题目:IST改进算法之Two-Step Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding(TwIST)
本篇介绍IST的一种改进算法TwIST,该改进算法由以下文献提出:
Bioucas-DiasJ M, Figueiredo M AT.A new TwIST: two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for imagerestoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image processing, 2007, 16(12): 2992-3004.
据文献介绍,相比于IST,TwIST旨在使算法收敛的更快。
TwIST解决的问题是目标函数为式(1)的优化问题:
注意:最后一行无穷右边的中括号并没有错,这表示开区间,而0左边的中括号表示闭区间。
1、TwIST算法内容
相比于IST,TwIST主要是迭代公式的变化:
其中Ψλ定义为:
Ψλ的表达式与式(1)中的正则项Φ(x)有关,当Φ(x)=||x||1时:
即软阈值函数。更一般的,Φ(x)为式(10)时:
例如文中提到的当p=2时:
因此
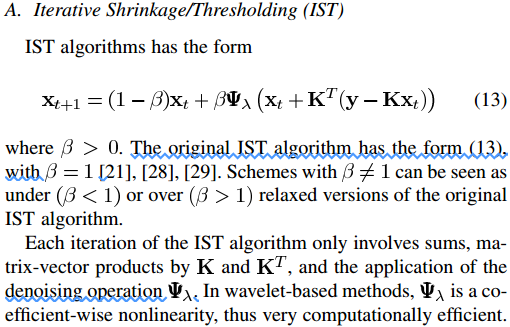
2、TwIST算法的提出思路
TwIST实际上是IST与TwSIM的结合:
注意式(13)是推广的IST迭代公式,原始版的IST迭代公式是令式(13)中的β=1。而TwSIM实际上是式(14)一种实现形式(当矩阵At较大时)
其中式(14)如下(即IterativeRe-Weighted Shrinkage (IRS)):
如何将IST和TwSIM结合得到TwIST的呢?这个过程有点悬:
注意这个结合过程,文中说:若令式(16)中α=1并将C-1替换为ψλ则可以得到式(13)。由此相似性可以得到一个two-step版本的IST:(这个idea来的好突然)
既然TwIST结合了IST和TwSIM,因此TwIST算法希望能达到如下特性:
为什么叫two-step IST呢?
比较一下IST迭代公式式(13)和TwIST迭代公式式(18)可以发现,IST迭代公式等号右边只有xt,而TwIST迭代公式等号右边有xt和xt-1。
3、TwIST算法的参数设置
TwIST算法主页:http://www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/TwIST/TwIST.htm
在TwIST主页可以下载到最新版本TwIST的Matlab实现代码。
首先,这里重点介绍一下TwIST迭代公式(18)中α和β两个关键参数如何设置?文中式(22)和式(23)给出了α和β的计算方法,相关公式如下图:
在TwIST官方代码中,与参数α和β有关的代码如图所示(Notepad++打开截图):
参数α和β可由外部输入(参见第265~268行),若未输入,则默认按第319~326行计算(其中在第235~236行已将α和β置零,若第265~268行未赋值,则执行第319~326行),参数α计算公式与文中的式(22)看来不一样,但其实是相同的,推导如下:
先将式(20)代入式(22)化简一下:
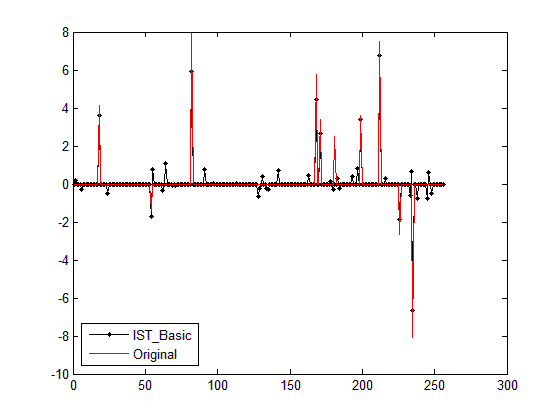
程序中的lam1即为ξ1(可选输入参数,参见程序第263~264行,默认为10-4,参见程序第242行),lamN即为ξm(恒为1,参见程序第242行),而κ=ξ1/ξm,因此程序中的rho0
将rho0代入
因此文中式(22)和程序中的设置是一样的。文中又提到TwIST对参数α和β并不是很敏感,也就是“very robust”:
4、TwIST算法的MATLAB代码
官方版本的TwIST算法Matlab代码超过700行,其实最核心的就是在一定条件下循环迭代式(18)而已,这里给出一个本人写的简化版本的TwIST代码,方便理解:
- function [ x ] = TwIST_Basic( y,Phi,lambda,beta,alpha,epsilon,loopmax,lam1,lamN )
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- %Version: 1.0 written by jbb0523 @2016-08-12
- if nargin < 9
- lamN = 1;
- end
- if nargin < 8
- lam1 = 1e-4;
- end
- if nargin < 7
- loopmax = 10000;
- end
- if nargin < 6
- epsilon = 1e-2;
- end
- if nargin < 5
- rho0 = (1-lam1/lamN)/(1+lam1/lamN);
- alpha = 2/(1+sqrt(1-rho0^2));
- end
- if nargin < 4
- beta = alpha*2/(lam1+lamN);
- end
- if nargin < 3
- lambda = 0.1*max(abs(Phi’*y));
- end
- [y_rows,y_columns] = size(y);
- if y_rows<y_columns
- y = y’;%y should be a column vector
- end
- soft = @(x,T) sign(x).*max(abs(x) - T,0);
- n = size(Phi,2);
- loop = 0;
- fprintf(‘\n’);
- x_pre2 = zeros(n,1);%Initialize x0=0
- %Initialize x1=soft(x0+Phi’*(y-Phi*x0),lambda)
- x_pre1 = soft(x_pre2+Phi’*(y-Phi*x_pre2),lambda);
- f_pre1 = 0.5*(y-Phi*x_pre1)’*(y-Phi*x_pre1)+lambda*sum(abs(x_pre1));
- while 1
- %(1)compute x_(t+1)
- x_temp = soft(x_pre1+Phi’*(y-Phi*x_pre1),lambda);
- %following 3 lines are important for reconstruction successfully
- mask = (x_temp ~= 0);
- x_pre2 = x_pre2.* mask;
- x_pre1 = x_pre1.* mask;
- x=(1-alpha)*x_pre2+(alpha-beta)*x_pre1+beta*x_temp;
- %(2)update x_(t-1)
- x_pre2 = x_pre1;
- f_pre2 = f_pre1;
- %(3)update x_t
- x_pre1 = x;
- f_pre1 = 0.5*(y-Phi*x_pre1)’*(y-Phi*x_pre1)+lambda*sum(abs(x_pre1));
- loop = loop + 1;
- %fprintf(‘Iter %d:f_pre1 = %f\n’,loop,f_pre1);
- if abs(f_pre1-f_pre2)/f_pre2<epsilon
- fprintf(‘abs(f_pre1-f_pre2)/f_pre2<%f\n’,epsilon);
- fprintf(‘TwIST loop is %d\n’,loop);
- break;
- end
- if loop >= loopmax
- fprintf(‘loop > %d\n’,loopmax);
- break;
- end
- if norm(x_pre1-x_pre2)<epsilon
- fprintf(‘norm(x-x_pre)<%f\n’,epsilon);
- fprintf(‘TwIST loop is %d\n’,loop);
- break;
- end
- end
- end
function [ x ] = TwIST_Basic( y,Phi,lambda,beta,alpha,epsilon,loopmax,lam1,lamN )
% Detailed explanation goes here
%Version: 1.0 written by jbb0523 @2016-08-12
if nargin < 9
lamN = 1;
end
if nargin < 8
lam1 = 1e-4;
end
if nargin < 7
loopmax = 10000;
end
if nargin < 6
epsilon = 1e-2;
end
if nargin < 5
rho0 = (1-lam1/lamN)/(1+lam1/lamN);
alpha = 2/(1+sqrt(1-rho0^2));
end
if nargin < 4
beta = alpha*2/(lam1+lamN);
end
if nargin < 3
lambda = 0.1*max(abs(Phi'*y));
end
[y_rows,y_columns] = size(y);
if y_rows<y_columns
y = y';%y should be a column vector
end
soft = @(x,T) sign(x).*max(abs(x) - T,0);
n = size(Phi,2);
loop = 0;
fprintf('\n');
x_pre2 = zeros(n,1);%Initialize x0=0
%Initialize x1=soft(x0+Phi'*(y-Phi*x0),lambda)
x_pre1 = soft(x_pre2+Phi'*(y-Phi*x_pre2),lambda);
f_pre1 = 0.5*(y-Phi*x_pre1)'*(y-Phi*x_pre1)+lambda*sum(abs(x_pre1));
while 1
%(1)compute x_(t+1)
x_temp = soft(x_pre1+Phi'*(y-Phi*x_pre1),lambda);
%following 3 lines are important for reconstruction successfully
mask = (x_temp ~= 0);
x_pre2 = x_pre2.* mask;
x_pre1 = x_pre1.* mask;
x=(1-alpha)*x_pre2+(alpha-beta)*x_pre1+beta*x_temp;
%(2)update x_(t-1)
x_pre2 = x_pre1;
f_pre2 = f_pre1;
%(3)update x_t
x_pre1 = x;
f_pre1 = 0.5*(y-Phi*x_pre1)'*(y-Phi*x_pre1)+lambda*sum(abs(x_pre1));
loop = loop + 1;
%fprintf('Iter %d:f_pre1 = %f\n',loop,f_pre1);
if abs(f_pre1-f_pre2)/f_pre2<epsilon
fprintf('abs(f_pre1-f_pre2)/f_pre2<%f\n',epsilon);
fprintf('TwIST loop is %d\n',loop);
break;
end
if loop >= loopmax
fprintf('loop > %d\n',loopmax);
break;
end
if norm(x_pre1-x_pre2)<epsilon
fprintf('norm(x-x_pre)<%f\n',epsilon);
fprintf('TwIST loop is %d\n',loop);
break;
