线程创建的三种方式
线程创建的三种方式

1、继承Thread类,重写run()方法,调用start()方法
//创建线程的方法之一:继承Thread类,重写run()方法,调用start()方法启动线程
public class StartThread01 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("这是线程体" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StartThread01 startThread01 = new StartThread01();
//一定要注意,这里是调用start()方法
startThread01.start();//两个方法是同步执行的,如果此处调用run(); 那么就是先执行run();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习" + i);
}
}
}
可以看到,两条线程是同步交替执行的

一个例子:多线程同时下载三张图片
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
//小练习:多线程同时下载三张图片
public class StartThread02 extends Thread{
private String url;
private String name;
//含参构造
public StartThread02(String url,String name) {
this.url=url;
this.name=name;
}
//重写Thread类中的run()方法
@Override
public void run() {
//执行下载器
WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader();
webDownLoader.downLode(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件:"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StartThread02 s1 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "1.png");
StartThread02 s2 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "2.png");
StartThread02 s3 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "3.png");
s1.start();
s2.start();
s3.start();
}
}
//下载器 在项目中导入这样一个io工具包-->"commons-io-2.11.0.jar"
class WebDownLoader {
public void downLode(String url, String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));//io工具包为我们提供了这样一个下载文件的方法
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO异常,下载失败");
}
}
}
//main方法是静态方法,不能访问非静态成员变量和非静态方法的!

可以看到三次下载的线程是同步执行的,而不是顺序执行
2、继承runnable接口,重写run()方法,丢入runnable接口实现类,调用start方法
//创建线程的方法之二:继承runnable接口,重写run()方法,线程中丢入runnable接口实现类,调用start方法
public class StartThread03 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("这是线程体" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//runnabel接口实现类
StartThread03 startThread03 = new StartThread03();
new Thread(startThread03).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习" + i);
}
}
}
和第一种方法的效果是一样 的
第二种方法修改方法1中的例子
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
//小练习:多线程同时下载三张图片
public class StartThread04 implements Runnable{
private String url;
private String name;
public StartThread04(String url,String name) {
this.url=url;
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader();
webDownLoader.downLode(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件:"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StartThread02 s1 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "1.png");
StartThread02 s2 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "2.png");
StartThread02 s3 = new StartThread02("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "3.png");
new Thread(s1).start();
new Thread(s2).start();
new Thread(s3).start();
}
}
//下载器 在项目中导入这样一个io工具包-->"commons-io-2.11.0.jar"
class WebDownLoader {
public void downLode(String url, String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));//io工具包为我们提供了这样一个下载文件的方法
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO异常,下载失败");
}
}
}
继承Runnable接口,可以多个线程同时操作一个对象,模拟一下抢火车票的例子
//模拟一下抢火车票
//继承Runnable接口,可以多个线程同时操作一个对象
public class StartThread05 implements Runnable{
//假设有10张票
int ticketNums=10;
//重写run方法
@Override
public void run() {
//只要票数大于0,就执行抢票
while(true){
if(ticketNums<=0){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");//Thread.currentThread().getName()获取线程名字
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StartThread05 startThread05 = new StartThread05();
//多个线程操作一个对象
new Thread(startThread05,"小明").start();
new Thread(startThread05,"老师").start();
new Thread(startThread05,"黄牛党").start();
}
}
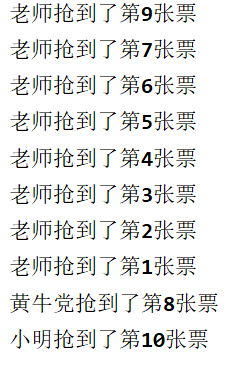
可见老师手速极快,10张票他抢走了8张,这时候可以在while循环中添加一个模拟延时
//模拟延时
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
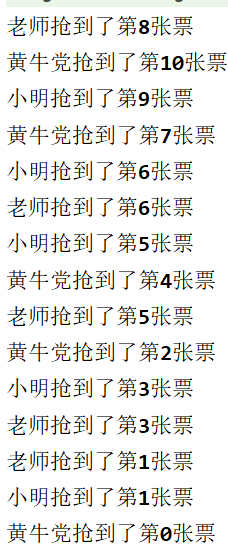
然后就发现。。。。。。有点问题
多个线程操作同一个对象的情况下,数据不安全了,数据紊乱,
这时候,就需要解决一下并发问题
多线程模拟龟兔赛跑
//多线程模拟龟兔赛跑
public class Race implements Runnable {
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
//比赛100米
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
boolean flag = gameOver(i);
if (flag == true) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "跑了" + i + "米");
}
}
}
//判断是否有胜利者
public boolean gameOver(int distance) {
if(winner!=null){
return true;
}
if (distance >= 100) {
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("哦哦哦" + winner + "赢了");
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race=new Race();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
}
}
3、继承callable接口,重写call方法,返回一个布尔值
还是用一下下载图片的例子,效果是一样的
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
//创建线程方法3:继承callable接口,重写call方法,返回一个boolean类型值
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String url;
private String name;
public TestCallable(String url,String name) {
this.url=url;
this.name=name;
}
//重写的是call方法,返回值为boolean类型
@Override
public Boolean call() {
WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader();
webDownLoader.downLode(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件:"+name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t1 = new TestCallable("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "1.png");
TestCallable t2 = new TestCallable("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "2.png");
TestCallable t3 = new TestCallable("https://fc1tn.baidu.com/it/u=2315837439,1898534895&fm=202&mola=new&crop=v1", "3.png");
//1、创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//2、提交服务
Future<Boolean> sb1 = ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> sb2 = ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> sb3 = ser.submit(t3);
//3、获取结果
Boolean r1 = sb1.get();
Boolean r2 = sb2.get();
Boolean r3 = sb3.get();
//4、关闭服务
ser.shutdown();
}
}
//下载器 在项目中导入这样一个io工具包-->"commons-io-2.11.0.jar"
class WebDownLoader {
public void downLode(String url, String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));//io工具包为我们提供了这样一个下载文件的方法
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO异常,下载失败");
}
}
}
执行线程的四个步骤
//1、创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//2、提交服务
Future<Boolean> sb1 = ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> sb2 = ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> sb3 = ser.submit(t3);
//3、获取结果:会返回三个布尔值
Boolean r1 = sb1.get();
Boolean r2 = sb2.get();
Boolean r3 = sb3.get();
//4、关闭服务
ser.shutdown();
线程池























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








