1.AFDP(抽象工厂设计模式)
AFDP 定义了一个抽象类来创建相关的家族对象但未指定其具体子类
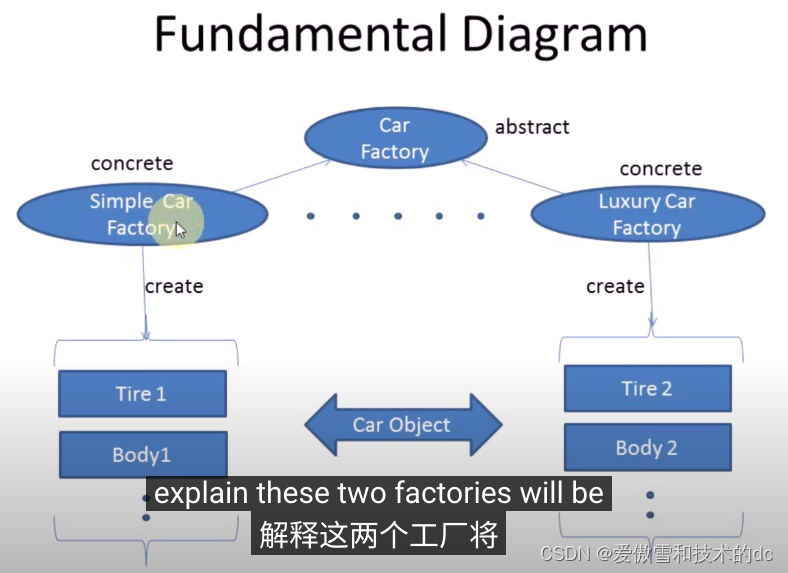
2.基本原理图
3.为什么/何时使用AFDP
1.你需要系统独立于对象的创建、组合和表示方式。
2.显示接口而不是实现。
3.系统需要配置多个对象系列之一
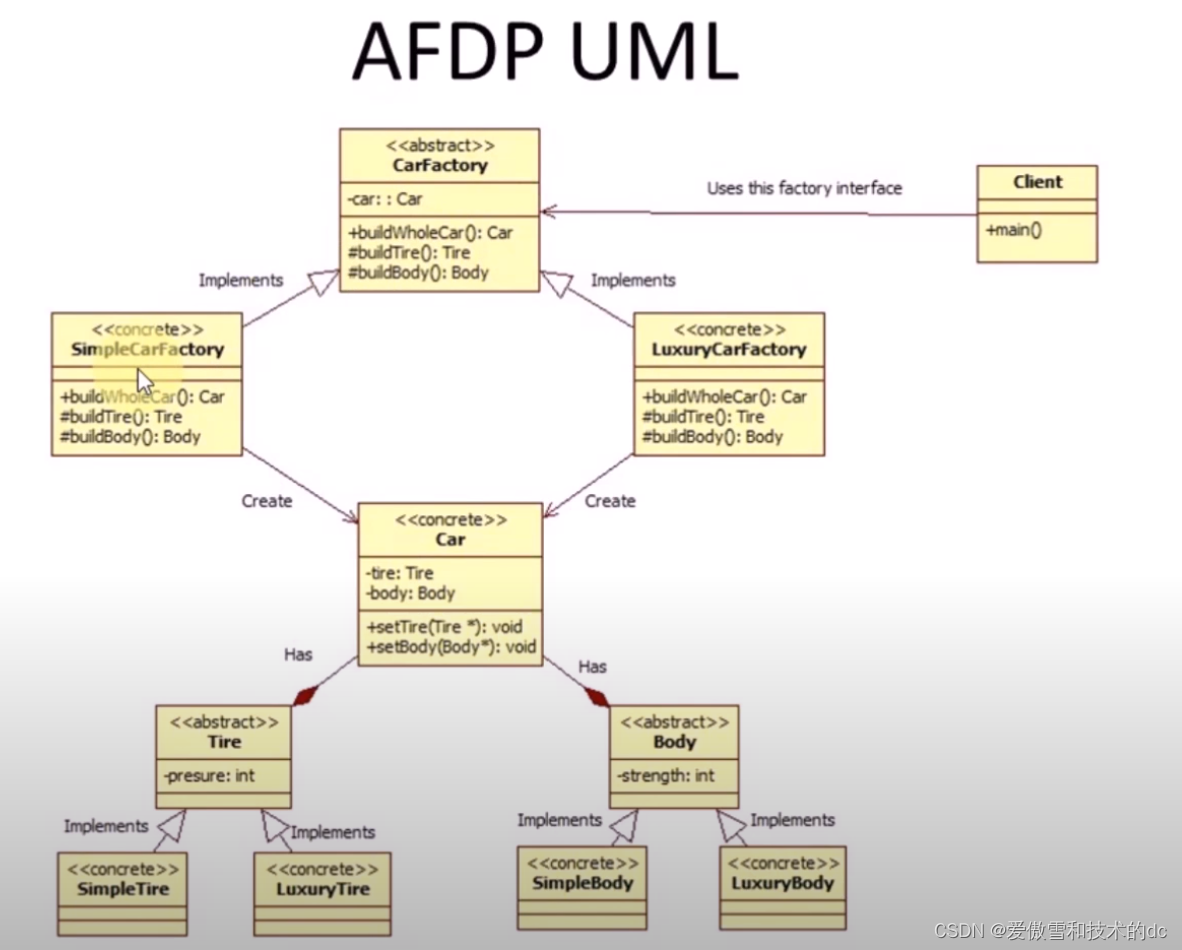
4.UML图
5.C++程序
 继承中的访问:
继承中的访问:protected 最关键的特性是它允许派生类访问基类中的受保护成员。这意味着如果一个基类中的成员被声明为 protected,则任何直接或间接的派生类都可以访问这些成员。这一点与 private 成员不同,private 成员即使在派生类中也是不可访问的。
Car.cpp
#ifndef __io__
#define __io__
#include <iostream>
#endif
class Tire {
protected:
std::string name;
int presure;
public:
Tire(std::string n, int presure):name(n), presure(presure){};
std::string getName() { return name;}
int getPresure() {return presure;}
};
class SimpleTire:public Tire {
public:
SimpleTire(): Tire("SimpleTire", 75) {}
};
class LuxuryTire : public Tire {
public:
LuxuryTire(): Tire("LuxuryTire", 100) {}
};
class Body {
protected:
std::string name;
int strength;
public:
Body(std::string n, int strength): name(n) , strength(strength) {}
std::string getName() {return name;}
int getStrenth() {return strength;}
};
class SimpleBody: public Body {
public:
SimpleBody(): Body("SimpleBody", 75) {}
};
class LuxuryBody: public Body {
public:
LuxuryBody(): Body("LuxuryBody", 100) {}
};
class Car {
protected:
std::string name;
Tire* tire;
Body* body;
public:
Car(std::string n): name(n) {}
void setTire(Tire* t) {tire = t;}
void setBody(Body* b) {body = b;}
void printDetails() {
std::cout << std::endl << "car:" << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "tire:" << tire->getName() << "pressure:" << tire->getPresure() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Body:" << body->getName() << "strength:" << body->getStrenth() << std::endl;
}
};CarFactory.cpp
#ifndef __io__
#define __io__
#include <iostream>
#endif
class Tire {
protected:
std::string name;
int presure;
public:
Tire(std::string n, int presure):name(n), presure(presure){};