end
end
end值得注意的是,本基本版TwIST_Basic仅解决当文中式(1)正则项Φ(x)=||x||1时的情况,而官方版本的TwIST通过参数配置可以解决当Φ(x)为其它表达式时的情况。
这里最核心的是第40~45行,即:
- x_temp = soft(x_pre1+Phi’*(y-Phi*x_pre1),lambda);
- %following 3 lines are important for reconstruction successfully
- mask = (x_temp ~= 0);
- x_pre2 = x_pre2.* mask;
- x_pre1 = x_pre1.* mask;
- x=(1-alpha)*x_pre2+(alpha-beta)*x_pre1+beta*x_temp;
x_temp = soft(x_pre1+Phi'*(y-Phi*x_pre1),lambda);
%following 3 lines are important for reconstruction successfully
mask = (x_temp ~= 0);
x_pre2 = x_pre2.* mask;
x_pre1 = x_pre1.* mask;
x=(1-alpha)*x_pre2+(alpha-beta)*x_pre1+beta*x_temp;即执行TwIST迭代公式(18)的过程。值得注意的是起初本人并没有加入第42~44行,当然,也基本无法成功重构,但官方版本的TwIST却可以重构成功,于是本人仔细对比了与TwIST的差别,最终发现关键点在官方版本的以下几行:
于是在我的基本版本里新加入了即第42~44行,重构效果明显改善。
为了保证本篇的完整性,这里也同时也给出官方版本的TwIST算法Matlab代码:
(TwIST算法主页:http://www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/TwIST/TwIST.htm)
- function [x,x_debias,objective,times,debias_start,mses,max_svd] = …
- TwIST(y,A,tau,varargin)
- %
- % Usage:
- % [x,x_debias,objective,times,debias_start,mses] = TwIST(y,A,tau,varargin)
- %
- % This function solves the regularization problem
- %
- % arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - A x ||_2^2 + tau phi( x ),
- %
- % where A is a generic matrix and phi(.) is a regularizarion
- % function such that the solution of the denoising problem
- %
- % Psi_tau(y) = arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - x ||_2^2 + tau \phi( x ),
- %
- % is known.
- %
- % For further details about the TwIST algorithm, see the paper:
- %
- % J. Bioucas-Dias and M. Figueiredo, “A New TwIST: Two-Step
- % Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding Algorithms for Image
- % Restoration”, IEEE Transactions on Image processing, 2007.
- %
- % and
- %
- % J. Bioucas-Dias and M. Figueiredo, “A Monotonic Two-Step
- % Algorithm for Compressive Sensing and Other Ill-Posed
- % Inverse Problems”, submitted, 2007.
- %
- % Authors: Jose Bioucas-Dias and Mario Figueiredo, October, 2007.
- %
- % Please check for the latest version of the code and papers at
- % www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/TwIST
- %
- % ———————————————————————–
- % Copyright (2007): Jose Bioucas-Dias and Mario Figueiredo
- %
- % TwIST is distributed under the terms of
- % the GNU General Public License 2.0.
- %
- % Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software for
- % any purpose without fee is hereby granted, provided that this entire
- % notice is included in all copies of any software which is or includes
- % a copy or modification of this software and in all copies of the
- % supporting documentation for such software.
- % This software is being provided “as is”, without any express or
- % implied warranty. In particular, the authors do not make any
- % representation or warranty of any kind concerning the merchantability
- % of this software or its fitness for any particular purpose.”
- % ———————————————————————-
- %
- % ===== Required inputs =============
- %
- % y: 1D vector or 2D array (image) of observations
- %
- % A: if y and x are both 1D vectors, A can be a
- % k*n (where k is the size of y and n the size of x)
- % matrix or a handle to a function that computes
- % products of the form A*v, for some vector v.
- % In any other case (if y and/or x are 2D arrays),
- % A has to be passed as a handle to a function which computes
- % products of the form A*x; another handle to a function
- % AT which computes products of the form A’*x is also required
- % in this case. The size of x is determined as the size
- % of the result of applying AT.
- %
- % tau: regularization parameter, usually a non-negative real
- % parameter of the objective function (see above).
- %
- %
- % ===== Optional inputs =============
- %
- % ‘Psi’ = denoising function handle; handle to denoising function
- % Default = soft threshold.
- %
- % ‘Phi’ = function handle to regularizer needed to compute the objective
- % function.
- % Default = ||x||_1
- %
- % ‘lambda’ = lam1 parameters of the TwIST algorithm:
- % Optimal choice: lam1 = min eigenvalue of A’*A.
- % If min eigenvalue of A’*A == 0, or unknwon,
- % set lam1 to a value much smaller than 1.
- %
- % Rule of Thumb:
- % lam1=1e-4 for severyly ill-conditioned problems
- % lam1=1e-2 for mildly ill-conditioned problems
- % lam1=1 for A unitary direct operators
- %
- % Default: lam1 = 0.04.
- %
- % Important Note: If (max eigenvalue of A’*A) > 1,
- % the algorithm may diverge. This is be avoided
- % by taking one of the follwoing measures:
- %
- % 1) Set ‘Monontone’ = 1 (default)
- %
- % 2) Solve the equivalenve minimization problem
- %
- % min_x = 0.5*|| (y/c) - (A/c) x ||_2^2 + (tau/c^2) \phi( x ),
- %
- % where c > 0 ensures that max eigenvalue of (A’A/c^2) <= 1.
- %
- % ‘alpha’ = parameter alpha of TwIST (see ex. (22) of the paper)
- % Default alpha = alpha(lamN=1, lam1)
- %
- % ‘beta’ = parameter beta of twist (see ex. (23) of the paper)
- % Default beta = beta(lamN=1, lam1)
- %
- % ‘AT’ = function handle for the function that implements
- % the multiplication by the conjugate of A, when A
- % is a function handle.
- % If A is an array, AT is ignored.
