0、直接使用
单通道图片计算指标代码看2.2
三通道图片计算指标代码看2.3
1、PSNR,SSIM的知识点讲解、原理分析
1.1 PSNR
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio 峰值信噪比 单位为 d B dB dB
给定一个大小为
m
×
n
m \times n
m×n的干净图像
I
I
I和噪声图像
K
K
K,均方误差
M
S
E
MSE
MSE定义为:
M
S
E
=
1
m
n
∑
i
=
0
m
−
1
∑
j
=
0
n
−
1
[
I
(
i
,
j
)
−
K
(
i
,
j
)
]
2
M S E=\frac{1}{m n} \sum_{i=0}^{m-1} \sum_{j=0}^{n-1}[I(i, j)-K(i, j)]^{2}
MSE=mn1i=0∑m−1j=0∑n−1[I(i,j)−K(i,j)]2
然后
P
S
N
R
PSNR
PSNR就定义为:
P
S
N
R
=
10
⋅
log
10
(
M
A
X
I
2
M
S
E
)
或
者
P
S
N
R
=
20
⋅
log
10
(
M
A
X
I
M
S
E
)
P S N R=10 \cdot \log _{10}\left(\frac{M A X_{I}^{2}}{M S E}\right)\\ 或者\\ P S N R=20 \cdot \log _{10}\left(\frac{M A X_{I}}{\sqrt{M S E}}\right)
PSNR=10⋅log10(MSEMAXI2)或者PSNR=20⋅log10(MSEMAXI)
其中
M
A
X
I
2
M A X_{I}^{2}
MAXI2为图片可能的最大像素值。如果每个像素都由 8 位二进制来表示,那么就为 255。通常,如果像素值由位
B
B
B二进制来表示,那么
M
A
X
I
=
2
B
−
1
M A X_{I}=2^{B}-1
MAXI=2B−1。
一般地,针对 uint8 数据,最大像素值为 255;针对浮点型数据,最大像素值为 1。
上面是针对灰度图像的计算方法,如果是彩色图像,通常有三种方法来计算。其中,第二和第三种方法比较常见。
- 分别计算 RGB 三个通道的 PSNR,然后取平均值。
- 计算 RGB 三通道的 MSE ,然后再除以 3 。
- 将图片转化为 YCbCr 格式,然后只计算 Y 分量也就是亮度分量的 PSNR。
针对超光谱图像,我们需要针对不同波段分别计算 P S N R PSNR PSNR,然后取平均值,这个指标称为 M P S N R MPSNR MPSNR。
1.2 SSIM
Structural SIMilarity 结构相似性
S
S
I
M
SSIM
SSIM公式基于样本
x
x
x和之
y
y
y间的三个比较衡量:亮度 (luminance)、对比度 (contrast) 和结构 (structure)。
l
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
μ
x
μ
y
+
c
1
μ
x
2
+
μ
y
2
+
c
1
c
(
x
,
y
)
=
2
σ
x
σ
y
+
c
2
σ
x
2
+
σ
y
2
+
c
2
s
(
x
,
y
)
=
σ
x
y
+
c
3
σ
x
σ
y
+
c
3
l(x, y)=\frac{2 \mu_{x} \mu_{y}+c_{1}}{\mu_{x}^{2}+\mu_{y}^{2}+c_{1}}\\c(x, y)=\frac{2 \sigma_{x} \sigma_{y}+c_{2}}{\sigma_{x}^{2}+\sigma_{y}^{2}+c_{2}}\\s(x, y)=\frac{\sigma_{x y}+c_{3}}{\sigma_{x} \sigma_{y}+c_{3}}
l(x,y)=μx2+μy2+c12μxμy+c1c(x,y)=σx2+σy2+c22σxσy+c2s(x,y)=σxσy+c3σxy+c3
一般取
c
3
=
c
2
/
2
c_{3}=c_{2} / 2
c3=c2/2。
- μ x \mu_x μx为 x x x的均值
- μ y \mu_y μy为 y y y的均值
- σ x 2 \sigma_x^2 σx2为 x x x的方差
- σ y 2 \sigma_y^2 σy2为 y y y的方差
- σ x y \sigma_{xy} σxy为 x x x和 y y y的协方差
- c 1 = ( k 1 L ) 2 , c 2 = ( k 2 L ) 2 c_{1}=\left(k_{1} L\right)^{2}, c_{2}=\left(k_{2} L\right)^{2} c1=(k1L)2,c2=(k2L)2为两个常数,避免除零
- L L L为像素值的范围, 2 B − 1 2^B-1 2B−1
- k 1 = 0.01 , k 2 = 0.03 k_{1}=0.01, k_{2}=0.03 k1=0.01,k2=0.03为默认值