std::string getName() { return name;}
int getPresure() {return presure;}
};
class SimpleTire:public Tire {
public:
SimpleTire(): Tire("SimpleTire", 75) {}
};
class LuxuryTire : public Tire {
public:
LuxuryTire(): Tire("LuxuryTire", 100) {}
};
class Body {
protected:
std::string name;
int strength;
public:
Body(std::string n, int strength): name(n) , strength(strength) {}
std::string getName() {return name;}
int getStrenth() {return strength;}
};
class SimpleBody: public Body {
public:
SimpleBody(): Body("SimpleBody", 75) {}
};
class LuxuryBody: public Body {
public:
LuxuryBody(): Body("LuxuryBody", 100) {}
};
class Car {
protected:
std::string name;
Tire* tire;
Body* body;
public:
Car(std::string n): name(n) {}
void setTire(Tire* t) {tire = t;}
void setBody(Body* b) {body = b;}
void printDetails() {
std::cout << std::endl << "car:" << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "tire:" << tire->getName() << "pressure:" << tire->getPresure() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Body:" << body->getName() << "strength:" << body->getStrenth() << std::endl;
}
};client.cpp
#ifndef __io__
#define __io__
#include <iostream>
#endif
#include "CarFactory.cpp"
#define SIMPLE_CAR 1
// #define LUXURY_CAR 1
int main() {
#ifdef SIMPLE_CAR
CarFactory* factory = new SimpleCarFactory;
#elif LUXURY_CAR
CarFactory* factory = new LuxuryCarFactory;
#endif
Car *car = factory -> buildWholeCar();
car -> printDetails();
return 0;
}github见GitHub - daichang01/factory-design-in-cplusplus




 本文介绍了抽象工厂设计模式(AFDP),展示了如何在C++中使用该模式创建和管理相关对象系列,以及其在系统独立性和对象配置方面的优势。通过继承和protected特性,实现在Car类和CarFactory之间的灵活组装。
本文介绍了抽象工厂设计模式(AFDP),展示了如何在C++中使用该模式创建和管理相关对象系列,以及其在系统独立性和对象配置方面的优势。通过继承和protected特性,实现在Car类和CarFactory之间的灵活组装。
















 1389
1389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