- %
- % ‘StopCriterion’ = type of stopping criterion to use
- % 0 = algorithm stops when the relative
- % change in the number of non-zero
- % components of the estimate falls
- % below ‘ToleranceA’
- % 1 = stop when the relative
- % change in the objective function
- % falls below ‘ToleranceA’
- % 2 = stop when the relative norm of the difference between
- % two consecutive estimates falls below toleranceA
- % 3 = stop when the objective function
- % becomes equal or less than toleranceA.
- % Default = 1.
- %
- % ‘ToleranceA’ = stopping threshold; Default = 0.01
- %
- % ‘Debias’ = debiasing option: 1 = yes, 0 = no.
- % Default = 0.
- %
- % Note: Debiasing is an operation aimed at the
- % computing the solution of the LS problem
- %
- % arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - A’ x’ ||_2^2
- %
- % where A’ is the submatrix of A obatained by
- % deleting the columns of A corresponding of components
- % of x set to zero by the TwIST algorithm
- %
- %
- % ‘ToleranceD’ = stopping threshold for the debiasing phase:
- % Default = 0.0001.
- % If no debiasing takes place, this parameter,
- % if present, is ignored.
- %
- % ‘MaxiterA’ = maximum number of iterations allowed in the
- % main phase of the algorithm.
- % Default = 1000
- %
- % ‘MiniterA’ = minimum number of iterations performed in the
- % main phase of the algorithm.
- % Default = 5
- %
- % ‘MaxiterD’ = maximum number of iterations allowed in the
- % debising phase of the algorithm.
- % Default = 200
- %
- % ‘MiniterD’ = minimum number of iterations to perform in the
- % debiasing phase of the algorithm.
- % Default = 5
- %
- % ‘Initialization’ must be one of {0,1,2,array}
- % 0 -> Initialization at zero.
- % 1 -> Random initialization.
- % 2 -> initialization with A’*y.
- % array -> initialization provided by the user.
- % Default = 0;
- %
- % ‘Monotone’ = enforce monotonic decrease in f.
- % any nonzero -> enforce monotonicity
- % 0 -> don’t enforce monotonicity.
- % Default = 1;
- %
- % ‘Sparse’ = {0,1} accelarates the convergence rate when the regularizer
- % Phi(x) is sparse inducing, such as ||x||_1.
- % Default = 1
- %
- %
- % ‘True_x’ = if the true underlying x is passed in
- % this argument, MSE evolution is computed
- %
- %
- % ‘Verbose’ = work silently (0) or verbosely (1)
- %
- % ===================================================
- % ============ Outputs ==============================
- % x = solution of the main algorithm
- %
- % x_debias = solution after the debiasing phase;
- % if no debiasing phase took place, this
- % variable is empty, x_debias = [].
- %
- % objective = sequence of values of the objective function
- %
- % times = CPU time after each iteration
- %
- % debias_start = iteration number at which the debiasing
- % phase started. If no debiasing took place,
- % this variable is returned as zero.
- %
- % mses = sequence of MSE values, with respect to True_x,
- % if it was given; if it was not given, mses is empty,
- % mses = [].
- %
- % max_svd = inverse of the scaling factor, determined by TwIST,
- % applied to the direct operator (A/max_svd) such that
- % every IST step is increasing.
- % ========================================================
- %————————————————————–
- % test for number of required parametres
- %————————————————————–
- if (nargin-length(varargin)) ~= 3
- error(‘Wrong number of required parameters’);
- end
- %————————————————————–
- % Set the defaults for the optional parameters
- %————————————————————–
- stopCriterion = 1;
- tolA = 0.01;
- debias = 0;
- maxiter = 1000;
- maxiter_debias = 200;
- miniter = 5;
- miniter_debias = 5;
- init = 0;
- enforceMonotone = 1;
- compute_mse = 0;
- plot_ISNR = 0;
- AT = 0;
- verbose = 1;
- alpha = 0;
- beta = 0;
- sparse = 1;
- tolD = 0.001;
- phi_l1 = 0;
- psi_ok = 0;
- % default eigenvalues
- lam1=1e-4; lamN=1;
- %
- % constants ans internal variables
- for_ever = 1;
- % maj_max_sv: majorizer for the maximum singular value of operator A
- max_svd = 1;
- % Set the defaults for outputs that may not be computed
- debias_start = 0;
- x_debias = [];
- mses = [];
- %————————————————————–
- % Read the optional parameters
- %————————————————————–
- if (rem(length(varargin),2)==1)
- error(‘Optional parameters should always go by pairs’);
- else
- for i=1:2:(length(varargin)-1)
- switch upper(varargin{i})
- case ‘LAMBDA’
- lam1 = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘ALPHA’
- alpha = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘BETA’
- beta = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘PSI’
- psi_function = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘PHI’
- phi_function = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘STOPCRITERION’
- stopCriterion = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘TOLERANCEA’
- tolA = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘TOLERANCED’
- tolD = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘DEBIAS’
- debias = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘MAXITERA’
- maxiter = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘MAXIRERD’
- maxiter_debias = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘MINITERA’
- miniter = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘MINITERD’
- miniter_debias = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘INITIALIZATION’
- if prod(size(varargin{i+1})) > 1 % we have an initial x
- init = 33333; % some flag to be used below
- x = varargin{i+1};
- else
- init = varargin{i+1};
- end
- case ‘MONOTONE’
- enforceMonotone = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘SPARSE’
- sparse = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘TRUE_X’
- compute_mse = 1;
- true = varargin{i+1};
- if prod(double((size(true) == size(y))))
- plot_ISNR = 1;
- end
- case ‘AT’
- AT = varargin{i+1};
- case ‘VERBOSE’
- verbose = varargin{i+1};
- otherwise
- % Hmmm, something wrong with the parameter string
- error([‘Unrecognized option: ”’ varargin{i} ””]);
- end;
- end;
- end
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- % twist parameters
- rho0 = (1-lam1/lamN)/(1+lam1/lamN);
- if alpha == 0
- alpha = 2/(1+sqrt(1-rho0^2));
- end
- if beta == 0
- beta = alpha*2/(lam1+lamN);
- end
- if (sum(stopCriterion == [0 1 2 3])==0)
- error([‘Unknwon stopping criterion’]);
- end
- % if A is a function handle, we have to check presence of AT,
- if isa(A, ‘function_handle’) & ~isa(AT,’function_handle’)
- error([‘The function handle for transpose of A is missing’]);
- end
- % if A is a matrix, we find out dimensions of y and x,
- % and create function handles for multiplication by A and A’,
- % so that the code below doesn’t have to distinguish between
- % the handle/not-handle cases
- if ~isa(A, ‘function_handle’)
- AT = @(x) A’*x;
- A = @(x) A*x;
- end
- % from this point down, A and AT are always function handles.
- % Precompute A’*y since it’ll be used a lot
- Aty = AT(y);
- % if phi was given, check to see if it is a handle and that it
- % accepts two arguments
- if exist(‘psi_function’,’var’)
- if isa(psi_function,’function_handle’)
- try % check if phi can be used, using Aty, which we know has
- % same size as x
- dummy = psi_function(Aty,tau);
- psi_ok = 1;
- catch
- error([‘Something is wrong with function handle for psi’])
- end
- else
- error([‘Psi does not seem to be a valid function handle’]);
- end
- else %if nothing was given, use soft thresholding
- psi_function = @(x,tau) soft(x,tau);
- end
- % if psi exists, phi must also exist
- if (psi_ok == 1)
- if exist(‘phi_function’,’var’)
- if isa(phi_function,’function_handle’)
- try % check if phi can be used, using Aty, which we know has
- % same size as x
- dummy = phi_function(Aty);
- catch
- error([‘Something is wrong with function handle for phi’])
- end
- else
- error([‘Phi does not seem to be a valid function handle’]);
- end
- else
- error([‘If you give Psi you must also give Phi’]);
- end
- else % if no psi and phi were given, simply use the l1 norm.
