本文内容整理自西安交通大学软件学院李晨老师的课件,仅供学习使用,请勿转载
计算机组成原理系列笔记汇总:计算机组成原理笔记及思维导图汇总附复习建议_Qlz的博客-CSDN博客
文章目录
文章目录
本章思维导图
Brief History of Computer
-
1950 ~ 59 Vacuum tube
-
1960 ~ 68 Transistor
-
1969 ~ 77 Integrated Circuits
-
1978 ~ ? Large-scale integration (LSI) and Very-large-scale integration (VLSI)
-
2009~? Intelligence
Vacuum tube Computer
ENIAC
The first general-purpose computer
-
Can conditional Jump and be programmable, distinguished it from earlier ones
-
Used for computing artillery firing tables
-
Started 1943 and Finished 1946
details
- Decimal (not binary)
- 20 accumulators of 10 digits
- Programmed manually by switches
- 18,000 vacuum tubes
- 30 tons
- 15,000 square feet
- 140 kW power consumption
- 5,000 additions per second
图灵机
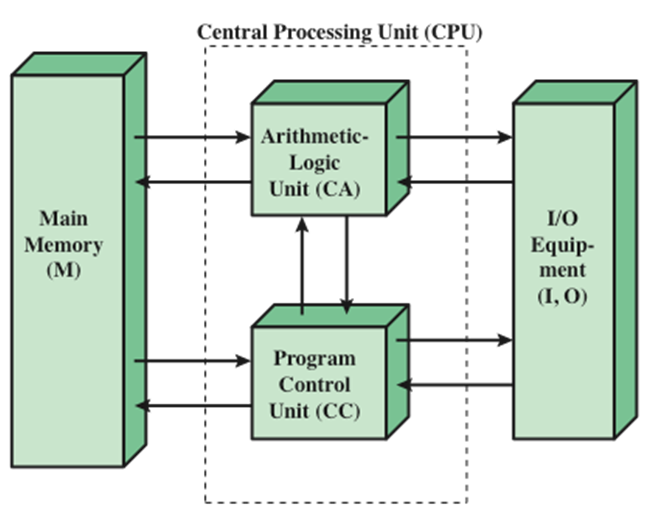
Von Neumann/Turing(IAS)
- Stored program concept
- Begin 1946, but not completed 1952
- Main memory storing programs and data
- ALU operating on binary data
- Control unit interpreting instructions from memory and executing them
- Input and output equipment operated by control unit
- Princeton Institute for Advanced Studies – IAS
Structure of the IAS computer
IAS Memory Formats
- The memory of the IAS consists of 1000 storage locations (called words) of 40 bits each
- Both data and instructions are stored there
- Numbers are represented in binary form and each instruction is a binary code
IAS Registers
- Memory buffer register (MBR)
- Contains a word to be stored in memory or sent to the I/O unit
- Or is used to receive a word from memory or from the I/O unit
- 内存中取出的指令、数据,以及将被送到内存的数据都要经过MBR
- Memory address register (MAR)
- Specifies the address in memory of the word to be written from or read into the MBR
- 将要被操作(取指,取数据,存数据)的地址
- Instruction register (IR)
- Contains the 8-bit opcode instruction being executed
- 正在和执行的8位操作码指令
- Instruction buffer register (IBR)
- Employed to temporarily hold the right-hand instruction from a word in memory
- Program counter (PC)
- Contains the address of the next instruction pair to be fetched from memory
- 下一条将被执行的指令地址
- Accumulator (AC) and multiplier quotient (MQ)
- Employed to temporarily hold operands and results of ALU operations
- AC:暂时存储ALU的计算结果
Expanded structure of IAS computer
首先将PC中的下一条要被执行的指令地址放入MAR中,控制单元根据MAR中的地址取主存中取指令放入MBR中,MBR将左右指令分开,左指令放入IR中,右指令放入IBR中,接下来控制单元对IR中的指令进行解析。产生一系列的控制信号,如果需要操作数据的话,需要将数据的地址放入MAR中,控制单元根据MAR中的地址取主存中寻找对应的数据,并将其放入MBR中,完成后将右指令从IBR中放入IR中,接下来一样的操作,如果需要与I/O进行交互的话需要将数据先放入MBR才可以
IAS Instruction Set
- 21 Instructions
- Data Transfer
- Unconditional Branch
- Conditional Branch
- Arithmetic
- Address Modify
UNIVAC
the Universal Automatic Computer
the first computer company – Electronic Control Corp 第一家计算机公司–电子控制公司。
UNIVAC tasks involve scientific and commercial applications
Transistor Computer
- More complex arithmetic and logic units and control units
- The use of high-level programming languages
- Provision of system software which provided the ability to:
- load programs
- move data to peripherals(外围设备) and libraries
- perform common computations
IC Computer
Integrated Circuits (IC) 集成电路
- SSI & MSI based computer is the 3rd computer
- SSI :small scale integration(小规模集成电路)
- MSI :medium scale integration(中规模集成电路)
Family concept
- Similar or identical instruction set
- Similar or identical operating system
- Increasing speed, increasing number of I/O ports, Increasing memory size and Increasing cost
Transistor, resistance, capacitance made from semiconductor, together with whole circuit can be put in a silicon wafer
晶体管、电阻、电容,以及整个电路都可以放在硅片中
Moore’s Law
1965,Gordon Moore - cofounder of Intel
Number of transistors on a chip will double every year 每两年翻一番
Since 1970’s development has slowed a little ,Number of transistors doubles every 18 months
- Cost of a chip has remained almost unchanged
- Higher packing density means shorter electrical paths, giving higher performance
- Smaller size gives increased flexibility
