从b站学习springcloud,现在进行总结,该总结除去了视频中出现的小错误,对有些易错的地方进行了提醒
b站链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Gt411N7HF?p=2
资料链接:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1o0Aju3IydKA15Vo1pP4z5w
提取码: 21ru
上一节链接:
下一节链接:
下面的内容总结:
本节是底层原理,代码了解即可
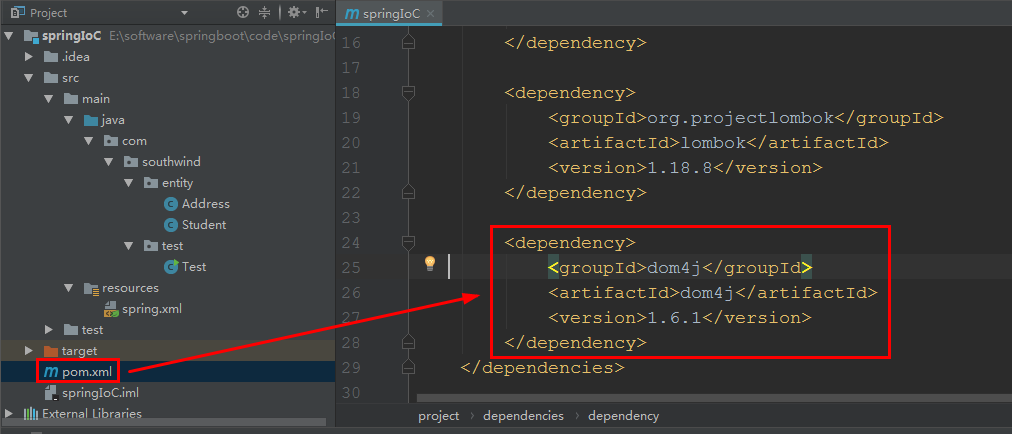
1 在 pom 文件中加入代码:
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
2 实现接口:

实现这两个红框
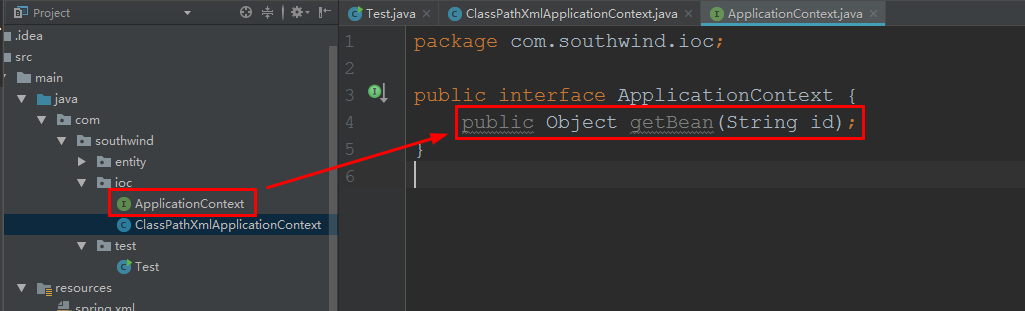
2.1 在 southwind 中创包 ioc,其内创建接口 ApplicationContext ,加入代码:
package com.southwind.ioc;
public interface ApplicationContext {
public Object getBean(String id);
}
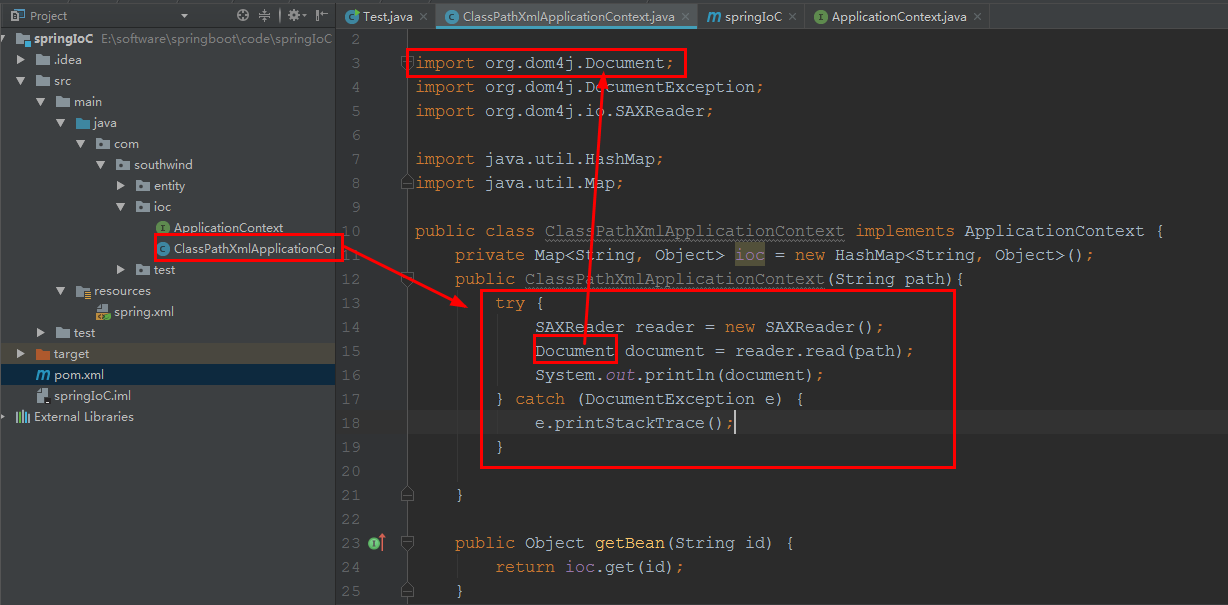
2.2 southwind 中创建 类 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); 用到了 ctrl + alt + t
加入代码 :
package com.southwind.ioc;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path){
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(path);
System.out.println(document);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return ioc.get(id);
}
}
2.3 在 ioc 中新建 类 Test