- phi_function = @(x) sum(abs(x(:)));
- phi_l1 = 1;
- end
- %————————————————————–
- % Initialization
- %————————————————————–
- switch init
- case 0 % initialize at zero, using AT to find the size of x
- x = AT(zeros(size(y)));
- case 1 % initialize randomly, using AT to find the size of x
- x = randn(size(AT(zeros(size(y)))));
- case 2 % initialize x0 = A’*y
- x = Aty;
- case 33333
- % initial x was given as a function argument; just check size
- if size(A(x)) ~= size(y)
- error([‘Size of initial x is not compatible with A’]);
- end
- otherwise
- error([‘Unknown ”Initialization” option’]);
- end
- % now check if tau is an array; if it is, it has to
- % have the same size as x
- if prod(size(tau)) > 1
- try,
- dummy = x.*tau;
- catch,
- error([‘Parameter tau has wrong dimensions; it should be scalar or size(x)’]),
- end
- end
- % if the true x was given, check its size
- if compute_mse & (size(true) ~= size(x))
- error([‘Initial x has incompatible size’]);
- end
- % if tau is large enough, in the case of phi = l1, thus psi = soft,
- % the optimal solution is the zero vector
- if phi_l1
- max_tau = max(abs(Aty(:)));
- if (tau >= max_tau)&(psi_ok==0)
- x = zeros(size(Aty));
- objective(1) = 0.5*(y(:)’*y(:));
- times(1) = 0;
- if compute_mse
- mses(1) = sum(true(:).^2);
- end
- return
- end
- end
- % define the indicator vector or matrix of nonzeros in x
- nz_x = (x ~= 0.0);
- num_nz_x = sum(nz_x(:));
- % Compute and store initial value of the objective function
- resid = y-A(x);
- prev_f = 0.5*(resid(:)’*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(x);
- % start the clock
- t0 = cputime;
- times(1) = cputime - t0;
- objective(1) = prev_f;
- if compute_mse
- mses(1) = sum(sum((x-true).^2));
- end
- cont_outer = 1;
- iter = 1;
- if verbose
- fprintf(1,’\nInitial objective = %10.6e, nonzeros=%7d\n’,…
- prev_f,num_nz_x);
- end
- % variables controling first and second order iterations
- IST_iters = 0;
- TwIST_iters = 0;
- % initialize
- xm2=x;
- xm1=x;
- %————————————————————–
- % TwIST iterations
- %————————————————————–
- while cont_outer
- % gradient
- grad = AT(resid);
- while for_ever
- % IST estimate
- x = psi_function(xm1 + grad/max_svd,tau/max_svd);
- if (IST_iters >= 2) | ( TwIST_iters ~= 0)
- % set to zero the past when the present is zero
- % suitable for sparse inducing priors
- if sparse
- mask = (x ~= 0);
- xm1 = xm1.* mask;
- xm2 = xm2.* mask;
- end
- % two-step iteration
- xm2 = (alpha-beta)*xm1 + (1-alpha)*xm2 + beta*x;
- % compute residual
- resid = y-A(xm2);
- f = 0.5*(resid(:)’*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(xm2);
- if (f > prev_f) & (enforceMonotone)
- TwIST_iters = 0; % do a IST iteration if monotonocity fails
- else
- TwIST_iters = TwIST_iters+1; % TwIST iterations
- IST_iters = 0;
- x = xm2;
- if mod(TwIST_iters,10000) == 0
- max_svd = 0.9*max_svd;
- end
- break; % break loop while
- end
- else
- resid = y-A(x);
- f = 0.5*(resid(:)’*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(x);
- if f > prev_f
- % if monotonicity fails here is because
- % max eig (A’A) > 1. Thus, we increase our guess
- % of max_svs
- max_svd = 2*max_svd;
- if verbose
- fprintf(‘Incrementing S=%2.2e\n’,max_svd)
- end
- IST_iters = 0;
- TwIST_iters = 0;
- else
- TwIST_iters = TwIST_iters + 1;
- break; % break loop while
- end
- end
- end
- xm2 = xm1;
- xm1 = x;
- %update the number of nonzero components and its variation
- nz_x_prev = nz_x;
- nz_x = (x~=0.0);
- num_nz_x = sum(nz_x(:));
- num_changes_active = (sum(nz_x(:)~=nz_x_prev(:)));
- % take no less than miniter and no more than maxiter iterations
- switch stopCriterion
- case 0,
- % compute the stopping criterion based on the change
- % of the number of non-zero components of the estimate
- criterion = num_changes_active;
- case 1,
- % compute the stopping criterion based on the relative
- % variation of the objective function.
- criterion = abs(f-prev_f)/prev_f;
- case 2,
- % compute the stopping criterion based on the relative
- % variation of the estimate.
- criterion = (norm(x(:)-xm1(:))/norm(x(:)));
- case 3,
- % continue if not yet reached target value tolA
- criterion = f;
- otherwise,
- error([‘Unknwon stopping criterion’]);
- end
- cont_outer = ((iter <= maxiter) & (criterion > tolA));
- if iter <= miniter
- cont_outer = 1;
- end
- iter = iter + 1;
- prev_f = f;
- objective(iter) = f;
- times(iter) = cputime-t0;
- if compute_mse
- err = true - x;
- mses(iter) = (err(:)’*err(:));
- end
- % print out the various stopping criteria
- if verbose
- if plot_ISNR
- fprintf(1,’Iteration=%4d, ISNR=%4.5e objective=%9.5e, nz=%7d, criterion=%7.3e\n’,…
- iter, 10*log10(sum((y(:)-true(:)).^2)/sum((x(:)-true(:)).^2) ), …
- f, num_nz_x, criterion/tolA);
- else
- fprintf(1,’Iteration=%4d, objective=%9.5e, nz=%7d, criterion=%7.3e\n’,…
- iter, f, num_nz_x, criterion/tolA);
- end
- end
- end
- %————————————————————–
- % end of the main loop
- %————————————————————–
- % Printout results
- if verbose
- fprintf(1,’\nFinished the main algorithm!\nResults:\n’)
- fprintf(1,’||A x - y ||_2 = %10.3e\n’,resid(:)’*resid(:))
- fprintf(1,’||x||_1 = %10.3e\n’,sum(abs(x(:))))
- fprintf(1,’Objective function = %10.3e\n’,f);
- fprintf(1,’Number of non-zero components = %d\n’,num_nz_x);
- fprintf(1,’CPU time so far = %10.3e\n’, times(iter));
- fprintf(1,’\n’);
- end
- %————————————————————–
- % If the ‘Debias’ option is set to 1, we try to
- % remove the bias from the l1 penalty, by applying CG to the
- % least-squares problem obtained by omitting the l1 term
- % and fixing the zero coefficients at zero.