那么
S
S
I
M
(
x
,
y
)
=
[
l
(
x
,
y
)
α
⋅
c
(
x
,
y
)
β
⋅
s
(
x
,
y
)
γ
]
S S I M(x, y)=\left[l(x, y)^{\alpha} \cdot c(x, y)^{\beta} \cdot s(x, y)^{\gamma}\right]
SSIM(x,y)=[l(x,y)α⋅c(x,y)β⋅s(x,y)γ]
将
α
,
β
,
γ
\alpha, \beta, \gamma
α,β,γ设为1,可以得到
S
S
I
M
(
x
,
y
)
=
(
2
μ
x
μ
y
+
c
1
)
(
2
σ
x
y
+
c
2
)
(
μ
x
2
+
μ
y
2
+
c
1
)
(
σ
x
2
+
σ
y
2
+
c
2
)
S S I M(x, y)=\frac{\left(2 \mu_{x} \mu_{y}+c_{1}\right)\left(2 \sigma_{x y}+c_{2}\right)}{\left(\mu_{x}^{2}+\mu_{y}^{2}+c_{1}\right)\left(\sigma_{x}^{2}+\sigma_{y}^{2}+c_{2}\right)}
SSIM(x,y)=(μx2+μy2+c1)(σx2+σy2+c2)(2μxμy+c1)(2σxy+c2)
每次计算的时候都从图片上取一个
N
×
N
N×N
N×N的窗口,然后不断滑动窗口进行计算,最后取平均值作为全局的 SSIM。
对于多通道的SSIM
- 分别计算 RGB 各个通道上的 PSNR\SSIM均值,然后取平均值(除以3)。
- 将图像转换为YCbCr格式,然后只计算Y分量(亮度分量)的PSNR\SSIM。
针对超光谱图像,我们需要针对不同波段分别计算 SSIM,然后取平均值,这个指标称为 MSSIM。
2、计算代码
2.1 看一下skimage的源码
def peak_signal_noise_ratio(image_true, image_test, *, data_range=None):
"""
Compute the peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) for an image.
Parameters
----------
image_true : ndarray
Ground-truth image, same shape as im_test.
image_test : ndarray
Test image.
data_range : int, optional
The data range of the input image (distance between minimum and
maximum possible values). By default, this is estimated from the image
data-type.
Returns
-------
psnr : float
The PSNR metric.
Notes
-----
.. versionchanged:: 0.16
This function was renamed from ``skimage.measure.compare_psnr`` to
``skimage.metrics.peak_signal_noise_ratio``.
References
----------
.. [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peak_signal-to-noise_ratio
"""
check_shape_equality(image_true, image_test)
if data_range is None:
if image_true.dtype != image_test.dtype:
warn("Inputs have mismatched dtype. Setting data_range based on "
"image_true.")
dmin, dmax = dtype_range[image_true.dtype.type]#在dtype_range这个字典中会存储不同numpy类型所对应的可能去到的最大最小值 这个字典在下面一代码中
true_min, true_max = np.min(image_true), np.max(image_true)
if true_max > dmax or true_min < dmin:
raise ValueError(
"image_true has intensity values outside the range expected "
"for its data type. Please manually specify the data_range.")
