from_tensor_slices()、repeat()、batch()、interleave()使用
一、from_tensor_slices()使用
from_tensor_slices(
tensors
)
在最简单的情况下,tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices函数接收一个array并返回一个表示array切片的tf.data.Dataset。例如,mnist训练集的shape是(60000, 28, 28)。将这个array传递给from_tensor_slices将返回一个包含60000个切片的数据集对象,每个切片大小为28X28的图像。(其实这个API就是把array的第一维切开)。
示例:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
#form_tensor_slices()
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(np.arange(10))
print(dataset)
for item in dataset:
print(item)
<TensorSliceDataset shapes: (), types: tf.int32>
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
y = np.array(["cat", "dog", "fox"])
#from_tensor_slices 会将元组的第一维切开返回一个数组
dataset2 = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y))
print(dataset2)
for item in dataset2:
print(item)
for item_x, item_y in dataset2:
print(item_x, item_y)
for item_x, item_y in dataset2:
print(item_x.numpy(), item_y.numpy())
<TensorSliceDataset shapes: ((2,), ()), types: (tf.int32, tf.string)>
(<tf.Tensor: id=26, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([1, 2])>, <tf.Tensor: id=27, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b’cat’>)
(<tf.Tensor: id=28, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([3, 4])>, <tf.Tensor: id=29, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b’dog’>)
(<tf.Tensor: id=30, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([5, 6])>, <tf.Tensor: id=31, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b’fox’>)
tf.Tensor([1 2], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(b’cat’, shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor([3 4], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(b’dog’, shape=(), dtype=string)
tf.Tensor([5 6], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(b’fox’, shape=(), dtype=string)
[1 2] b’cat’
[3 4] b’dog’
[5 6] b’fox’
#以字典的形式
dataset3 = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices({"feature": x,
"label" : y})
for item in dataset3:
print(item)
for item in dataset3:
print(item["feature"].numpy(), item["label"].numpy())
{'feature': <tf.Tensor: id=62, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([1, 2])>, 'label': <tf.Tensor: id=63, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'cat'>}
{'feature': <tf.Tensor: id=64, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([3, 4])>, 'label': <tf.Tensor: id=65, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'dog'>}
{'feature': <tf.Tensor: id=66, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([5, 6])>, 'label': <tf.Tensor: id=67, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'fox'>}
[1 2] b'cat'
[3 4] b'dog'
[5 6] b'fox'
二、repeat()使用
repeat(
count=None
)
作用:重复此数据集,count为重复的次数。
注意如果repeat无参数则重复无数次
示例:
#repeat()
dataset = dataset.repeat(3)
for item in dataset:
print(item)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
三、batch()使用
batch(
batch_size,drop_remainder=False
)
作用:将数据集按照顺序,一组为batch_size的大小组成新的tensor。
batch_size: 一批的元素个数;drop_remainder: 表示如果最后一个批的元素小于batch_size,是否应删除它;默认行为是不删除较小的批。
示例:
dataset = dataset.batch(7)
for item in dataset:
print(item)
tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4 5 6], shape=(7,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([7 8 9 0 1 2 3], shape=(7,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([4 5 6 7 8 9 0], shape=(7,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([1 2 3 4 5 6 7], shape=(7,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([8 9], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
四、interleave()使用
interleave(
map_func,
cycle_length=-1,
block_length=1,
num_parallel_calls=None
)
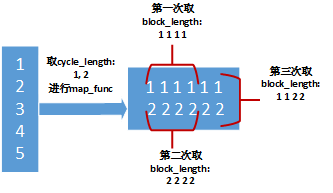
map_func: 将数据集元素映射到数据集的函数。cycle_length:将同时处理的输入元素个数。block_length: 在循环到另一个输入元素之前,从每个输入元素生成的连续元素的数目。
首先该方法会从该Dataset中取出cycle_length个元素,然后将这些元素应用到map_func函数中去, 得到cycle_length个新的Dataset对象。然后从这些新生成的Dataset对象中取数据,每个Dataset对象一次取block_length个数据。当新生成的某个Dataset的对象取尽时,从原Dataset中再取一个元素,然后应用到map_func函数中去,以此类推。
示例一:
a = tf.data.Dataset.range(1, 6) # ==> [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
# NOTE: New lines indicate "block" boundaries.
b=a.interleave(lambda x: tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(x).repeat(6),
cycle_length=2, block_length=4)
for item in b:
print(item.numpy(),end=', ')
1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5,
图片引用:https://blog.csdn.net/menghuanshen/article/details/104240189
示例二:
#interleave(map_func, cycle_length=-1, block_length=1, num_parallel_calls=None)
dataset4 = dataset.interleave(
lambda x : tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x),
cycle_length = 5,
block_length = 5,
)
for item in dataset4:
print(item)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(8, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(5, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(6, shape=(), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(7, shape=(), dtype=int32)






















 1042
1042

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