- %————————————————————–
- if debias
- if verbose
- fprintf(1,’\n’)
- fprintf(1,’Starting the debiasing phase…\n\n’)
- end
- x_debias = x;
- zeroind = (x_debias~=0);
- cont_debias_cg = 1;
- debias_start = iter;
- % calculate initial residual
- resid = A(x_debias);
- resid = resid-y;
- resid_prev = eps*ones(size(resid));
- rvec = AT(resid);
- % mask out the zeros
- rvec = rvec .* zeroind;
- rTr_cg = rvec(:)’*rvec(:);
- % set convergence threshold for the residual || RW x_debias - y ||_2
- tol_debias = tolD * (rvec(:)’*rvec(:));
- % initialize pvec
- pvec = -rvec;
- % main loop
- while cont_debias_cg
- % calculate A*p = Wt * Rt * R * W * pvec
- RWpvec = A(pvec);
- Apvec = AT(RWpvec);
- % mask out the zero terms
- Apvec = Apvec .* zeroind;
- % calculate alpha for CG
- alpha_cg = rTr_cg / (pvec(:)’* Apvec(:));
- % take the step
- x_debias = x_debias + alpha_cg * pvec;
- resid = resid + alpha_cg * RWpvec;
- rvec = rvec + alpha_cg * Apvec;
- rTr_cg_plus = rvec(:)’*rvec(:);
- beta_cg = rTr_cg_plus / rTr_cg;
- pvec = -rvec + beta_cg * pvec;
- rTr_cg = rTr_cg_plus;
- iter = iter+1;
- objective(iter) = 0.5*(resid(:)’*resid(:)) + …
- tau*phi_function(x_debias(:));
- times(iter) = cputime - t0;
- if compute_mse
- err = true - x_debias;
- mses(iter) = (err(:)’*err(:));
- end
- % in the debiasing CG phase, always use convergence criterion
- % based on the residual (this is standard for CG)
- if verbose
- fprintf(1,’ Iter = %5d, debias resid = %13.8e, convergence = %8.3e\n’, …
- iter, resid(:)’*resid(:), rTr_cg / tol_debias);
- end
- cont_debias_cg = …
- (iter-debias_start <= miniter_debias )| …
- ((rTr_cg > tol_debias) & …
- (iter-debias_start <= maxiter_debias));
- end
- if verbose
- fprintf(1,’\nFinished the debiasing phase!\nResults:\n’)
- fprintf(1,’||A x - y ||_2 = %10.3e\n’,resid(:)’*resid(:))
- fprintf(1,’||x||_1 = %10.3e\n’,sum(abs(x(:))))
- fprintf(1,’Objective function = %10.3e\n’,f);
- nz = (x_debias~=0.0);
- fprintf(1,’Number of non-zero components = %d\n’,sum(nz(:)));
- fprintf(1,’CPU time so far = %10.3e\n’, times(iter));
- fprintf(1,’\n’);
- end
- end
- if compute_mse
- mses = mses/length(true(:));
- end
- %————————————————————–
- % soft for both real and complex numbers
- %————————————————————–
- function y = soft(x,T)
- %y = sign(x).*max(abs(x)-tau,0);
- y = max(abs(x) - T, 0);
- y = y./(y+T) .* x;
function [x,x_debias,objective,times,debias_start,mses,max_svd] = ...
TwIST(y,A,tau,varargin)
%
% Usage:
% [x,x_debias,objective,times,debias_start,mses] = TwIST(y,A,tau,varargin)
%
% This function solves the regularization problem
%
% arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - A x ||_2^2 + tau phi( x ),
%
% where A is a generic matrix and phi(.) is a regularizarion
% function such that the solution of the denoising problem
%
% Psi_tau(y) = arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - x ||_2^2 + tau \phi( x ),
%
% is known.
%
% For further details about the TwIST algorithm, see the paper:
%
% J. Bioucas-Dias and M. Figueiredo, "A New TwIST: Two-Step
% Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding Algorithms for Image
% Restoration", IEEE Transactions on Image processing, 2007.
%
% and
%
% J. Bioucas-Dias and M. Figueiredo, "A Monotonic Two-Step
% Algorithm for Compressive Sensing and Other Ill-Posed
% Inverse Problems", submitted, 2007.
%
% Authors: Jose Bioucas-Dias and Mario Figueiredo, October, 2007.
%
% Please check for the latest version of the code and papers at
% www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/TwIST
%
% -----------------------------------------------------------------------
% Copyright (2007): Jose Bioucas-Dias and Mario Figueiredo
%
% TwIST is distributed under the terms of
% the GNU General Public License 2.0.
%
% Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software for
% any purpose without fee is hereby granted, provided that this entire
% notice is included in all copies of any software which is or includes
% a copy or modification of this software and in all copies of the
% supporting documentation for such software.
% This software is being provided "as is", without any express or
% implied warranty. In particular, the authors do not make any
% representation or warranty of any kind concerning the merchantability
% of this software or its fitness for any particular purpose."
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
% ===== Required inputs =============
%
% y: 1D vector or 2D array (image) of observations
%
% A: if y and x are both 1D vectors, A can be a
% k*n (where k is the size of y and n the size of x)
% matrix or a handle to a function that computes
% products of the form A*v, for some vector v.
% In any other case (if y and/or x are 2D arrays),
% A has to be passed as a handle to a function which computes
% products of the form A*x; another handle to a function
% AT which computes products of the form A'*x is also required
% in this case. The size of x is determined as the size
% of the result of applying AT.
%
% tau: regularization parameter, usually a non-negative real
% parameter of the objective function (see above).
%
%
% ===== Optional inputs =============
%
% 'Psi' = denoising function handle; handle to denoising function
% Default = soft threshold.
%
% 'Phi' = function handle to regularizer needed to compute the objective
% function.
% Default = ||x||_1
%
% 'lambda' = lam1 parameters of the TwIST algorithm:
% Optimal choice: lam1 = min eigenvalue of A'*A.
% If min eigenvalue of A'*A == 0, or unknwon,
% set lam1 to a value much smaller than 1.
%
% Rule of Thumb:
% lam1=1e-4 for severyly ill-conditioned problems
% lam1=1e-2 for mildly ill-conditioned problems
% lam1=1 for A unitary direct operators
%
% Default: lam1 = 0.04.
%
% Important Note: If (max eigenvalue of A'*A) > 1,
% the algorithm may diverge. This is be avoided
% by taking one of the follwoing measures:
%
% 1) Set 'Monontone' = 1 (default)
%
% 2) Solve the equivalenve minimization problem
%
% min_x = 0.5*|| (y/c) - (A/c) x ||_2^2 + (tau/c^2) \phi( x ),
%
% where c > 0 ensures that max eigenvalue of (A'A/c^2) <= 1.
%
% 'alpha' = parameter alpha of TwIST (see ex. (22) of the paper)
% Default alpha = alpha(lamN=1, lam1)
%
% 'beta' = parameter beta of twist (see ex. (23) of the paper)
% Default beta = beta(lamN=1, lam1)
%
% 'AT' = function handle for the function that implements
% the multiplication by the conjugate of A, when A
% is a function handle.
% If A is an array, AT is ignored.
%
% 'StopCriterion' = type of stopping criterion to use
% 0 = algorithm stops when the relative
% change in the number of non-zero
% components of the estimate falls
% below 'ToleranceA'
% 1 = stop when the relative
% change in the objective function
% falls below 'ToleranceA'
% 2 = stop when the relative norm of the difference between
% two consecutive estimates falls below toleranceA
% 3 = stop when the objective function
% becomes equal or less than toleranceA.
% Default = 1.
%
% 'ToleranceA' = stopping threshold; Default = 0.01
%
% 'Debias' = debiasing option: 1 = yes, 0 = no.
% Default = 0.
%
% Note: Debiasing is an operation aimed at the
% computing the solution of the LS problem
%
% arg min_x = 0.5*|| y - A' x' ||_2^2
%
% where A' is the submatrix of A obatained by
% deleting the columns of A corresponding of components
% of x set to zero by the TwIST algorithm
%
%
% 'ToleranceD' = stopping threshold for the debiasing phase:
% Default = 0.0001.
% If no debiasing takes place, this parameter,
% if present, is ignored.
%
% 'MaxiterA' = maximum number of iterations allowed in the
% main phase of the algorithm.
% Default = 1000
%
% 'MiniterA' = minimum number of iterations performed in the
% main phase of the algorithm.
% Default = 5
%
% 'MaxiterD' = maximum number of iterations allowed in the
% debising phase of the algorithm.
% Default = 200
%
% 'MiniterD' = minimum number of iterations to perform in the
% debiasing phase of the algorithm.
% Default = 5
%
% 'Initialization' must be one of {0,1,2,array}
% 0 -> Initialization at zero.
% 1 -> Random initialization.
% 2 -> initialization with A'*y.
% array -> initialization provided by the user.
% Default = 0;
%
% 'Monotone' = enforce monotonic decrease in f.
% any nonzero -> enforce monotonicity
% 0 -> don't enforce monotonicity.
% Default = 1;
%
% 'Sparse' = {0,1} accelarates the convergence rate when the regularizer
% Phi(x) is sparse inducing, such as ||x||_1.
% Default = 1
%
%
% 'True_x' = if the true underlying x is passed in
% this argument, MSE evolution is computed
%
%
% 'Verbose' = work silently (0) or verbosely (1)
%
% ===================================================
% ============ Outputs ==============================
% x = solution of the main algorithm
%
% x_debias = solution after the debiasing phase;
% if no debiasing phase took place, this
% variable is empty, x_debias = [].