# 真实图片最小值是不是会取到负的
# 针对无符号整型 dmin, dmax 为0,255 data_range为255
# 针对无符号整型 dmin, dmax 为-1,1 data_range为1
if true_min >= 0:
# most common case (255 for uint8, 1 for float)
data_range = dmax
else:
data_range = dmax - dmin
image_true, image_test = _as_floats(image_true, image_test)
err = mean_squared_error(image_true, image_test)
return 10 * np.log10((data_range ** 2) / err)
字典代码
dtype_range = {bool: (False, True),
np.bool_: (False, True),
np.bool8: (False, True),
float: (-1, 1),
np.float_: (-1, 1),
np.float16: (-1, 1),
np.float32: (-1, 1),
np.float64: (-1, 1)}
dtype_range.update(_integer_ranges)#还补充了整型数据的取值范围 实际取值我算了一下是
测试一下这个dtype_range
image = image.astype(np.uint8)
print("数据类型:",type(image))
print("数据结构:",image.dtype)
print("最大最小值:",dtype_range[image.dtype.type])

image = image.astype(np.float64)
print("数据类型:",type(image))
print("数据结构:",image.dtype)
print("最大最小值:",dtype_range[image.dtype.type])

2.2 实际使用情况1:单通道情况
用这两张图片进行计算举例


尽可能将输入转化为
数据类型为uint8,范围为0-255的图像image1,image2
数据类型为float64,范围为0-1.0的图像image1,image2
错误示范:输入不符合标准
float64 对应的范围应该归一化到0-1,判断的时候会出错报错说你的范围超过了数据类型所对应的范围
from skimage.metrics import peak_signal_noise_ratio
from skimage.metrics import structural_similarity
import skimage.io as io
image_path1 = "./1.png"
image_path2 = "./2.png"
# 因为是张彩色图片所以截取出一个通道
image1 = io.imread(image_path1)[...,0]
image2 = io.imread(image_path2)[...,0]
image1 = image1/1.0
image2 = image2/1.0
# 至此image1为float64 且0-255.0 就会报错
print(image1.dtype)
psnr_val = peak_signal_noise_ratio(image1, image2)
ssim_val = structural_similarity(image1,image2,win_size=11,gaussian_weights=True,multichannel=True,data_range=1.0,K1=0.01,K2=0.03,sigma=1.5)
print("psnr_val",psnr_val)
print("ssim_val",ssim_val)
Windows 下面的报错是这样的

Linux下面的报错是这样的

正确示例:数据类型为uint8,范围为0-255的图像image1,image2
注意range应该设置为255
from skimage.metrics import peak_signal_noise_ratio
from skimage.metrics import structural_similarity
import skimage.io as io
image_path1 = "./1.png"
image_path2 = "./2.png"
# 因为是张彩色图片所以截取出一个通道
image1 = io.imread(image_path1)[...,0]
image2 = io.imread(image_path2)[...,0]
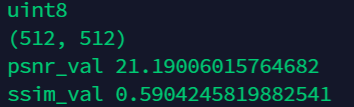
print(image1.dtype)# uint8 范围0-255
print(image1.shape)
psnr_val = peak_signal_noise_ratio(image1, image2)
ssim_val = structural_similarity(image1,image2,win_size=11,gaussian_weights=True,multichannel=False,data_range=255,K1=0.01,K2=0.03,sigma=1.5)
print("psnr_val",psnr_val)
print("ssim_val",ssim_val)
这里需要注意一个问题
如果图像已经是单通道了请记得一定要把multichannel关掉我下面举两个例子
(1)multichannel=True

(2)multichannel=False
为什么说我们后面一种方式是对的呢。我对图片进行了生维度,让他有了通道维度并且维度为1,的时候把multichannel打开
image1 = image1[:,:,np.newaxis]
image2 = image2[:,:,np.newaxis]
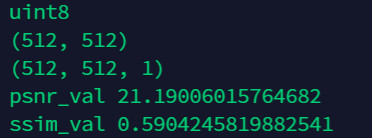
注意ssim在两种情况下是不一样的,如果打开了multichannel 他就会默认第二个维度是通道,也就是裁剪成一个一个小条形,然后进行计算之后求平均
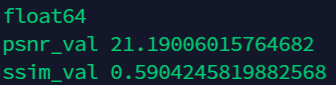
正确示例:数据类型为float64,范围为0-1.0的图像image1,image2
注意range应该设置为1.0
from skimage.metrics import peak_signal_noise_ratio
from skimage.metrics import structural_similarity
import skimage.io as io
image_path1 = "./1.png"
