结构体
基本概念
结构体属于用户自定义的数据类型,允许用户存储不同的数据类型。
结构体的定义和使用
语法
struct 结构体名{ 结构体成员列表 }
结构体的使用
- struct Student s1 (创建结构体对象时struct可以省略,定义时不可以)
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//创建学生数据类型
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
//结构体的定义与使用
//1.struct Student s1 (创建结构体对象时struct可以省略,定义时不可以)
struct Student s1;
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 11;
s1.score = 80;
cout << "学生姓名:" << s1.name << "年龄:" << s1.age << "分数" << s1.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- struct Student s2 = { … };
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//创建学生数据类型
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
//2.struct Student s2 = { .. };
struct Student s2 = { "王五",23,90 };
cout << "学生姓名:" << s2.name << "年龄:" << s2.age << "分数" << s2.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
- 定义结构体时顺便创建
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//创建学生数据类型
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
}s3;//顺便创建结构体
int main() {
//3.顺便创建
s3.name = "李四";
s3.age = 23;
s3.score = 100;
cout << "学生姓名:" << s3.name << "年龄:" << s3.age << "分数" << s3.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体数组
功能
将结构体放在数组中,便于管理
创建结构体数组
struct 结构体 数组名[] = {{},{},{}...};
案例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
//创建结构体数组
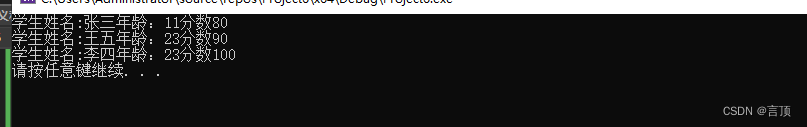
struct Student stuArr[] = { {"张三",24,90},{"李四",23,80} ,{"王五",84,100} };
//遍历结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < size(stuArr); i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << stuArr[i].name << "年龄" << stuArr[i].age << "分数" << stuArr[i].score << endl;
}
//修改结构体数组的元素
stuArr[2].name = "赵六";
stuArr[2].age = 30;
stuArr[2].score = 60;
cout << "修改后的结构体数组:" << endl;
//遍历结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < size(stuArr); i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << stuArr[i].name << "年龄" << stuArr[i].age << "分数" << stuArr[i].score << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:

结构体指针
作用
通过指针访问结构体的成员
访问结构体属性
通过结构体指针访问结构体属性,需要利用“->"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
int main() {
//创建结构体
Student stu = {"王五",84,100} ;
//访问结构体
cout << "直接访问结构体属性:" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄 " << stu.age << " 分数 " << stu.score << endl;
Student* p = &stu;
cout << "通过结构体指针访问结构体属性:" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << p ->name << " 年龄 " << p->age << " 分数 " << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体嵌套结构体
一个结构体里的属性包含一个或多个结构体
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct Teacher {
int id;
string name;
int age;
struct Student stu;
};
int main() {
//创建结构体
Teacher t;
t.id = 10000;
t.name = "老王";
t.age = 60;
Student s1 = { "王五",84,100 };
t.stu = s1;
//访问结构体
cout << "老师的id " << t.id << " 老师的姓名 " << t.name << " 老师的年龄 " << t.age <<
" 老师辅导的学生姓名: " << t.stu.name << " 老师辅导的学生的年龄 " << t.stu.age
<< " 老师辅导学生的成绩 " << t.stu.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:

结构体做函数的参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
//打印学生信息的函数1
void printlnStu1(Student s1) {
s1.age = 100;
cout << " 函数1学生姓名: " << s1.name << " 学生的年龄 " << s1.age
<< " 学生的成绩 " << s1.score << endl;
}
//打印学生信息的函数2
void printlnStu2(Student *p) {
p->age = 100;
cout << " 函数2学生姓名: " << p->name << " 学生的年龄 " << p->age
<< " 学生的成绩 " << p->score << endl;
}
int main() {
//创建结构体
Student s1 = { "王五",34,100 };
//访问结构体
cout <<" 学生姓名: " << s1.name << " 学生的年龄 " <<s1.age
<< " 学生的成绩 " << s1.score << endl;
//值传递
cout << "值传递:" << endl;
printlnStu1(s1);
cout << " 学生姓名: " << s1.name << " 学生的年龄 " << s1.age
<< " 学生的成绩 " << s1.score << endl;
//地址传递
cout << "地址传递:" << endl;
printlnStu2(&s1);
cout << " 学生姓名: " << s1.name << " 学生的年龄 " << s1.age
<< " 学生的成绩 " << s1.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体const使用场景
作用
用const来防止误操作
将函数中的参数改为指针,可以减少内存空间,而且不会新增副本。
由于函数中的参数改为指针则为地址传递,若地址中的数值变化会影响到形参,为了避免误操作。
在将指针作为函数的参数时,可以添加const修饰,若强改地址的值则会报错。
只可以读取地址的值,不能改数据。
案例
需求:结构体数组,以结构体的年龄属性作为排序的条件,按冒泡排序升序排列结构体数组。
# include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct People {
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
void bubbleSort(People p[], int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <len - i - 1; j++) {
if (p[j].age > p[j + 1].age) {
People pTemp = p[j];
p[j] = p[j + 1];
p[j + 1] = pTemp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
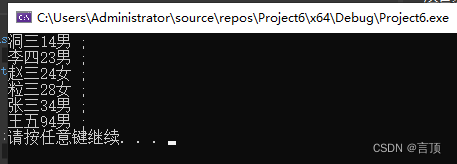
People p[] = { {"张三",34,"男" }, {"李四",23,"男"}, {"王五",94,"男"}, {"赵三",24,"女"}, {"洞三",14,"男"}, {"粒三",28,"女"}};
int len = size(p);
bubbleSort(p,len);
for (int i = 0; i < size(p); i++){
cout << p[i].name << p[i].age << p[i].sex << " ;";
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








