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.max(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf
# 具体策略:最小 RMS
class MinRMSStrategy(AudioProcessingStrategy):
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.min(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf
# 具体策略:平均 RMS
class AvgRMSStrategy(AudioProcessingStrategy):
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
rms_values = []
for start in range(0, len(audio_data), window_size):
end = min(start + window_size, len(audio_data))
window = audio_data[start:end]
if len(window) > 0:
rms = 20 * np.log10(np.sqrt(np.mean(window ** 2)) + 1.0e-9)
rms_values.append(rms)
return np.mean(rms_values) if rms_values else -np.inf
# 具体策略:峰值幅度
class PeakAmplitudeStrategy(AudioProcessingStrategy):
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
return 20 * np.log10(np.max(np.abs(audio_data)) + 1.0e-9)
# 上下文
# 上下文
class AudioProcessor:
def __init__(self, strategy: AudioProcessingStrategy):
self.strategy = strategy
def set_strategy(self, strategy: AudioProcessingStrategy):
self.strategy = strategy
return self # 返回自身以支持链式调用
def calculate_rms(self, audio_data, window_size=None):
return self.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data, window_size)
def adjust_volume(self, audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, window_size=None):
return self.strategy.adjust_volume(audio_data, target_rms_dbfs, window_size)
if __name__ == "__main__":
audio_path = './test_volume.wav'
audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=None)
# 创建上下文并设置策略
audio_processor = AudioProcessor(TotalRMSStrategy())
# 计算总 RMS 并调整音量
adjusted_audio_total = audio_processor.set_strategy(TotalRMSStrategy()).adjust_volume(audio_data, -20)
total_rms = audio_processor.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data)
print(f"Total RMS (dBFS): {total_rms:.2f}")
sf.write('./adjusted_audio_total.wav', adjusted_audio_total, sr)
# 计算最大 RMS 并调整音量
adjusted_audio_max = audio_processor.set_strategy(MaxRMSStrategy()).adjust_volume(audio_data, -20, window_size=1024)
max_rms = audio_processor.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data, window_size=1024)
print(f"Max RMS (dBFS): {max_rms:.2f}")
sf.write('./adjusted_audio_max.wav', adjusted_audio_max, sr)
# 计算最小 RMS 并调整音量
adjusted_audio_min = audio_processor.set_strategy(MinRMSStrategy()).adjust_volume(audio_data, -20, window_size=1024)
min_rms = audio_processor.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data, window_size=1024)
print(f"Min RMS (dBFS): {min_rms:.2f}")
sf.write('./adjusted_audio_min.wav', adjusted_audio_min, sr)
# 计算平均 RMS 并调整音量
adjusted_audio_avg = audio_processor.set_strategy(AvgRMSStrategy()).adjust_volume(audio_data, -20, window_size=1024)
avg_rms = audio_processor.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data, window_size=1024)
print(f"Avg RMS (dBFS): {avg_rms:.2f}")
sf.write('./adjusted_audio_avg.wav', adjusted_audio_avg, sr)
# 计算峰值幅度并调整音量
adjusted_audio_peak = audio_processor.set_strategy(PeakAmplitudeStrategy()).adjust_volume(audio_data, -20)
peak_amplitude = audio_processor.strategy.calculate_rms(audio_data)
print(f"Peak Amplitude (dBFS): {peak_amplitude:.2f}")
sf.write('./adjusted_audio_peak.wav', adjusted_audio_peak, sr)





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