- Reduced power and cooling requirements
- Fewer interconnections increases reliability
LSI & VLSI Computer
Semiconductor memories(半导体存储)
the first relatively capacious(相对大规模) semiconductor memory(1970, Fairchild)
Quantity and Unit in common use
- Bit – b
- Byte – B: 8bit= 23
- K (Hz, bytes): 1 0 3 10^{3} 103 --1024= 2 10 2^{10} 210
- M: Mega (bytes,Hz): 1 0 6 10^{6} 106 – 102 4 2 1024^{2} 10242= 2 20 2^{20} 220
- G: Giga (bytes,Hz): 1 0 9 10^{9} 109 – 102 4 3 1024^{3} 10243= 2 30 2^{30} 230
- T: tera (bytes,Hz): 1 0 12 10^{12} 1012 – 102 4 4 1024^{4} 10244= 2 40 2^{40} 240
- P: peta (bytes,Hz): 1 0 15 10^{15} 1015 – 102 4 5 1024^{5} 10245= 2 50 2^{50} 250
Designing for Performance
Microprocessor speed
The techniques for meet the CPU speed
- Branch prediction(分支预测)
- Data flow analysis(数据流分析)
- Speculative execution(推测执行)
Other critical components speed lags of CPU’s speed
- CPU has to wait
- Bottleneck
- Reduce the whole performance
- Especially, main memory
Solutions
Optimize system structure, balancing the whole performance of CPU, memory and I/O
- Improve the interface between CPU and memory
- The interface is the key path responsible for transferring instruction and data
- Increase number of bits retrieved at one time
- Make DRAM “wider” rather than “deeper”
- Change DRAM interface
- Cache
- Reduce frequency of memory access
- More complex cache and cache on chip
- Increase interconnection bandwidth
- High speed buses
- Hierarchy of buses
- Caching and buffering schemes(缓存和缓冲机制)
- Higher-speed interconnection buses and more elaborate(复杂) interconnection structures
- Use of multiple-processor configurations can aid in satisfying I/O demands
- Increase hardware speed of processor
- Fundamentally due to shrinking logic gate size
- More gates, packed more tightly, increasing clock rate
- Propagation time for signals reduced
- Fundamentally due to shrinking logic gate size
- Increase size and speed of caches
- Dedicating part of processor chip
- Cache access times drop significantly
- Dedicating part of processor chip
- Change processor organization and architecture
- Increase effective speed of instruction execution
- Parallelism
- Power
- Power density increases with density of logic and clock speed
- Dissipating heat(散热)
- RC delay
- Speed at which electrons flow limited by resistance and capacitance of metal wires connecting them
- Delay increases as RC product increases
- Wire interconnects thinner, increasing resistance
- Wires closer together, increasing capacitance
- Memory latency(内存延迟)
- Memory speeds lag processor speeds
Multicore, MICs and GPGPUs
Multicore(多核)
- The use of multiple processors on the same chip provides the potential to increase performance without increasing the clock rate
- Strategy is to use two simpler processors on the chip rather than one more complex processor
- With two processors larger caches are justified(合理的)
- As caches became larger it made performance sense to create two and then three levels of cache on a chip(多级缓存)
Many Integrated Core (MIC)集成众核
- The Leap(飞跃) in performance as well as the challenges in developing software to exploit(利用) such a large number of cores
- MIC is a software architecture for Co-Processor
- The multicore and MIC strategy involves a homogeneous collection of general purpose processors(通用处理器) on a single chip
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Core designed to perform parallel operations on graphics data
- Traditionally found on a plug-in graphics card, it is used to encode and render(渲染) 2D and 3D graphics as well as process video
- Used as vector processors for a variety of applications that require repetitive computations
- A GPU can support a broad range of applications — GPGPU
- Deep learning
Embedded System and the ARM
Embedded System
- Def.: A combination of computer hardware and software, and perhaps additional mechanical or other parts, designed to perform a dedicated (专用的) function.