%
% objective = sequence of values of the objective function
%
% times = CPU time after each iteration
%
% debias_start = iteration number at which the debiasing
% phase started. If no debiasing took place,
% this variable is returned as zero.
%
% mses = sequence of MSE values, with respect to True_x,
% if it was given; if it was not given, mses is empty,
% mses = [].
%
% max_svd = inverse of the scaling factor, determined by TwIST,
% applied to the direct operator (A/max_svd) such that
% every IST step is increasing.
% ========================================================
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% test for number of required parametres
%--------------------------------------------------------------
if (nargin-length(varargin)) ~= 3
error('Wrong number of required parameters');
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% Set the defaults for the optional parameters
%--------------------------------------------------------------
stopCriterion = 1;
tolA = 0.01;
debias = 0;
maxiter = 1000;
maxiter_debias = 200;
miniter = 5;
miniter_debias = 5;
init = 0;
enforceMonotone = 1;
compute_mse = 0;
plot_ISNR = 0;
AT = 0;
verbose = 1;
alpha = 0;
beta = 0;
sparse = 1;
tolD = 0.001;
phi_l1 = 0;
psi_ok = 0;
% default eigenvalues
lam1=1e-4; lamN=1;
%
% constants ans internal variables
for_ever = 1;
% maj_max_sv: majorizer for the maximum singular value of operator A
max_svd = 1;
% Set the defaults for outputs that may not be computed
debias_start = 0;
x_debias = [];
mses = [];
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% Read the optional parameters
%--------------------------------------------------------------
if (rem(length(varargin),2)==1)
error('Optional parameters should always go by pairs');
else
for i=1:2:(length(varargin)-1)
switch upper(varargin{i})
case 'LAMBDA'
lam1 = varargin{i+1};
case 'ALPHA'
alpha = varargin{i+1};
case 'BETA'
beta = varargin{i+1};
case 'PSI'
psi_function = varargin{i+1};
case 'PHI'
phi_function = varargin{i+1};
case 'STOPCRITERION'
stopCriterion = varargin{i+1};
case 'TOLERANCEA'
tolA = varargin{i+1};
case 'TOLERANCED'
tolD = varargin{i+1};
case 'DEBIAS'
debias = varargin{i+1};
case 'MAXITERA'
maxiter = varargin{i+1};
case 'MAXIRERD'
maxiter_debias = varargin{i+1};
case 'MINITERA'
miniter = varargin{i+1};
case 'MINITERD'
miniter_debias = varargin{i+1};
case 'INITIALIZATION'
if prod(size(varargin{i+1})) > 1 % we have an initial x
init = 33333; % some flag to be used below
x = varargin{i+1};
else
init = varargin{i+1};
end
case 'MONOTONE'
enforceMonotone = varargin{i+1};
case 'SPARSE'
sparse = varargin{i+1};
case 'TRUE_X'
compute_mse = 1;
true = varargin{i+1};
if prod(double((size(true) == size(y))))
plot_ISNR = 1;
end
case 'AT'
AT = varargin{i+1};
case 'VERBOSE'
verbose = varargin{i+1};
otherwise
% Hmmm, something wrong with the parameter string
error(['Unrecognized option: ''' varargin{i} '''']);
end;
end;
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% twist parameters
rho0 = (1-lam1/lamN)/(1+lam1/lamN);
if alpha == 0
alpha = 2/(1+sqrt(1-rho0^2));
end
if beta == 0
beta = alpha*2/(lam1+lamN);
end
if (sum(stopCriterion == [0 1 2 3])==0)
error(['Unknwon stopping criterion']);
end
% if A is a function handle, we have to check presence of AT,
if isa(A, 'function_handle') & ~isa(AT,'function_handle')
error(['The function handle for transpose of A is missing']);
end
% if A is a matrix, we find out dimensions of y and x,
% and create function handles for multiplication by A and A',
% so that the code below doesn't have to distinguish between
% the handle/not-handle cases
if ~isa(A, 'function_handle')
AT = @(x) A'*x;
A = @(x) A*x;
end
% from this point down, A and AT are always function handles.
% Precompute A'*y since it'll be used a lot
Aty = AT(y);
% if phi was given, check to see if it is a handle and that it
% accepts two arguments
if exist('psi_function','var')
if isa(psi_function,'function_handle')
try % check if phi can be used, using Aty, which we know has
% same size as x
dummy = psi_function(Aty,tau);
psi_ok = 1;
catch
error(['Something is wrong with function handle for psi'])
end
else
error(['Psi does not seem to be a valid function handle']);
end
else %if nothing was given, use soft thresholding
psi_function = @(x,tau) soft(x,tau);
end
% if psi exists, phi must also exist
if (psi_ok == 1)
if exist('phi_function','var')
if isa(phi_function,'function_handle')
try % check if phi can be used, using Aty, which we know has
% same size as x
dummy = phi_function(Aty);
catch
error(['Something is wrong with function handle for phi'])
end
else
error(['Phi does not seem to be a valid function handle']);
end
else
error(['If you give Psi you must also give Phi']);
end
else % if no psi and phi were given, simply use the l1 norm.
phi_function = @(x) sum(abs(x(:)));
phi_l1 = 1;
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% Initialization
%--------------------------------------------------------------
switch init
case 0 % initialize at zero, using AT to find the size of x
x = AT(zeros(size(y)));
case 1 % initialize randomly, using AT to find the size of x
x = randn(size(AT(zeros(size(y)))));
case 2 % initialize x0 = A'*y
x = Aty;
case 33333
% initial x was given as a function argument; just check size
if size(A(x)) ~= size(y)
error(['Size of initial x is not compatible with A']);
end
otherwise
error(['Unknown ''Initialization'' option']);
end
% now check if tau is an array; if it is, it has to
% have the same size as x
if prod(size(tau)) > 1
try,
dummy = x.*tau;
catch,
error(['Parameter tau has wrong dimensions; it should be scalar or size(x)']),
end
end
% if the true x was given, check its size
if compute_mse & (size(true) ~= size(x))
error(['Initial x has incompatible size']);
end
% if tau is large enough, in the case of phi = l1, thus psi = soft,
% the optimal solution is the zero vector
if phi_l1
max_tau = max(abs(Aty(:)));
if (tau >= max_tau)&(psi_ok==0)
x = zeros(size(Aty));
objective(1) = 0.5*(y(:)'*y(:));
times(1) = 0;
if compute_mse
mses(1) = sum(true(:).^2);
end
return
end
end
% define the indicator vector or matrix of nonzeros in x
nz_x = (x ~= 0.0);
num_nz_x = sum(nz_x(:));
% Compute and store initial value of the objective function
resid = y-A(x);
prev_f = 0.5*(resid(:)'*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(x);
% start the clock
t0 = cputime;
times(1) = cputime - t0;
objective(1) = prev_f;
if compute_mse
mses(1) = sum(sum((x-true).^2));
end
cont_outer = 1;
iter = 1;
if verbose
fprintf(1,'\nInitial objective = %10.6e, nonzeros=%7d\n',...
