A common technique we use in Machine Learning and Deep Learning is to normalize our data. It often leads to a better performance because gradient descent converges faster after normalization. Here, by normalization we mean changing x to :
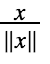
(dividing each row vector of x by its norm).
For example, if (3)x=[034264]x =
\begin{bmatrix}
0 & 3 & 4 \\
2 & 6 & 4 \\
\end{bmatrix}\tag{3}x=[023644](3) then (4)∥x∥=np.linalg.norm(x,axis=1,keepdims=True)=[556]\| x\| = np.linalg.norm(x, axis = 1, keepdims = True) = \begin{bmatrix}
5 \\
\sqrt{56} \\
\end{bmatrix}\tag{4} ∥x∥=np.linalg.norm(x,axis=1,keepdims=True)=[556](4)and (5)x_normalized=x∥x∥=[03545256656456] x\_normalized = \frac{x}{\| x\|} = \begin{bmatrix}
0 & \frac{3}{5} & \frac{4}{5} \\
\frac{2}{\sqrt{56}} & \frac{6}{\sqrt{56}} & \frac{4}{\sqrt{56}} \\
\end{bmatrix}\tag{5}x_normalized=∥x∥x=[05625356654564](5)
Exercise: Implement normalizeRows() to normalize the rows of a matrix. After applying this function to an input matrix x, each row of x should be a vector of unit length (meaning length 1).
implement
# GRADED FUNCTION: normalizeRows
def normalizeRows(x):
"""
Implement a function that normalizes each row of the matrix x (to have unit length).
Argument:
x -- A numpy matrix of shape (n, m)
Returns:
x -- The normalized (by row) numpy matrix. You are allowed to modify x.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
# Compute x_norm as the norm 2 of x. Use np.linalg.norm(..., ord = 2, axis = ..., keepdims = True)
x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x,axis=1,keepdims=True)
# Divide x by its norm.
x = x/x_norm
### END CODE HERE ###
return x
x = np.array([
[0, 3, 4],
[1, 6, 4]])
print("normalizeRows(x) = " str(normalizeRows(x)))
output:

 机器学习中数据标准化技巧
机器学习中数据标准化技巧







 本文探讨了在机器学习和深度学习中数据标准化的重要性和实施方法。标准化数据能加速梯度下降过程,提升模型性能。文章详细介绍了如何通过计算矩阵各行的范数并进行归一化处理来实现这一目标。
本文探讨了在机器学习和深度学习中数据标准化的重要性和实施方法。标准化数据能加速梯度下降过程,提升模型性能。文章详细介绍了如何通过计算矩阵各行的范数并进行归一化处理来实现这一目标。
















 1478
1478

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