- In many cases, embedded systems are part of a larger system or product, as in the case of an antilock braking system in a car.
Acorn RISC Machine (ARM)
- Family of RISC-based microprocessors and microcontrollers
- Designs microprocessor and multicore architectures and licenses them to manufacturers(设计微处理器和多核架构,并将其授权给制造商)
- Chips are high-speed processors that are known for their small die size(小模具尺寸) and low power requirements
- Widely used in PDAs and other handheld devices
- Most widely used processor architecture of any kind
Performance Assessment
Clock frequency
- Operations performed by a processor are governed by a system clock
- Speed of processor is dictated(决定) by the pulse frequency by the system clock, measured in cycles per second(Hz) — clock frequency处理器的速度由系统时钟的脉冲频率决定,以每秒(Hz)为周期测量——时钟频率
- imprecise(不准确的)
Processor time T
- Time needed that a processor execute a given program (执行给定程序耗费的时间)
- T= *CPU clock cycles for a program clock cycle τ
= CPU clock cycles for a program/clock rate - T = C P I × I C × c l o c k c y c l e ( τ ) = C P I × I C / c l o c k r a t e T= CPI ×I_C × clock cycle (τ) = CPI ×I_C / clock rate T=CPI×IC×clockcycle(τ)=CPI×IC/clockrate
- CPI: average cycles per instruction
- I C I_C IC: instruction count
- Influenced by the instruction set architecture, compiler technology, processor implementation and memory hierarchy
Processor Speed
- rate at which instructions are executed, expressed as millions of instructions per second (MIPS)
- referred to as the MIPS rate
M I P S r a t e = I C T × 1 0 6 = f C P I × 1 0 6 MIPS\, rate=\frac{I_C}{T\times 10^6}=\frac{f}{CPI\times 10^6} MIPSrate=T×106IC=CPI×106f
- millions of floating-point instructions per second (MFLOPS)
- For scientific and game application
M F L O P S r a t e = N u m b e r o f e x e c u t e d f l o a t i n g − p o i n t o p e r a t i o n s i n a p r o g r a m E x e c u t i o n t i m e × 1 0 6 MFLOPS \, rate=\frac{Number\, of\, executed\, floating-point\, operations\, in\, a\, program}{Execution\, time \times 10^6} MFLOPSrate=Executiontime×106Numberofexecutedfloating−pointoperationsinaprogram
Benchmark suite(基准程序)
- A collection of programs, defined in a high-level language
- Attempts to provide a representative test of a computer in a particular application or system programming area
Desirable characteristics of a benchmark(基准测试的理想特征)
- Written in a high-level language, making it portable across different machines
- Representative of a particular kind of programming style, such as systems
- programming, numerical programming, or commercial programming
- Measured easily
- Wide distribution
SPEC (Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation)
- An industry consortium(组织)
- Defines and maintains the best known collection of benchmark suites
- Performance measurements are widely used for comparison and research purposes
Amdahl Law
- The improved performance of using a faster execution mode is limited by the fraction of the execution time of faster mode in total execution time 使用更快的执行模式的改进性能受到更快模式在总执行时间中的执行时间的限制
- The improved performance is limited by the frequency of using a faster mode 改进的性能受到使用一个更快的模式的频率的限制
- Amdahl Law defines speed-up that can be gained by using a particular technology