prev_f,num_nz_x);
end
% variables controling first and second order iterations
IST_iters = 0;
TwIST_iters = 0;
% initialize
xm2=x;
xm1=x;
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% TwIST iterations
%--------------------------------------------------------------
while cont_outer
% gradient
grad = AT(resid);
while for_ever
% IST estimate
x = psi_function(xm1 + grad/max_svd,tau/max_svd);
if (IST_iters >= 2) | ( TwIST_iters ~= 0)
% set to zero the past when the present is zero
% suitable for sparse inducing priors
if sparse
mask = (x ~= 0);
xm1 = xm1.* mask;
xm2 = xm2.* mask;
end
% two-step iteration
xm2 = (alpha-beta)*xm1 + (1-alpha)*xm2 + beta*x;
% compute residual
resid = y-A(xm2);
f = 0.5*(resid(:)'*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(xm2);
if (f > prev_f) & (enforceMonotone)
TwIST_iters = 0; % do a IST iteration if monotonocity fails
else
TwIST_iters = TwIST_iters+1; % TwIST iterations
IST_iters = 0;
x = xm2;
if mod(TwIST_iters,10000) == 0
max_svd = 0.9*max_svd;
end
break; % break loop while
end
else
resid = y-A(x);
f = 0.5*(resid(:)'*resid(:)) + tau*phi_function(x);
if f > prev_f
% if monotonicity fails here is because
% max eig (A'A) > 1. Thus, we increase our guess
% of max_svs
max_svd = 2*max_svd;
if verbose
fprintf('Incrementing S=%2.2e\n',max_svd)
end
IST_iters = 0;
TwIST_iters = 0;
else
TwIST_iters = TwIST_iters + 1;
break; % break loop while
end
end
end
xm2 = xm1;
xm1 = x;
%update the number of nonzero components and its variation
nz_x_prev = nz_x;
nz_x = (x~=0.0);
num_nz_x = sum(nz_x(:));
num_changes_active = (sum(nz_x(:)~=nz_x_prev(:)));
% take no less than miniter and no more than maxiter iterations
switch stopCriterion
case 0,
% compute the stopping criterion based on the change
% of the number of non-zero components of the estimate
criterion = num_changes_active;
case 1,
% compute the stopping criterion based on the relative
% variation of the objective function.
criterion = abs(f-prev_f)/prev_f;
case 2,
% compute the stopping criterion based on the relative
% variation of the estimate.
criterion = (norm(x(:)-xm1(:))/norm(x(:)));
case 3,
% continue if not yet reached target value tolA
criterion = f;
otherwise,
error(['Unknwon stopping criterion']);
end
cont_outer = ((iter <= maxiter) & (criterion > tolA));
if iter <= miniter
cont_outer = 1;
end
iter = iter + 1;
prev_f = f;
objective(iter) = f;
times(iter) = cputime-t0;
if compute_mse
err = true - x;
mses(iter) = (err(:)'*err(:));
end
% print out the various stopping criteria
if verbose
if plot_ISNR
fprintf(1,'Iteration=%4d, ISNR=%4.5e objective=%9.5e, nz=%7d, criterion=%7.3e\n',...
iter, 10*log10(sum((y(:)-true(:)).^2)/sum((x(:)-true(:)).^2) ), ...
f, num_nz_x, criterion/tolA);
else
fprintf(1,'Iteration=%4d, objective=%9.5e, nz=%7d, criterion=%7.3e\n',...
iter, f, num_nz_x, criterion/tolA);
end
end
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% end of the main loop
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% Printout results
if verbose
fprintf(1,'\nFinished the main algorithm!\nResults:\n')
fprintf(1,'||A x - y ||_2 = %10.3e\n',resid(:)'*resid(:))
fprintf(1,'||x||_1 = %10.3e\n',sum(abs(x(:))))
fprintf(1,'Objective function = %10.3e\n',f);
fprintf(1,'Number of non-zero components = %d\n',num_nz_x);
fprintf(1,'CPU time so far = %10.3e\n', times(iter));
fprintf(1,'\n');
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% If the 'Debias' option is set to 1, we try to
% remove the bias from the l1 penalty, by applying CG to the
% least-squares problem obtained by omitting the l1 term
% and fixing the zero coefficients at zero.
%--------------------------------------------------------------
if debias
if verbose
fprintf(1,'\n')
fprintf(1,'Starting the debiasing phase...\n\n')
end
x_debias = x;
zeroind = (x_debias~=0);
cont_debias_cg = 1;
debias_start = iter;
% calculate initial residual
resid = A(x_debias);
resid = resid-y;
resid_prev = eps*ones(size(resid));
rvec = AT(resid);
% mask out the zeros
rvec = rvec .* zeroind;
rTr_cg = rvec(:)'*rvec(:);
% set convergence threshold for the residual || RW x_debias - y ||_2
tol_debias = tolD * (rvec(:)'*rvec(:));
% initialize pvec
pvec = -rvec;
% main loop
while cont_debias_cg
% calculate A*p = Wt * Rt * R * W * pvec
RWpvec = A(pvec);
Apvec = AT(RWpvec);
% mask out the zero terms
Apvec = Apvec .* zeroind;
% calculate alpha for CG
alpha_cg = rTr_cg / (pvec(:)'* Apvec(:));
% take the step
x_debias = x_debias + alpha_cg * pvec;
resid = resid + alpha_cg * RWpvec;
rvec = rvec + alpha_cg * Apvec;
rTr_cg_plus = rvec(:)'*rvec(:);
beta_cg = rTr_cg_plus / rTr_cg;
pvec = -rvec + beta_cg * pvec;
rTr_cg = rTr_cg_plus;
iter = iter+1;
objective(iter) = 0.5*(resid(:)'*resid(:)) + ...
tau*phi_function(x_debias(:));
times(iter) = cputime - t0;
if compute_mse
err = true - x_debias;
mses(iter) = (err(:)'*err(:));
end
% in the debiasing CG phase, always use convergence criterion
% based on the residual (this is standard for CG)
if verbose
fprintf(1,' Iter = %5d, debias resid = %13.8e, convergence = %8.3e\n', ...
iter, resid(:)'*resid(:), rTr_cg / tol_debias);
end
cont_debias_cg = ...
(iter-debias_start <= miniter_debias )| ...
((rTr_cg > tol_debias) & ...
(iter-debias_start <= maxiter_debias));
end
if verbose
fprintf(1,'\nFinished the debiasing phase!\nResults:\n')
fprintf(1,'||A x - y ||_2 = %10.3e\n',resid(:)'*resid(:))
fprintf(1,'||x||_1 = %10.3e\n',sum(abs(x(:))))
fprintf(1,'Objective function = %10.3e\n',f);
nz = (x_debias~=0.0);
fprintf(1,'Number of non-zero components = %d\n',sum(nz(:)));
fprintf(1,'CPU time so far = %10.3e\n', times(iter));
fprintf(1,'\n');
end
end
if compute_mse
mses = mses/length(true(:));
end
%--------------------------------------------------------------
% soft for both real and complex numbers
%--------------------------------------------------------------