image_path2 = "./2.png"
image1 = io.imread(image_path1)[...,0]
image2 = io.imread(image_path2)[...,0]
image1 = image1/1.0
image2 = image2/1.0
# 至此image1为float64 且0-255.0
# 归一化到0-1.0
image1 = image1/255.0
image2 = image2/255.0
print(image1.dtype)
psnr_val = peak_signal_noise_ratio(image1, image2)
ssim_val = structural_similarity(image1,image2,win_size=11,gaussian_weights=True,multichannel=False,data_range=1.0,K1=0.01,K2=0.03,sigma=1.5)
print("psnr_val",psnr_val)
print("ssim_val",ssim_val)
2.3 实际使用情况2:RGB三通道
需要先转换成YCbCr空间然后对亮度进行求解PSNR,转换方法可以参照我的另一篇博客
RGB图像转换成YCbCr图像,rgb2ycbcr的使用,转换参数_呆呆象呆呆的博客-CSDN博客
同时也要保证数值范围和数值类型要相符合,尽可能将输入转化为
数据类型为uint8,范围为0-255的图像image1,image2(不太推荐因为算出Y通道后,大概率都是浮点型的数据,强行转换成uint8这样精度会下降,所以比较推荐下面一种方式)
数据类型为float64,范围为0-1.0的图像image1,image2
正确示例1:使用rgb2ycbcr计算Y通道后求PSNR或者SSIM
from skimage.metrics import peak_signal_noise_ratio
from skimage.metrics import structural_similarity
import skimage.io as io
import numpy as np
image_path1 = "./1.png"
image_path2 = "./2.png"
# 因为是张彩色图片 所以选一个通道
image1 = io.imread(image_path1)
image2 = io.imread(image_path2)
#我认为最简单的方法
image1 = image1/255.0
image2 = image2/255.0
image1 = 65.481 * image1[:,:,0] + 128.553 * image1[:,:,1] + 24.966 * image1[:,:,2] + 16 # 不加16是因为之后会抵消(计算PSNR的时候可以不加,但是SSIM需要加上)
image2 = 65.481 * image2[:,:,0] + 128.553 * image2[:,:,1] + 24.966 * image2[:,:,2] + 16
image1 = image1/255.0
image2 = image2/255.0
# 只计算Y通道的值
print(image1.dtype)
image1 = np.expand_dims(image1,axis=2)
image2 = np.expand_dims(image2,axis=2)# 为什么要升维度,因为structural_similarity默认输入shape最后一个为通道数量,如果不加上的话,他求解的ssim就会是[H*W]所有[H*1]这样小图片的平均值源码地址可以参考本文备注的ssim源码 中间搜索变量 nch 就能发现
print(image1.shape)
psnr_val = peak_signal_noise_ratio(image1, image2)
ssim_val = structural_similarity(image1,image2,win_size=11,gaussian_weights=True,multichannel=False,data_range=1.0,K1=0.01,K2=0.03,sigma=1.5)
print("psnr_val",psnr_val)
print("ssim_val",ssim_val)
三通道转换成Y通道后的PSNR和上面一个例子中单通道的PSNR肯定是不一样的

正确示例2:直接计算Y通道后求PSNR或者SSIM
from skimage.metrics import peak_signal_noise_ratio
from skimage.metrics import structural_similarity
from skimage.color import rgb2ycbcr
import skimage.io as io
image_path1 = "./1.png"
image_path2 = "./2.png"
image1 = io.imread(image_path1)
image2 = io.imread(image_path2)
# rgb2ycbcr的输入需要归一化到0-1.0的float
#这个在上一篇blog中讲过了rgb2ycbcr输出为浮点型且范围是0-255.0 所以需要再次归一化0-1
image1 = image1/255.0
image2 = image2/255.0
image1 = rgb2ycbcr(image1)[:, :, 0:1]
image2 = rgb2ycbcr(image2)[:, :, 0:1]
image1 = image1/255.0
image2 = image2/255.0
print(image1.dtype)
print(image1.shape)
psnr_val = peak_signal_noise_ratio(image1, image2)
ssim_val = structural_similarity(image1,image2,win_size=11,gaussian_weights=True,multichannel=True,data_range=1.0,K1=0.01,K2=0.03,sigma=1.5)
print("psnr_val",psnr_val)
print("ssim_val",ssim_val)

LAST、参考文献
scikit-image/simple_metrics.py at main · scikit-image/scikit-image · GitHub
PSNR与SSIM对于彩色图像和灰度图像的计算区别_风雪夜归人o的博客-CSDN博客
图像质量的客观评估指标PSNR与SSIM_小村长技术blog-CSDN博客
备注 SSIM的源码