F e = t h e c o m p u t i n g t i m e o f p a r t t h a t c a n b e e n h a n c e d ( 可 以 被 加 速 部 分 的 时 间 ) t o t a l c o m p u t i n g t i m e b e f o r e e n h a n c e d ( 总 时 间 ) ≤ 1 S e = c o m p u t i n g t i m e o f p a r t t h a t c a n b e e n h a n c e d b e f o r e e n h a n c e m e n t ( 加 速 前 耗 费 时 间 ) c o m p u t i n g t i m e o f t h i s p a r t a f t e r e n h a n c e d ( 加 速 后 耗 费 时 间 ) ≥ 1 T 0 : t o t a l t a s k e x e c u t i o n t i m e b e f o r e e n h a n c e m e n t ( 未 被 加 速 前 所 用 总 时 间 ) F_e=\frac{the\,computing\, time\,of\,part\,that\,can\,be\,enhanced(可以被加速部分的时间)}{total\,computing\,time\,before\,enhanced(总时间)}\le1 \\ S_e=\frac{computing\, time\,of\,part\,that\,can\,be\,enhanced\,before\,enhancement(加速前耗费时间)}{computing\, time\,of\,this\,part\,after\,enhanced(加速后耗费时间)}\ge1 \\ T_0:total\,task\,execution\,time\,before\,enhancement(未被加速前所用总时间) Fe=totalcomputingtimebeforeenhanced(总时间)thecomputingtimeofpartthatcanbeenhanced(可以被加速部分的时间)≤1Se=computingtimeofthispartafterenhanced(加速后耗费时间)computingtimeofpartthatcanbeenhancedbeforeenhancement(加速前耗费时间)≥1T0:totaltaskexecutiontimebeforeenhancement(未被加速前所用总时间)
Execution time of total task after enhancement (总时间): T n = T 0 ( 1 − F e ) ( 未 被 加 速 的 部 分 ) + T 0 × F e S e ( 被 加 速 的 部 分 ) T_n=T_0(1-F_e)(未被加速的部分)+T_0\times \frac{F_e}{S_e}(被加速的部分) Tn=T0(1−Fe)(未被加速的部分)+T0×SeFe(被加速的部分)
System speed-up after enhancement(加速率) : S n = T 0 T n ( 加 速 前 总 时 间 比 加 速 后 总 时 间 ) = 1 ( 1 − F e ) + F e S e S_n=\frac{T_0}{T_n}(加速前总时间比加速后总时间)=\frac{1}{(1-F_e)+\frac{F_e}{S_e}} Sn=TnT0(加速前总时间比加速后总时间)=(1−Fe)+SeFe1
Relation between system speed-up and Fe
- When$ F_e=0, S_n=1$, this means no part can be enhanced
- When S e = ∞ , S n = 1 / ( 1 − F e ) S_e=∞, S_n=1/(1-F_e) Se=∞,Sn=1/(1−Fe)
- So, the system performance enhancement is strongly limited by F e F_e Fe
example:
Suppose that a task makes extensive use of floating-point operation, with 40% of the time is consumed by floating-point operations. With a new hardware design, the floating-point module is speeded up by a factor of K. what is the overall speedup gained by this enhancement?
Solutions:
F e = 0.4 , S e = k F_e=0.4,S_e=k Fe=0.4,Se=k
S n = 1 ( 1 − F e ) + F e S e = 1 0.6 + 0.4 K S_n=\frac{1}{(1-F_e)+\frac{F_e}{S_e}}=\frac{1}{0.6+\frac{0.4}{K}} Sn=(1−Fe)+SeFe1=0.6+K0.41
while S e = ∞ , S n = 1.67 ( 优 化 到 极 致 ) S_e=\infty,S_n=1.67(优化到极致) Se=∞,Sn=1.67(优化到极致)
Vocabulary
-
Pipelining and parallel execution: 流水与并行执行
-
Speculative execution: 推测执行
-
Cache: 快速缓存
-
Decimal: 十进制
-
Binary: 二进制
-
General purpose computer: 通用计算机
-
Von Neumann Machine: 冯-诺依曼计算机
-
Opcode=operation code: 操作码
-
Instruction cycle: 指令周期
-
Fetch cycle: 取(读)周期
-
Flowchart: 流程图
-
Condition branch: 条件转移
-
Data transfer: 数据传送
-
Upward compatible: 向上兼容
-
Multiplexor: 复用器
-
Bus: 总线
-
Magnetic-core memory: 磁芯存储器
-
End user: 端用户
-
Speech recognition: 语音识别
-
Videoconferencing: 视频会议
-
Multimedia authoring: 多媒体编著
-
Workstation: 工作站
-
Client-server: 客户机-服务器
-
DRAM—dynamic random access memory: 动态随机存取存储器
-
Branch prediction: 转移预测
-
Throughput: 吞吐率
-
Trade-off : 折衷
-
Supercomputer: 超级计算机/巨型机
-
Parallelism: 并行性
Key points
- What is the first computer in the world?
- What features of von Nuemann machine is there? How about its structure?
- Moore law?
- What is multicore, MICs and GPU?
- CPI, I c I_c Ic, T, MIPS, MFLOPS
- Amdahl Law























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










