一,什么是迭代器
迭代器是一种Collection 集合遍历的接口,而实现该接口的类被称之为迭代类。
二,ListIterator
源码上ListIterator继承了Iterator,JDK8的源码中这样说道:An iterator for lists that allows the programmer ....,这是一个提供给我们专门遍历List集合的迭代接口。
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
// Query Operations三,迭代的一些概念
这里引用了Iterator详解这篇文章中的概念,图形化说明很清晰直白。
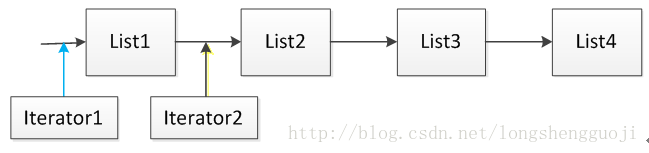
在使用java集合的时候,都需要使用Iterator。但是java集合中还有一个迭代器ListIterator,在使用List、ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector的时候可以使用。这两种迭代器有什么区别呢?下面我们详细分析。这里有一点需要明确的时候,迭代器指向的位置是元素之前的位置,如下图所示:
这里假设集合List由四个元素List1、List2、List3和List4组成,当使用语句Iterator it = List.Iterator()时,迭代器it指向的位置是上图中Iterator1指向的位置,当执行语句it.next()之后,迭代器指向的位置后移到上图Iterator2所指向的位置。
四,区别
之前已经提到过了ListIterator 继承了 Iterator ,继承的概念我这里就不多加赘述了。比较下到LIstIterator后,新增了那些原本父类没有的方法
A、hasPrevious()
用注解的话来说,这个方法用来对于从相反的方向去遍历这个list集合,如果前面仍然有元素,那么返回True,反之为false.
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the reverse direction. (In other words,
* returns {@code true} if {@link #previous} would return an element
* rather than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return {@code true} if the list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the reverse direction
*/
boolean hasPrevious();B、nexIndex()
用来返回下一个元素在List集合中的索引
/**
* Returns the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@link #next}. (Returns list size if the list
* iterator is at the end of the list.)
*
* @return the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@code next}, or list size if the list
* iterator is at the end of the list
*/
int nextIndex();C、previousIndex() & pervious()
用来返回前一个元素和前一个元素在集合List中的索引
/**
* Returns the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@link #previous}. (Returns -1 if the list
* iterator is at the beginning of the list.)
*
* @return the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@code previous}, or -1 if the list
* iterator is at the beginning of the list
*/
int previousIndex();
/**
* Returns the previous element in the list and moves the cursor
* position backwards. This method may be called repeatedly to
* iterate through the list backwards, or intermixed with calls to
* {@link #next} to go back and forth. (Note that alternating calls
* to {@code next} and {@code previous} will return the same
* element repeatedly.)
*
* @return the previous element in the list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no previous
* element
*/
E previous();D、set() & remove()
需要说明的是,remove()方法在Iterator中只是用来移除next()后指向的元素,但这里的remove方法可以用来移除previous指向的元素。这里的set()方法是用来替换next / previous指向的元素
/**
* Removes from the list the last element that was returned by {@link
* #next} or {@link #previous} (optional operation). This call can
* only be made once per call to {@code next} or {@code previous}.
* It can be made only if {@link #add} has not been
* called after the last call to {@code next} or {@code previous}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove}
* operation is not supported by this list iterator
* @throws IllegalStateException if neither {@code next} nor
* {@code previous} have been called, or {@code remove} or
* {@code add} have been called after the last call to
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
*/
void remove();
/**
* Replaces the last element returned by {@link #next} or
* {@link #previous} with the specified element (optional operation).
* This call can be made only if neither {@link #remove} nor {@link
* #add} have been called after the last call to {@code next} or
* {@code previous}.
*
* @param e the element with which to replace the last element returned by
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code set} operation
* is not supported by this list iterator
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some aspect of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalStateException if neither {@code next} nor
* {@code previous} have been called, or {@code remove} or
* {@code add} have been called after the last call to
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
*/
void set(E e);E、add()
对next \ previous 指向的位置插入新的元素
/**
* Inserts the specified element into the list (optional operation).
* The element is inserted immediately before the element that
* would be returned by {@link #next}, if any, and after the element
* that would be returned by {@link #previous}, if any. (If the
* list contains no elements, the new element becomes the sole element
* on the list.) The new element is inserted before the implicit
* cursor: a subsequent call to {@code next} would be unaffected, and a
* subsequent call to {@code previous} would return the new element.
* (This call increases by one the value that would be returned by a
* call to {@code nextIndex} or {@code previousIndex}.)
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code add} method is
* not supported by this list iterator
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some aspect of this element
* prevents it from being added to this list
*/
void add(E e);
总结:
之前有分析过save-fail , ArrayList的源码, 在每次对集合容器操作时都会对modCount++ ,通过modCount的值变化,两次判断是否在遍历的时候修改了容器的内容。当然这种方式也有说过了,是不能达到绝对线程安全的地步的,只是尽可能的把unmodifyCollectionException异常给抛出来提醒开发者。ListIterator的好处就在于相对于Iterator,它又不仅仅只是遍历了,它还有操作集合的方法。在遍历的过程中通过类似于“链表”的方式,next()指向来修改集合中的内容。






















 130
130











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








