字符串广泛应用 在 Java 编程中,在 Java 中字符串属于对象,Java 提供了 String 类来创建和操作字符串。
String类中的常用方法
一、字符串的构建
String 类有 11 种构造方法,这些方法提供不同的参数来初始化字符串。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 字符串常量创建,这是创建字符串最简单的方式
String s1 = "Hello CSDN";
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
// String对象的创建
String s2 = new String("Hello CSDN");
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2);
// 提供一个字符数组参数
char[] array = {'H','e','l','l','o','C','S','D','N'};
String s3 = new String(array);
System.out.println("s3 = " + s3);
}
}
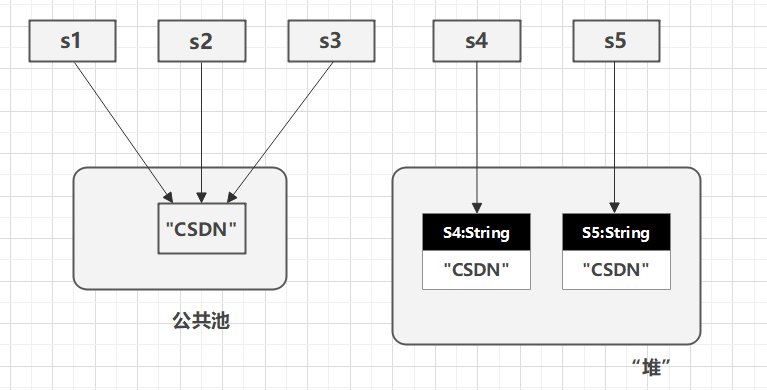
String创建的字符串存储在公共池中,而new创建的字符串对象在堆上。
//s1,s2,s3引用的是同一个对象
String s1 = "CSDN";
String s2 = "CSDN";
String s3 = s1;
//s4,s5引用的是不同对象
String s4 = new String("CSDN");
String s5 = new String("CSDN");
二、字符串的长度
用于获取有关对象的信息的方法称为访问器方法。
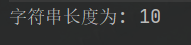
String 类的一个访问器方法是 length() 方法,它返回字符串对象包含的字符数。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String site = "Hello CSDN";
int len = site.length();
System.out.println( "字符串长度为: " + len );
}
三、连接字符串
String 类提供了连接两个字符串的方法:
string1.concat(string2);
返回 string2 连接 string1 的新字符串。也可以对字符串常量使用 concat() 方法,如:
// "Hello ".concat("CSDN");
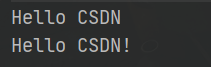
System.out.println("Hello ".concat("CSDN"));
更常用的是使用+操作符来连接字符串。
// "Hello" + "CSDN" + "!"
System.out.println("Hello " + "CSDN" + "!");
四、String对象的比较
字符串的比较是常见的操作之一,Java中提供了四种方式来对字符串进行比较。
1、使用==比较
使用==来比较是否引用同一个对象。对于内置类型,==比较的是变量中的值;对于引用类型==比较的是引用中的地址。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//内置类型,比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
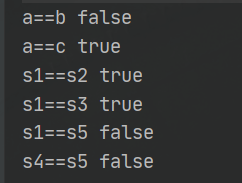
System.out.println("a==b "+ (a==b)); // false
System.out.println("a==c "+ (a==c)); // true
//引用类型,比较两个引用类型是否引用的为同一对象
String s1 = "CSDN";
String s2 = "CSDN";
String s3 = s1;
String s4 = new String("CSDN");
String s5 = new String("CSDN");
System.out.println("s1==s2 "+ (s1==s2)); // true
System.out.println("s1==s3 "+ (s1==s3)); // true
System.out.println("s1==s5 "+ (s1==s4)); // false
System.out.println("s4==s5 "+ (s4==s5)); // false
}
2、boolean equals(Object anObject)方法
boolean equals(Object anObject)方法:按照字典序进行比较。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
String s1 = "CSDN";
String s2 = "CSDN";
String s3 = s1;
String s4 = new String("CSDN");
String s5 = new String("CSDN");
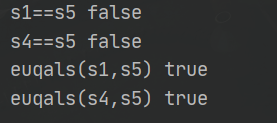
System.out.println("s1==s5 "+ (s1==s4));
System.out.println("s4==s5 "+ (s4==s5));
System.out.println("euqals(s1,s5) "+ (s1.equals(s5)));
System.out.println("euqals(s4,s5) "+ (s4.equals(s5)));
}
注: equals()源码
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
// 1. 检测this和anObject是否为同一对象,如果是返回true
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
// 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回false
if (anObject instanceof String) {
// 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
// 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回false
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
// 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3、int compareTo(String s)方法
按照字典序进行比较。equals()返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值。
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("Abc");
String s5 = new String("abcdef");
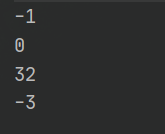
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 输出差值32
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s5)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}
4、int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)方法
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较.