摘录于 https://github.com/scikit-image/scikit-image/blob/main/skimage/metrics/_structural_similarity.py
from warnings import warn
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import uniform_filter, gaussian_filter
from ..util.dtype import dtype_range
from ..util.arraycrop import crop
from .._shared.utils import warn, check_shape_equality
__all__ = ['structural_similarity']
def structural_similarity(im1, im2,
*,
win_size=None, gradient=False, data_range=None,
multichannel=False, gaussian_weights=False,
full=False, **kwargs):
"""
Compute the mean structural similarity index between two images.
Parameters
----------
im1, im2 : ndarray
Images. Any dimensionality with same shape.
win_size : int or None, optional
The side-length of the sliding window used in comparison. Must be an
odd value. If `gaussian_weights` is True, this is ignored and the
window size will depend on `sigma`.
gradient : bool, optional
If True, also return the gradient with respect to im2.
data_range : float, optional
The data range of the input image (distance between minimum and
maximum possible values). By default, this is estimated from the image
data-type.
multichannel : bool, optional
If True, treat the last dimension of the array as channels. Similarity
calculations are done independently for each channel then averaged.
gaussian_weights : bool, optional
If True, each patch has its mean and variance spatially weighted by a
normalized Gaussian kernel of width sigma=1.5.
full : bool, optional
If True, also return the full structural similarity image.
Other Parameters
----------------
use_sample_covariance : bool
If True, normalize covariances by N-1 rather than, N where N is the
number of pixels within the sliding window.
K1 : float
Algorithm parameter, K1 (small constant, see [1]_).
K2 : float
Algorithm parameter, K2 (small constant, see [1]_).
sigma : float
Standard deviation for the Gaussian when `gaussian_weights` is True.
Returns
-------
mssim : float
The mean structural similarity index over the image.
grad : ndarray
The gradient of the structural similarity between im1 and im2 [2]_.
This is only returned if `gradient` is set to True.
S : ndarray
The full SSIM image. This is only returned if `full` is set to True.
Notes
-----
To match the implementation of Wang et. al. [1]_, set `gaussian_weights`
to True, `sigma` to 1.5, and `use_sample_covariance` to False.
.. versionchanged:: 0.16
This function was renamed from ``skimage.measure.compare_ssim`` to
``skimage.metrics.structural_similarity``.
References
----------
.. [1] Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., & Simoncelli, E. P.
(2004). Image quality assessment: From error visibility to
structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
13, 600-612.
https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~z70wang/publications/ssim.pdf,
:DOI:`10.1109/TIP.2003.819861`
.. [2] Avanaki, A. N. (2009). Exact global histogram specification
optimized for structural similarity. Optical Review, 16, 613-621.