选择自己写的接口
ApplicationContext 和 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 均选择自己写在 ioc中的文件
加入代码:
package com.southwind.ioc;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("./src/main/resources/spring.xml" );
}
}
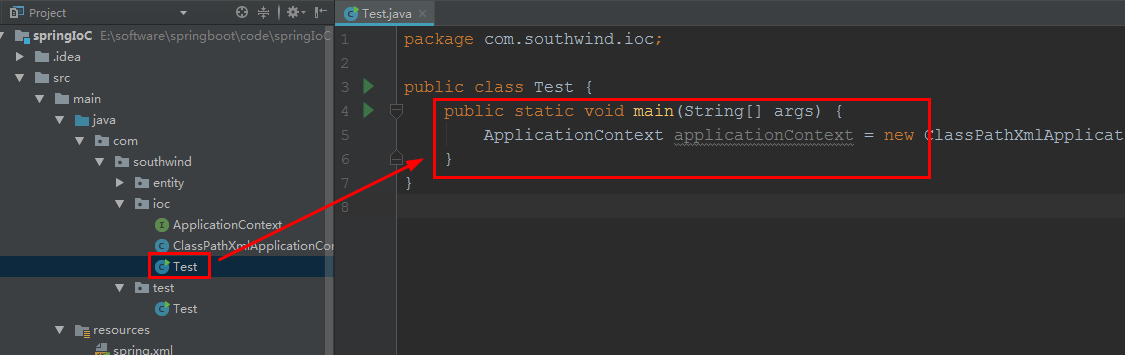
./ 表示 当前工程
2.4 启动 ioc/ Test:

2.5 觉得 ioc/ Test 中路径太麻烦,就在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中:


启动 ioc/ Test:

2.6 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
Element root = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println(root);
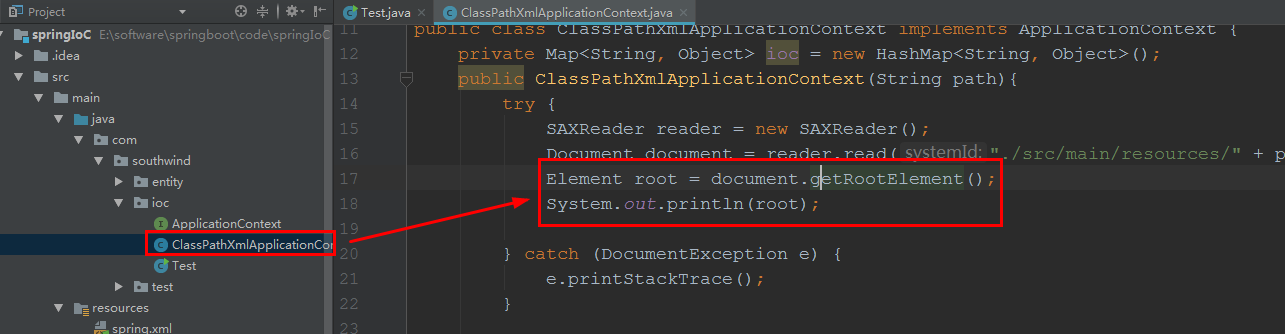
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.7 迭代操作,在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:

Iterator<Element> iterator = root.elementIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Element element = iterator.next();
System.out.println(element);
}
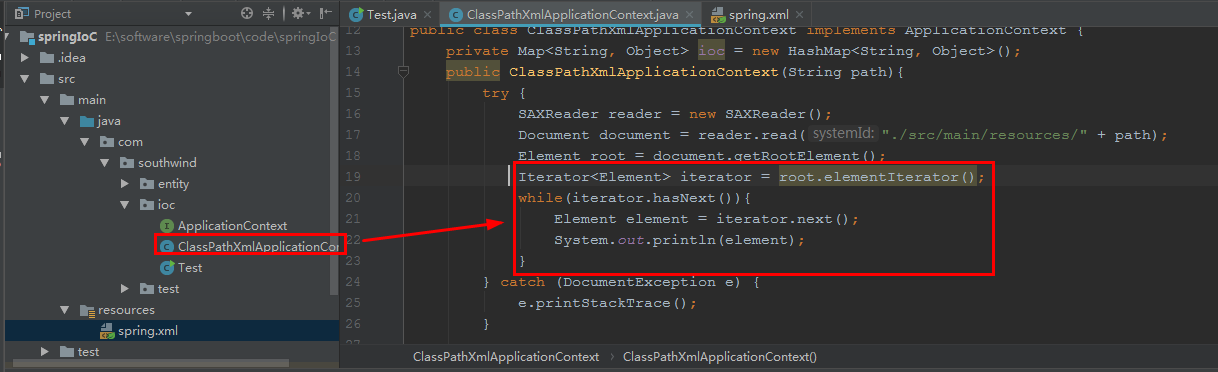
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.8 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String className = element.attributeValue("class");
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(className
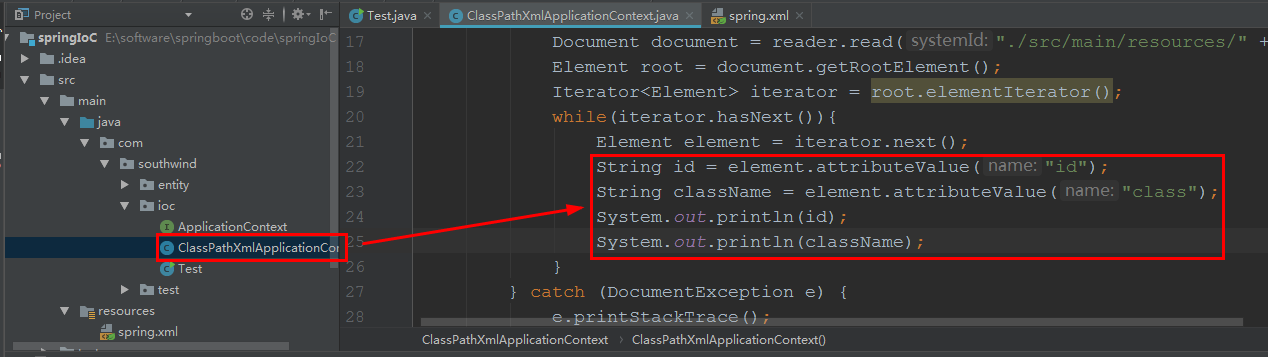
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.9 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
// 通过反射机制 创建对象,拿到class
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 获取 无参构造
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor);
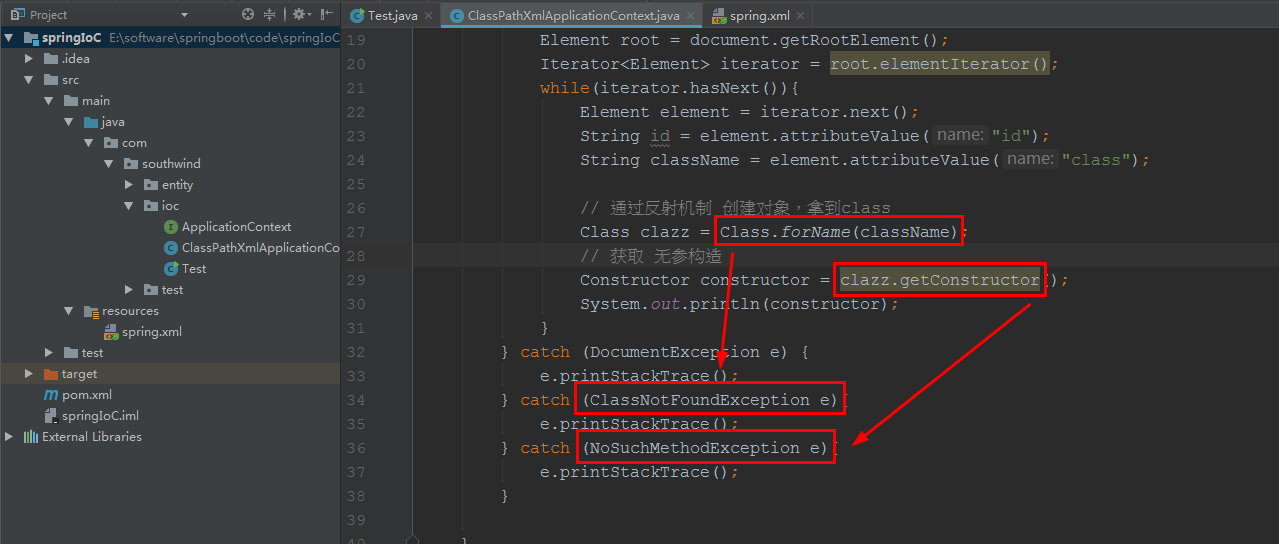
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.10 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
Object object = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(object);
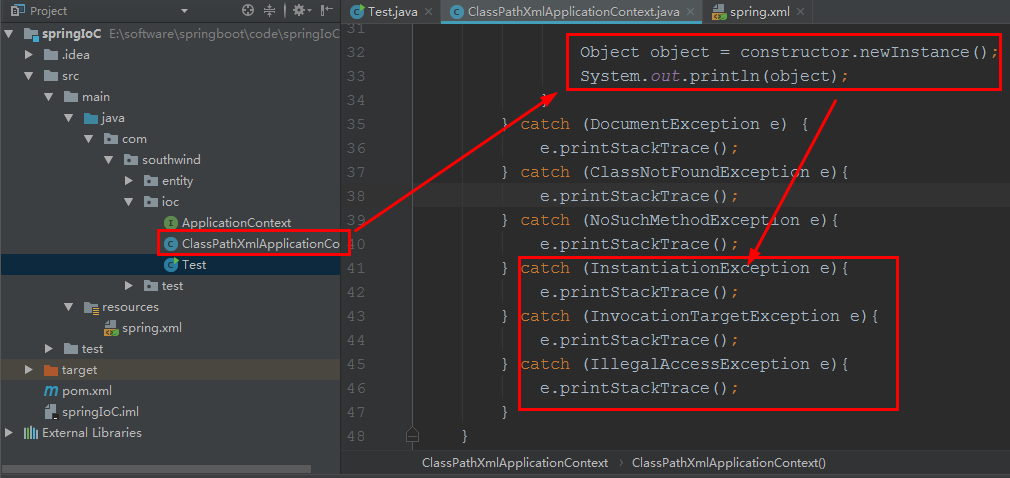
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.11 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
ioc.put(id, object);

