1. 分类回归树
Classification And Regression Tree(CART),一个用于监督学习的非参数模型。
二分递归分割:将当前样本集合划分为两个子样本集合,使得生成的每个非叶子结点都有两个分支。
树模型很容易过拟合,所以很多策略都是防止过拟合的,如提前终止、剪枝、Bagging…
1.1 CART算法只要分为两个步骤:
(1)将样本递归划分进行建树
令节点的样本集合为D,对候选分裂θ=(j, tm),选择特征j,分裂阈值为tm,将样本分裂为两个分支:
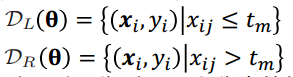
分裂原则:分裂后的两个分支样本越纯净越好

对于回归问题:
集合D的不纯净性为集合中样本的y值的差异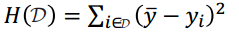
其中,
集合中样本的y值越接近越纯净,相当于损失函数取L2损失,选择最小L2损失的分裂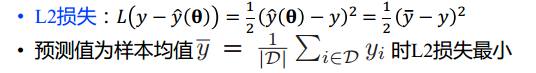
对于分类问题:
分布的估计值取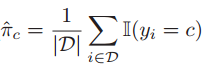

建树停止条件

(2)用验证数据进行剪枝

1.2 scikit-learn实现
分类树:DecisionTreeClassifier
回归树:DecisionTreeRegressor



2. 随机森林
回归树算法的缺点之一是高方差,降低算法方差的方式是平均多个模型的预测:Bagging(Bootstrap aggregating)


练习
蘑菇数据集,直接采用Kaggle竞赛中22维特征
代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
dpath = './data/'
data = pd.read_csv(dpath + 'mushrooms.csv')
# 将文本内容量化成数字
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
labelencoder = LabelEncoder()
for col in data.columns:
data[col] = labelencoder.fit_transform(data[col])
X = data.iloc[:, 1:23]#除label外的所有特征
y = data.iloc[:, 0]#label
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=4)
#逻辑回归
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
model_LR = LogisticRegression()
model_LR.fit(X_train,y_train)
#测试
y_prob = model_LR.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]
y_pred = np.where(y_prob > 0.5, 1, 0)#大于0.5为1,小于0.5为0
model_LR.score(X_test, y_pred)
auc_roc = metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
LR_model = LogisticRegression()
tuned_parameters = {'C': [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000] ,
'penalty':['l1','l2']
}
LR = GridSearchCV(LR_model, tuned_parameters, cv=10)
LR.fit(X_train,y_train)
# 决策树模型
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
model_DD = DecisionTreeClassifier()
tuned_parameters = {
'max_features':['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2'], 'min_samples_leaf':range(1,100,1), 'max_depth':range(1,50,1)
}
#If “auto”, then max_features=sqrt(n_features).
DD = GridSearchCV(model_DD, tuned_parameters,cv=10)
DD.fit(X_train, y_train)
#随机森林
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
model_RR = RandomForestClassifier()
tuned_parameters = {
'min_samples_leaf':range(10,100,10), 'n_estimators':range(10,100,10), 'max_features':['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2']
}
RR = GridSearchCV(model_RR, tuned_parameters,cv=10)
RR.fit(X_train,y_train)
#XGBoost
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
model_XGB = XGBClassifier()
model_XGB.fit(X_train, y_train)
#在XGBoost中特征重要性已经自动算好,存放在featureimportances中
print(model_XGB.feture_importances_)
#在XGBoost中特征重要性已经自动算好,存放在featureimportances中
print(model_XGB.feature_importances_)
# 按特征顺序打印重要性
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.bar(range(len(model_XGB.feature_importances_)), model_XGB.feature_importances_)
plt.show()
# 使用XGBoost内嵌的函数,按特征重要性排序
from xgboost import plot_importance
plot_importance(model_XGB)
plt.show()
# 根据特征重要性进行特征选择
from numpy import sort
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
thresholds = sort(model_XGB.feature_importances_)
for thresh in thresholds:
selection = SelectFromModel(model_XGB, threshold=thresh, prefit=True)
select_X_train = selection.transform(X_train)
selection_model = XGBClassifier()
selection_model.fit(select_X_train, y_train)
select_X_test = selection.transform(X_test)
y_pred = selection_model.predict(select_X_test)
predictions = [round(value) for value in y_pred]
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, predictions)
print("Thresh=%.3f, n=%d, Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (thresh, select_X_train.shape[1], accuracy*100.0))





















 2294
2294











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