:arxiv:`0901.0065`
:DOI:`10.1007/s10043-009-0119-z`
"""
check_shape_equality(im1, im2)
if multichannel:
# loop over channels
args = dict(win_size=win_size,
gradient=gradient,
data_range=data_range,
multichannel=False,
gaussian_weights=gaussian_weights,
full=full)
args.update(kwargs)
nch = im1.shape[-1]
mssim = np.empty(nch)
if gradient:
G = np.empty(im1.shape)
if full:
S = np.empty(im1.shape)
for ch in range(nch):
ch_result = structural_similarity(im1[..., ch],
im2[..., ch], **args)
if gradient and full:
mssim[..., ch], G[..., ch], S[..., ch] = ch_result
elif gradient:
mssim[..., ch], G[..., ch] = ch_result
elif full:
mssim[..., ch], S[..., ch] = ch_result
else:
mssim[..., ch] = ch_result
mssim = mssim.mean()
if gradient and full:
return mssim, G, S
elif gradient:
return mssim, G
elif full:
return mssim, S
else:
return mssim
K1 = kwargs.pop('K1', 0.01)
K2 = kwargs.pop('K2', 0.03)
sigma = kwargs.pop('sigma', 1.5)
if K1 < 0:
raise ValueError("K1 must be positive")
if K2 < 0:
raise ValueError("K2 must be positive")
if sigma < 0:
raise ValueError("sigma must be positive")
use_sample_covariance = kwargs.pop('use_sample_covariance', True)
if gaussian_weights:
# Set to give an 11-tap filter with the default sigma of 1.5 to match
# Wang et. al. 2004.
truncate = 3.5
if win_size is None:
if gaussian_weights:
# set win_size used by crop to match the filter size
r = int(truncate * sigma + 0.5) # radius as in ndimage
win_size = 2 * r + 1
else:
win_size = 7 # backwards compatibility
if np.any((np.asarray(im1.shape) - win_size) < 0):
raise ValueError(
"win_size exceeds image extent. If the input is a multichannel "
"(color) image, set multichannel=True.")
if not (win_size % 2 == 1):
raise ValueError('Window size must be odd.')
if data_range is None:
if im1.dtype != im2.dtype:
warn("Inputs have mismatched dtype. Setting data_range based on "
"im1.dtype.", stacklevel=2)
dmin, dmax = dtype_range[im1.dtype.type]
data_range = dmax - dmin
ndim = im1.ndim
if gaussian_weights:
filter_func = gaussian_filter
filter_args = {'sigma': sigma, 'truncate': truncate}
else:
filter_func = uniform_filter
filter_args = {'size': win_size}
# ndimage filters need floating point data
im1 = im1.astype(np.float64)
im2 = im2.astype(np.float64)
NP = win_size ** ndim
# filter has already normalized by NP
if use_sample_covariance:
cov_norm = NP / (NP - 1) # sample covariance
else:
cov_norm = 1.0 # population covariance to match Wang et. al. 2004
# compute (weighted) means
ux = filter_func(im1, **filter_args)
uy = filter_func(im2, **filter_args)
# compute (weighted) variances and covariances
uxx = filter_func(im1 * im1, **filter_args)
uyy = filter_func(im2 * im2, **filter_args)
uxy = filter_func(im1 * im2, **filter_args)
vx = cov_norm * (uxx - ux * ux)
vy = cov_norm * (uyy - uy * uy)
vxy = cov_norm * (uxy - ux * uy)
R = data_range
C1 = (K1 * R) ** 2
C2 = (K2 * R) ** 2
A1, A2, B1, B2 = ((2 * ux * uy + C1,
2 * vxy + C2,
ux ** 2 + uy ** 2 + C1,
vx + vy + C2))
D = B1 * B2
S = (A1 * A2) / D
# to avoid edge effects will ignore filter radius strip around edges
pad = (win_size - 1) // 2
# compute (weighted) mean of ssim
mssim = crop(S, pad).mean()
if gradient:
# The following is Eqs. 7-8 of Avanaki 2009.
grad = filter_func(A1 / D, **filter_args) * im1
grad += filter_func(-S / B2, **filter_args) * im2
grad += filter_func((ux * (A2 - A1) - uy * (B2 - B1) * S) / D,
**filter_args)
grad *= (2 / im1.size)
if full:
return mssim, grad, S
else:
return mssim, grad
else:
if full:
return mssim, S
else:
return mssim
























 690
690

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