在 ioc/ Test 加入代码:
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
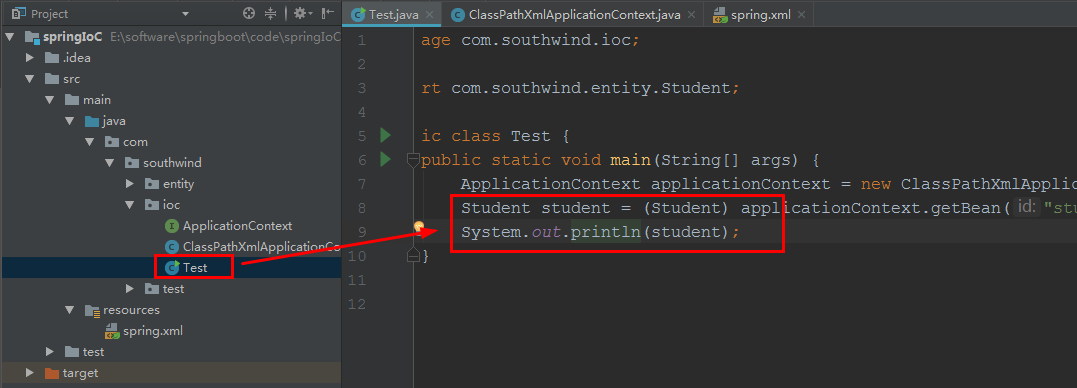
启动 ioc/ Test:

赋值:
2.12 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
// 给 目标对象 赋值
Iterator<Element> beanIter = element.elementIterator();
while(beanIter.hasNext()){
Element property = beanIter.next();
String name = property.attributeValue("name");
String value = property.attributeValue("value");
String methodName = "set" + name.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + name.substring(1);
System.out.println(methodName);
就是变成 set + Name 形式,如 setAge、setId

启动 ioc/ Test:

2.13 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(name);
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, field.getType());
System.out.println(method);
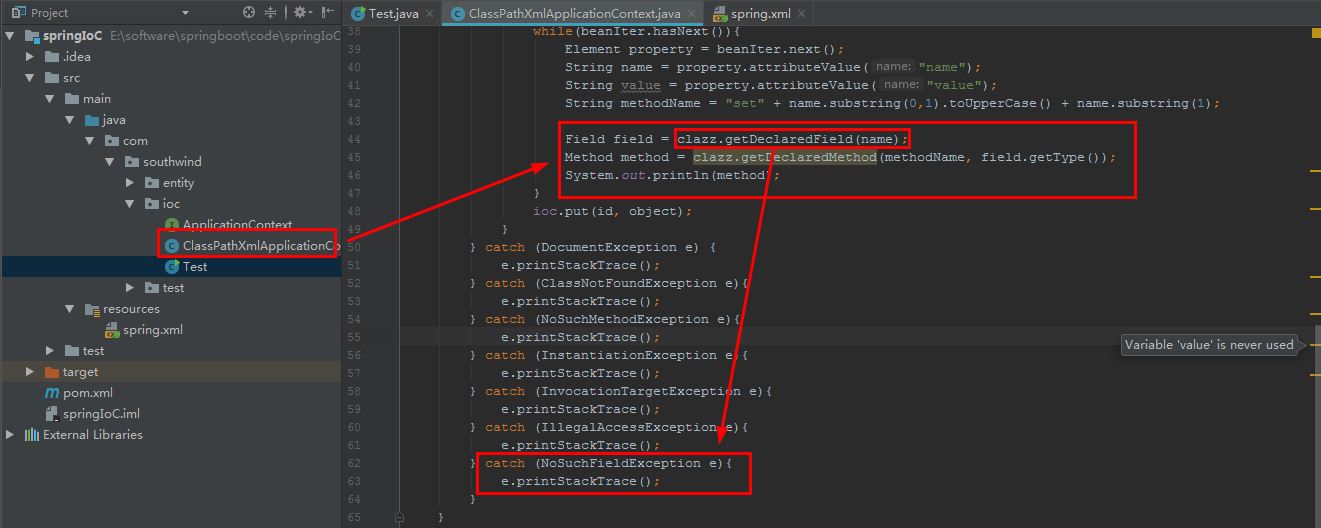
启动 ioc/ Test:

2.14 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:
// 根据成员变量的数据类型将 value 进行转换
Object value= null;
if(field.getType().getName() == "long"){
value = Long.parseLong(valueStr);
}
if(field.getType().getName() == "java.lang.String"){
value = valueStr;
}
if(field.getType().getName() == "int"){
value = Integer.parseInt(valueStr);
}
method.invoke(object, value);//赋值
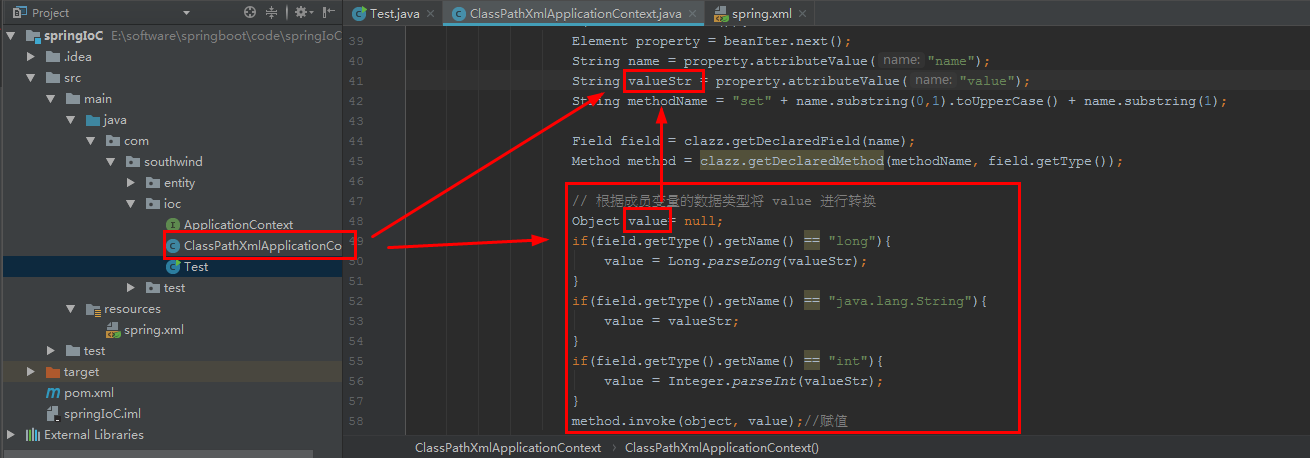
启动 ioc/ Test:

分析:
address 是 null,没被赋值,因为不是(object, value)类型,我要取 ref 赋值

2.15 在 ioc/ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中,加入代码:



总代码:
package com.southwind.ioc;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path){
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read("./src/main/resources/" + path);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
Iterator<Element> iterator = root.elementIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Element element = iterator.next();
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String className = element.attributeValue("class");
// 通过反射机制 创建对象,拿到class
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 获取 无参构造
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
Object object = constructor.newInstance();
// 给 目标对象 赋值
Iterator<Element> beanIter = element.elementIterator();
while(beanIter.hasNext()){
Element property = beanIter.next();
String name = property.attributeValue("name");
String valueStr = property.attributeValue("value");
String ref = property.attributeValue("ref");
if(ref == null){ // 普通赋值
String methodName = "set" + name.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + name.substring(1);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(name);
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, field.getType());
// 根据成员变量的数据类型将 value 进行转换
Object value= null;
if(field.getType().getName() == "long"){
value = Long.parseLong(valueStr);
}
if(field.getType().getName() == "java.lang.String"){
value = valueStr;
}
if(field.getType().getName() == "int"){
value = Integer.parseInt(valueStr);
}
method.invoke(object, value);//赋值
}
ioc.put(id, object);
}
}
Object obj1 = ioc.get("address");
Object obj2 = ioc.get("student");
System.out.println(obj1);
System.out.println(obj2);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean(String id) {
return ioc.get(id);
}
}
启动 ioc/ Test:

3 test/ Test 中:
getBean("student"); 改成 getBean(Student.class);


启动 test/ Test:

问题:
配置文件中,1个数据类型的对象 只能有1个实例,否则抛出异常
下面就是错的:

因为1个数据类型的对象 只能有1个实例,有了红框代码,1个数据类型的对象 就是2个实例了
启动 test/ Test:

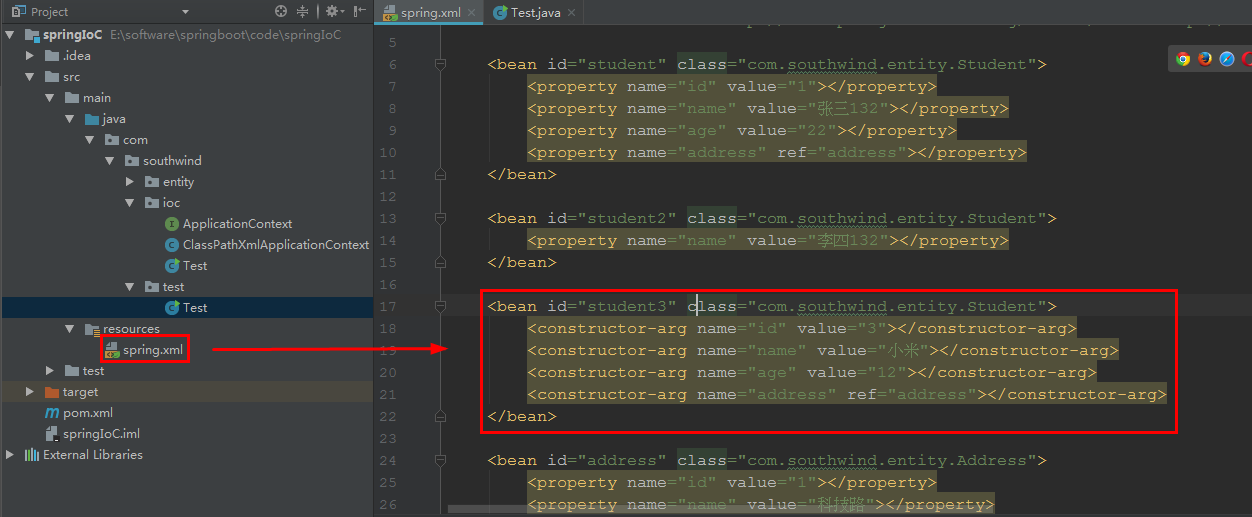
4 在 resources/ spring.xml 中,加入代码:
<bean id="student3" class="com.southwind.entity.Student">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="3"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="小米"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="12"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="address" ref="address"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
也可以:
<bean id="student3" class="com.southwind.entity.Student">
<constructor-arg value="3"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="小米"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="12"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg ref="address"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
上面代码的前提是:顺序和 类 Student 中 数据类型的顺序一致
若不一致,就是:
<bean id="student3" class="com.southwind.entity.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="3"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="小明"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="3" ref="address"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
test/ Test 中:Student.class 变成 "student3"

启动 test/ Test:
























 4021
4021

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