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("Abc");
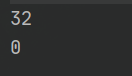
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 输出差值32
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); //输出差值0
}
五、字符串的查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
char charAt(int index) | 返回char指定索引处的值(index为负数或者越界则抛出异常) |
int indexOf(int ch) | 返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引(没有则返回-1) |
int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置(没有返回-1) |
int indexOf(int ch, intfromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置(没有则返回-1) |
int indexOf(String str, intfromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置(没有则返回-1) |
int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(int ch, intfromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(String str) | 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(String str, intfromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
示例:
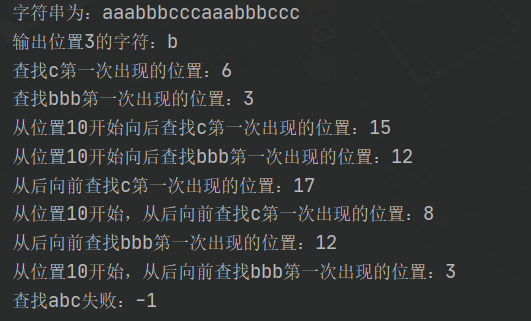
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println("输出位置3的字符:"+s.charAt(3));
System.out.println("查找c第一次出现的位置:"+s.indexOf('c'));
System.out.println("查找bbb第一次出现的位置:"+s.indexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println("从位置10开始向后查找c第一次出现的位置:"+s.indexOf('c', 10));
System.out.println("从位置10开始向后查找bbb第一次出现的位置:"+s.indexOf("bbb", 10));
System.out.println("从后向前查找c第一次出现的位置:"+s.lastIndexOf('c'));
System.out.println("从位置10开始,从后向前查找c第一次出现的位置:"+s.lastIndexOf('c', 10));
System.out.println("从后向前查找bbb第一次出现的位置:"+s.lastIndexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println("从位置10开始,从后向前查找bbb第一次出现的位置:"+s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10));
System.out.println("查找abc失败:"+s.lastIndexOf("abc",1));
六、字符串的转化
1、数值与字符串
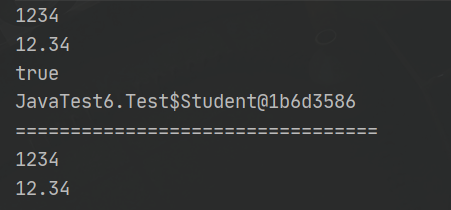
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字转字符串
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234); //整型
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34); //浮点型
String s3 = String.valueOf(true); //boolean类型
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("小明",18,"男")); //类对象
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}
2、大小写转换
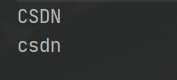
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "csdn";
String s2 = "CSDN";
//小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
//大写转小写
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}
3、字符串转数组
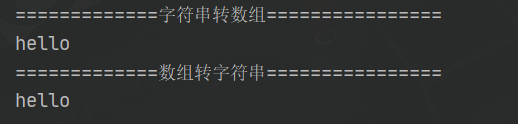
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
System.out.println("=============字符串转数组================");
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=============数组转字符串================");
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}
4、格式化
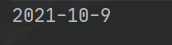
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2021, 10, 9);
System.out.println(s);
}






















 1325
1325











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








