正则表达式----(re库)
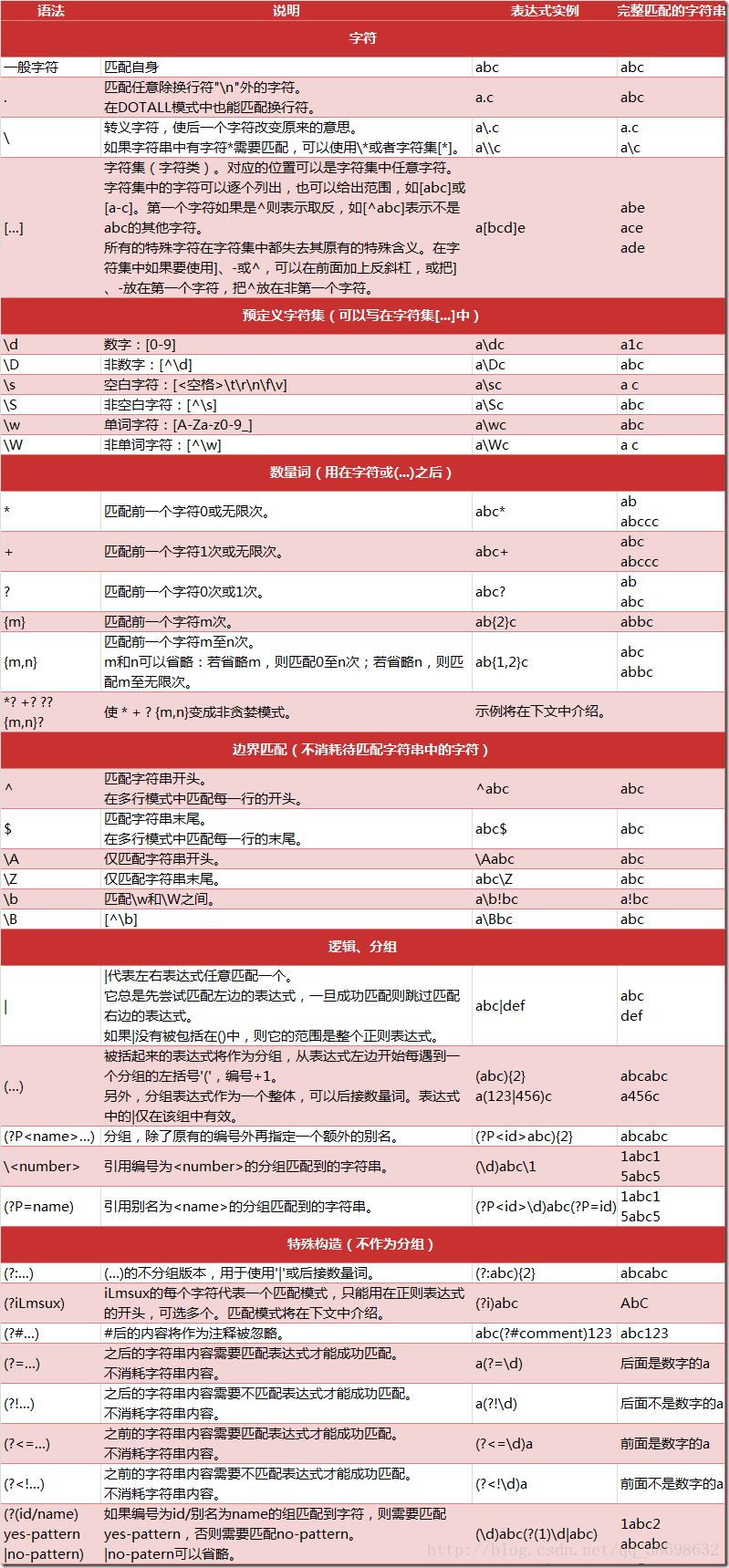
下面是Python中正则表达式的一些匹配规则,图片资料来自CSDN
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re#1.match()
# 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象,注意hello前面的r的意思是“原生字符串”
pattern = re.compile(r'hello')
# 使用re.match匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
result1 = re.match(pattern,'hello')
result2 = re.match(pattern,'helloo')
result3 = re.match(pattern,'helo')
result4 = re.match(pattern,'hello')
#如果1匹配成功
if result1:
# 使用Match获得分组信息
print result1.group()
else:
print '1匹配失败!'
#如果2匹配成功
if result2:
# 使用Match获得分组信息
print result2.group()
else:
print '2匹配失败!'
#如果3匹配成功
if result3:
# 使用Match获得分组信息
print result3.group()
else:
print '3匹配失败!'
#如果4匹配成功
if result4:
# 使用Match获得分组信息
print result4.group()
else:
print '4匹配失败!'
#2.re.search(pattern,string[,flags])
与match类似,区别在于match函数只检测re是不是在string的开始位置匹配,search会扫描整个string查找匹配
match只有在0位置匹配成功才返回;
#如果用match就错了
pattern=re.compile(r'world')
match=re.search(pattern,'hello world')
if match:
print match.group()
#3.re.split(pattern,string[,maxsplit])
#按照能过匹配的字符串将string分割后返回列表。maxsplit用于指定最大分割次数,不指定将全部分割
pattern=re.compile(r'\d+')
print re.split(pattern,'one1two1free234four33')
#4.re.findall(pattern,string[,flags])
#搜索string,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串
pattern=re.compile(r'\d+')
print re.findall(pattern,'1one2two3three4four4')
#5.re.finditer(pattern,string[,flags])
#搜索string,返回一个顺序访问每一个匹配结果的迭代器
pattern=re.compile(r'\d+')
for i in re.finditer(pattern,'one2two3three4four4'):
print i.group()
#以上内容根据静觅博客的内容进行学习
python os.path模块(原文链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/dkblog/archive/2011/03/25/1995537.html )
os库函数部分用法 原文链接:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-27838438-id-4087978.html
1、os.getcwd()函数
功能:获取当前目录,python 的工作目
- import os
-
- pwd = os.getcwd()
-
- print (pwd)
2、os.name 函数
功能:获取当前使用的操作系统(获取信息不够详细)
其中 'nt' 是 windows,'posix' 是 linux 或者 unix
- import os
-
- name = os.name
-
- if name == 'posix':
-
- print ("this is Linux or Unix")
-
- elif name == 'nt':
-
- print ("this is windows")
-
- else:
-
- print ("this is other system")
功能:删除指定文件
eg:删除 file.txt 文件
- import os
-
- os.remove(’file.txt‘)
4、os.removedirs()函数
功能:删除指定目录
eg:删除 file目录
- import os
-
- os.removedirs(‘file’)
5、os.system()函数
功能:运行shell命令
eg:执行ls -a > 1.txt命令
- import os
-
- os.system(‘ls -a > 1.txt’)
6、os.mkdir()函数
功能:创建一个新目录
eg:创建一个 file 目录
- import os
-
- os.mkdir(‘file’)
7、os.chdir()函数
功能:改变当前路径到指定路径
eg:我现在从当前路径到 filepath 所指定的路径下
- import os
-
- filepath = '/home'
-
- pwd = os.getcwd()
-
- print (pwd)
-
- os.chdir(filepath)
-
- pwd = os.getcwd()
-
- print (pwd)
8、os.listdir()函数
功能:返回指定目录下的所有目录和文件
eg:列出当前目录下的所有文件和目录
- import os
-
- pwd = os.getcwd()
-
- name = os.listdir(pwd)
-
- for filename in name:
-
- print (filename)






















 3483
3483

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








