如果你跟我一样想从非常简单的概念入手,学习最基本的pytorch代码,可以关注我的专栏,在目录中找到pytorch简易教程的文章部分,我会持续保持更新
理论部分
从一个简单的问题入手,假设我们是一间大学,来决定录取哪些学生,我们有这些学生的两个数据,一个是在校平时成绩Grades,一个是考试成绩test
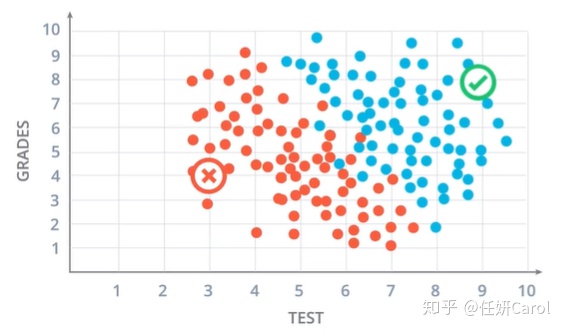
红色的点表示这些学生被拒绝,蓝色的点表示这些学生通过
很明显,如果能找到一条直线进行划分,那么下次再有学生来了,只要看他在直线的那一边,就可以决定这个学生是通过还是拒绝
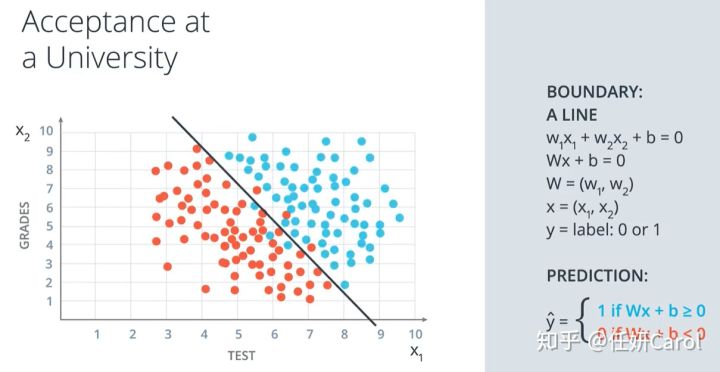
把上面的例子更一般化,就是下图,下图所示就是一个感知机,我们有n个变量,每个变量都有一种含义(上面的例子中变量就是GEADES和TEST),经过第一个节点,就是线性方程式,再经过第二个节点,是一个阶跃函数,就可以得到分类的结果

还回到刚刚的例子,如何才能找到这条直线呢?可以按照下面的步骤来进行:
1.随便画条直线
2. 找到那些没有满足条件的点,根据这些点对直线进行调整
3. 重复2很多轮直到满意
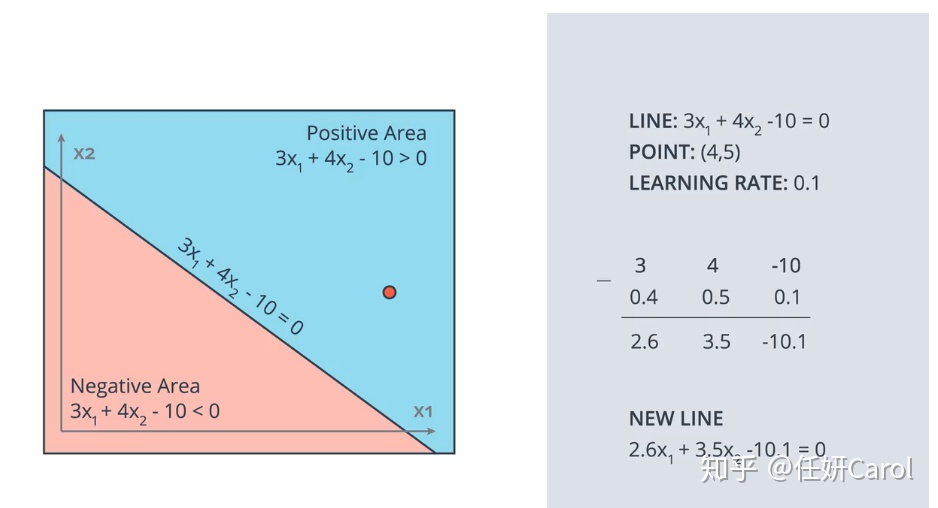
先随便画了一条线3x1+4x2-10=0,然后找到其中一个被错分的点(4,5),这个错分的点在>0的区域,我们希望这条线能往上移动一点,对应到方程中就是把w1和w2和b都减小一些
调整的幅度要设置得当,不能太大,不然一个点错误,直接矫枉过正,也不能太小,不然就挪动的太慢了。这个幅度就是learning rate学习率
代码部分
编写感知器算法,数据如下

import numpy as np
# Setting the random seed, feel free to change it and see different solutions.
np.random.seed(42)
def stepFunction(t):
if t >= 0:
return 1
return 0
def prediction(X, W, b):
return stepFunction((np.matmul(X,W)+b)[0])
# TODO: Fill in the code below to implement the perceptron trick.
# The function should receive as inputs the data X, the labels y,
# the weights W (as an array), and the bias b,
# update the weights and bias W, b, according to the perceptron algorithm,
# and return W and b.
def perceptronStep(X, y, W, b, learn_rate = 0.01):
for i in range(len(X)):
y_hat = prediction(X[i], W, b)
if y_hat - y[i] < 0:
W[0] += X[i][0]*learn_rate
W[1] += X[i][1]*learn_rate
b += learn_rate
elif y_hat - y[i] > 0:
W[0] -= X[i][0]*learn_rate
W[1] -= X[i][1]*learn_rate
b -= learn_rate
return W, b
# This function runs the perceptron algorithm repeatedly on the dataset,
# and returns a few of the boundary lines obtained in the iterations,
# for plotting purposes.
# Feel free to play with the learning rate and the num_epochs,
# and see your results plotted below.
def trainPerceptronAlgorithm(X, y, learn_rate = 0.01, num_epochs = 25):
x_min, x_max = min(X.T[0]), max(X.T[0])
y_min, y_max = min(X.T[1]), max(X.T[1])
W = np.array(np.random.rand(2,1))
b = np.random.rand(1)[0] + x_max
# These are the solution lines that get plotted below.
boundary_lines = []
for i in range(num_epochs):
# In each epoch, we apply the perceptron step.
W, b = perceptronStep(X, y, W, b, learn_rate)
boundary_lines.append((-W[0]/W[1], -b/W[1]))
return boundary_lines
上面的代码非常简单,看这样的代码可以清楚的了解这里面的步骤,值得一看
全部笔记请关注微信公众号【阿肉爱学习】,在菜单栏点击“利其器”,并选择“pytorch”查看






















 1398
1398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








