第2关:LL parser
本关任务:用C/C++编写一个LL(1)解析器
相关知识
为了完成本关任务,你需要掌握:
- LL文法
- C/C++ 编程语言基础
- C语言的基本结构知识
LL(1)解析器
在创建解析器之前,你应该创建一个下面文法的LL(1)分析表。
C/C++
本实训涉及函数、结构体,标准流输入输出,字符串等操作
实验要求
实验文法定义
program -> compoundstmt
stmt -> ifstmt | whilestmt | assgstmt | compoundstmt
compoundstmt -> { stmts }
stmts -> stmt stmts | E
ifstmt -> if ( boolexpr ) then stmt else stmt
whilestmt -> while ( boolexpr ) stmt
assgstmt -> ID = arithexpr ;
boolexpr -> arithexpr boolop arithexpr
boolop -> < | > | <= | >= | ==
arithexpr -> multexpr arithexprprime
arithexprprime -> + multexpr arithexprprime | - multexpr arithexprprime | E
multexpr -> simpleexpr multexprprime
multexprprime -> * simpleexpr multexprprime | / simpleexpr multexprprime | E
simpleexpr -> ID | NUM | ( arithexpr )
起始符
Program
保留字
{ } if ( ) then else while ( ) ID = > < >= <= == + - * / ID NUM E 是'空'
分隔方式
同一行的输入字符用一个空格字符分隔,例如: ID = NUM ; 红色标记为空格
错误处理
本实验需要考虑错误处理,如果程序不正确(包含语法错误),它应该打印语法错误消息(与行号一起),并且程序应该修正错误,并继续解析。
例如:
语法错误,第4行,缺少";"
输入
要求:在同一行中每个输入字符用一个空格字符分隔,无其余无关符号。
样例1输入
{ ID = NUM ; }
样例2输入
{ If E1 then s1 else If E2 Then S2 else S3 }
并没有E1,E2等符号,这只是指代表达式
输出
样例1输出
输出要求:在语法树同一层的叶子节点,在以下格式中有相同的缩进,用tab来控制缩减。如样例所示,相同颜色表示在语法树种他们在同一层。
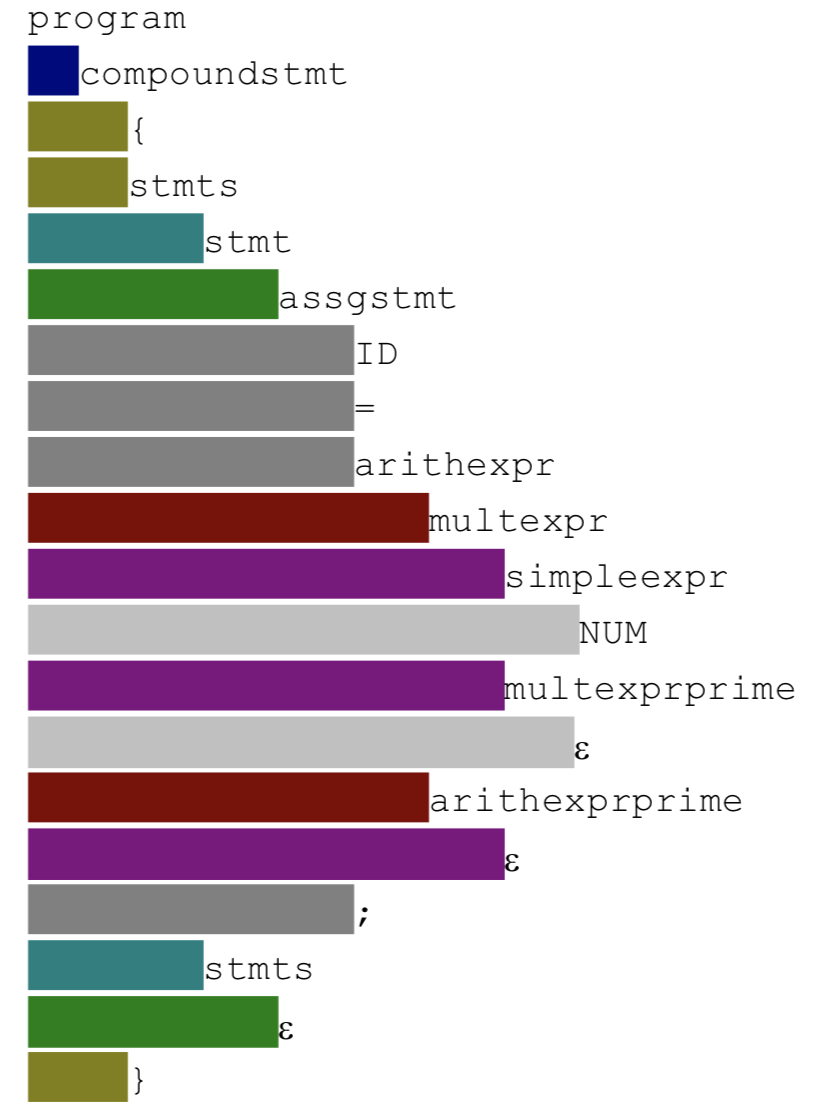
测试集
1
测试输入
{ ID = NUM ; }
预期输出
program
compoundstmt
{
stmts
stmt
assgstmt
ID
=
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
;
stmts
E
}
2
测试输入
{
ID = ID + NUM ;
}
预期输出
program
compoundstmt
{
stmts
stmt
assgstmt
ID
=
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
ID
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
+
multexpr
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
;
stmts
E
}
3
测试输入
{
while ( ID == NUM )
{
ID = NUM
}
}
预期输出
语法错误,第4行,缺少";"
program
compoundstmt
{
stmts
stmt
whilestmt
while
(
boolexpr
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
ID
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
boolop
==
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
)
stmt
compoundstmt
{
stmts
stmt
assgstmt
ID
=
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
;
stmts
E
}
stmts
E
}
4
测试输入
{
if ( ID == ID )
then
ID = NUM ;
else
ID = ID * NUM ;
}
预期输出
program
compoundstmt
{
stmts
stmt
ifstmt
if
(
boolexpr
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
ID
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
boolop
==
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
ID
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
)
then
stmt
assgstmt
ID
=
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
;
else
stmt
assgstmt
ID
=
arithexpr
multexpr
simpleexpr
ID
multexprprime
*
simpleexpr
NUM
multexprprime
E
arithexprprime
E
;
stmts
E
}
代码文件
LLparser.h
// C语言词法分析器
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/* 不要修改这个标准输入函数 */
void read_prog(string& prog)
{
char c;
while(scanf("%c",&c)!=EOF){
prog += c;
}
}
/* 你可以添加其他函数 */
void Analysis()
{
string prog;
read_prog(prog);
/* 请开始 */
/********* Begin *********/
/********* End *********/
}
LLparserMain
#include "LLparser.h"
int main()
{
Analysis();
return 0;
}






















 2058
2058











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