function y = soft(x,T)
%y = sign(x).*max(abs(x)-tau,0);
y = max(abs(x) - T, 0);
y = y./(y+T) .* x;5、TwIST算法测试
这里测试代码基本与IST测试代码相同,略作修改,对比本人所写的TwIST_Basic、IST_Basic(参见压缩感知重构算法之迭代软阈值(IST))以及官方版本的TwIST:
- clear all;close all;clc;
- M = 64;%观测值个数
- N = 256;%信号x的长度
- K = 10;%信号x的稀疏度
- Index_K = randperm(N);
- x = zeros(N,1);
- x(Index_K(1:K)) = 5*randn(K,1);%x为K稀疏的,且位置是随机的
- %x(Index_K(1:K)) = sign(5*randn(K,1));
- Phi = randn(M,N);%测量矩阵为高斯矩阵
- Phi = orth(Phi’)’;
- sigma = 0.005;
- e = sigma*randn(M,1);
- y = Phi * x + e;%得到观测向量y
- % y = Phi * x;%得到观测向量y
- % lamda = sigma*sqrt(2*log(N));
- lamda = 0.1*max(abs(Phi’*y));
- fprintf(‘\nlamda = %f\n’,lamda);
- %% 恢复重构信号x
- %(1)TwIST_Basic
- fprintf(‘\nTwIST_Basic begin…’);
- tic
- x_r1 = TwIST_Basic(y,Phi,lamda);
- toc
- %Debias
- [xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r1), ‘descend’);
- AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
- xI = pinv(AI’*AI)*AI’*y;
- x_bias1 = zeros(length(x),1);
- x_bias1(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
- %(2)IST_Basic
- fprintf(‘\nIST_Basic begin…’);
- tic
- x_r2 = IST_Basic(y,Phi,lamda);
- toc
- %Debias
- [xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r2), ‘descend’);
- AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
- xI = pinv(AI’*AI)*AI’*y;
- x_bias2 = zeros(length(x),1);
- x_bias2(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
- %(3)TwIST
- fprintf(‘\nTwIST begin…\n’);
- tic
- x_r3 = TwIST(y,Phi,lamda,’Monotone’,0,’Verbose’,0);
- toc
- %Debias
- [xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r3), ‘descend’);
- AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
- xI = pinv(AI’*AI)*AI’*y;
- x_bias3 = zeros(length(x),1);
- x_bias3(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
- %% 绘图
- figure;
- plot(x_bias1,’k.-‘);%绘出x的恢复信号
- hold on;
- plot(x,’r’);%绘出原信号x
- hold off;
- legend(‘TwIST\_Basic’,’Original’)
- fprintf(‘\n恢复残差(TwIST_Basic):’);
- fprintf(‘%f\n’,norm(x_bias1-x));%恢复残差
- %Debias
- figure;
- plot(x_bias2,’k.-‘);%绘出x的恢复信号
- hold on;
- plot(x,’r’);%绘出原信号x
- hold off;
- legend(‘IST\_Basic’,’Original’)
- fprintf(‘恢复残差(IST_Basic):’);
- fprintf(‘%f\n’,norm(x_bias2-x));%恢复残差
- %Debias1
- figure;
- plot(x_bias3,’k.-‘);%绘出x的恢复信号
- hold on;
- plot(x,’r’);%绘出原信号x
- hold off;
- legend(‘TwIST’,’Original’)
- fprintf(‘恢复残差(TwIST):’);
- fprintf(‘%f\n’,norm(x_bias3-x));%恢复残差
clear all;close all;clc;
M = 64;%观测值个数
N = 256;%信号x的长度
K = 10;%信号x的稀疏度
Index_K = randperm(N);
x = zeros(N,1);
x(Index_K(1:K)) = 5*randn(K,1);%x为K稀疏的,且位置是随机的
%x(Index_K(1:K)) = sign(5*randn(K,1));
Phi = randn(M,N);%测量矩阵为高斯矩阵
Phi = orth(Phi')';
sigma = 0.005;
e = sigma*randn(M,1);
y = Phi * x + e;%得到观测向量y
% y = Phi * x;%得到观测向量y
% lamda = sigma*sqrt(2*log(N));
lamda = 0.1*max(abs(Phi'*y));
fprintf('\nlamda = %f\n',lamda);
%% 恢复重构信号x
%(1)TwIST_Basic
fprintf('\nTwIST_Basic begin...');
tic
x_r1 = TwIST_Basic(y,Phi,lamda);
toc
%Debias
[xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r1), 'descend');
AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
xI = pinv(AI'*AI)*AI'*y;
x_bias1 = zeros(length(x),1);
x_bias1(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
%(2)IST_Basic
fprintf('\nIST_Basic begin...');
tic
x_r2 = IST_Basic(y,Phi,lamda);
toc
%Debias
[xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r2), 'descend');
AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
xI = pinv(AI'*AI)*AI'*y;
x_bias2 = zeros(length(x),1);
x_bias2(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
%(3)TwIST
fprintf('\nTwIST begin...\n');
tic
x_r3 = TwIST(y,Phi,lamda,'Monotone',0,'Verbose',0);
toc
%Debias
[xsorted inds] = sort(abs(x_r3), 'descend');
AI = Phi(:,inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3));
xI = pinv(AI'*AI)*AI'*y;
x_bias3 = zeros(length(x),1);
x_bias3(inds(xsorted(:)>1e-3)) = xI;
%% 绘图
figure;
plot(x_bias1,'k.-');%绘出x的恢复信号
hold on;
plot(x,'r');%绘出原信号x
hold off;
legend('TwIST\_Basic','Original')
fprintf('\n恢复残差(TwIST_Basic):');
fprintf('%f\n',norm(x_bias1-x));%恢复残差
%Debias
figure;
plot(x_bias2,'k.-');%绘出x的恢复信号
hold on;
plot(x,'r');%绘出原信号x
hold off;
legend('IST\_Basic','Original')
fprintf('恢复残差(IST_Basic):');
fprintf('%f\n',norm(x_bias2-x));%恢复残差
%Debias1
figure;
plot(x_bias3,'k.-');%绘出x的恢复信号
hold on;
plot(x,'r');%绘出原信号x
hold off;
legend('TwIST','Original')
fprintf('恢复残差(TwIST):');
fprintf('%f\n',norm(x_bias3-x));%恢复残差 运行结果如下:(信号为随机生成,所以每次结果均不一样)
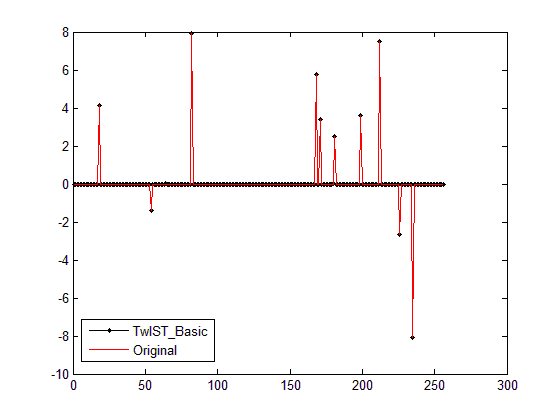
1)图(均为debias之后,参见压缩感知重构算法之迭代软阈值(IST))
2)Command Windows
lamda = 0.224183
TwIST_Basic begin…
abs(f_pre1-f_pre2)/f_pre2<0.010000
TwIST loop is 21
Elapsed time is 0.011497 seconds.
IST_Basic begin…
abs(f-f_pre)/f_pre<0.010000
IST loop is 14
Elapsed time is 0.006397 seconds.
TwIST begin…
Elapsed time is 0.029590 seconds.
恢复残差(TwIST_Basic):0.047943
恢复残差(IST_Basic):4.928160
恢复残差(TwIST):0.047943
注:重构经常失败,运行结果仅为挑了一次重构效果较好的附上;IST有时也可以较好的重构,凑巧这次重构效果不佳。
6、结束语
从重构结果来看,尤其是Command Windows的输出结果来看,TwIST相比于IST并没有什么优势,这可能是由于我的测试案例十分简单的原因吧。
另外,谈一下个人对TwIST_Basic函数中第42~44行(或TwIST函数中第490~494行)的理解:这几行很关键,直接影响着能否重构,虽然加上后也经常重构失败(但去掉这几行代码基本无法重构)。个人认为原因是这样的,TwIST容易发散,加上这几行代码后实际是把x非零值的位置依靠IST去决定(因为决定mask的实际是IST迭代公式计算结果),而x迭代则使用TwIST迭代公式。当然,这仅为个人看法。
最后再说一句,在文中压根就没提“压缩感知”,但由于TwIST可以求解基追踪降噪(BPDN)问题,所以也就可以拿来作为压缩感知重构算法了……
给出TwIST两位作者的个人主页:
Jose M. Bioucas Dias:http://www.lx.it.pt/~bioucas/
MárioA. T. Figueiredo:http://www.lx.it.pt/~mtf/
凑巧的是在第一作者主页上居然还发现了一个研究生同学,感叹世界好小,哈哈……








 本文介绍TwIST算法,一种加速图像修复的迭代收缩阈值算法。TwIST结合了IST与TwSIM算法的优势,通过两步迭代过程加快收敛速度。文章详细解析了TwIST的迭代公式、参数设置及MATLAB实现。
本文介绍TwIST算法,一种加速图像修复的迭代收缩阈值算法。TwIST结合了IST与TwSIM算法的优势,通过两步迭代过程加快收敛速度。文章详细解析了TwIST的迭代公式、参数设置及MATLAB实现。




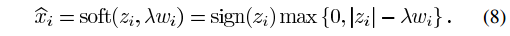









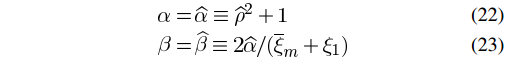





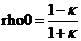




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








