验证回文串
如果在将所有大写字符转换为小写字符、并移除所有非字母数字字符之后,短语正着读和反着读都一样。则可以认为该短语是一个 回文串 。
代码解析:将获取到的字符串中的非数字和非字母的字符替换为"",将该字符串全部转化转化为小写的字符表示。使用 StringBuilder 的工具类,将字符串进行翻转,对比去重之后的字符是否一致,既可得知操作之后是否是回文串。
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
s = s.replaceAll("[^a-z^A-Z^0-9]", "").toLowerCase();
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(s);
return stringBuilder.reverse().toString().equals(s);
}
在业务中出现 高并发,高性能、高可用的需求时就需要考虑 StringBuffer 工具类。
JDK11 StringBuffer 源码分析
// 类
final class StringBuffer extends AbstractStringBuilder implements Serializable, Comparable<StringBuffer>, CharSequence
// 属性
private transient String toStringCache;
static final long serialVersionUID = 3388685877147921107L;
private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields;
// 无参构造函数
public StringBuffer() {
super(16);
}
// compareTo()
public synchronized int compareTo(StringBuffer another) {
return super.compareTo(another);
}
// 其中父类的CompareTo()
int compareTo(AbstractStringBuilder another) {
if (this == another) {
return 0;
} else {
byte[] val1 = this.value;
byte[] val2 = another.value;
int count1 = this.count;
int count2 = another.count;
if (this.coder == another.coder) {
return this.isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.compareTo(val1, val2, count1, count2) : StringUTF16.compareTo(val1, val2, count1, count2);
} else {
return this.isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.compareToUTF16(val1, val2, count1, count2) : StringUTF16.compareToLatin1(val1, val2, count1, count2);
}
}
}
// append()
public synchronized StringBuffer append(String str) {
this.toStringCache = null;
super.append(str);
return this;
}
// substring()
public synchronized String substring(int start) {
return this.substring(start, this.count);
}
// reverse()
public synchronized StringBuffer reverse() {
this.toStringCache = null;
super.reverse();
return this;
}
// toString()
public synchronized String toString() {
return this.toStringCache == null ? (this.toStringCache = this.isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.newString(this.value, 0, this.count) : StringUTF16.newString(this.value, 0, this.count)) : new String(this.toStringCache);
}
ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal 中填充的的是当前线程的变量,该变量对其他线程而言是封闭且隔离的,ThreadLocal 为变量在每个线程中创建了一个副本,这样每个线程都可以访问自己内部的副本变量。
使用场景
1、在进行对象跨层传递的时候,使用 ThreadLocal 可以避免多次传递,打破层次间的约束。
2、线程间数据隔离,解决线程安全的问题
3、进行事务操作,用于存储线程事务信息。
4、数据库连接,Session 会话管理
5、当作一个集合使用
ThreadLocal 内部结构图
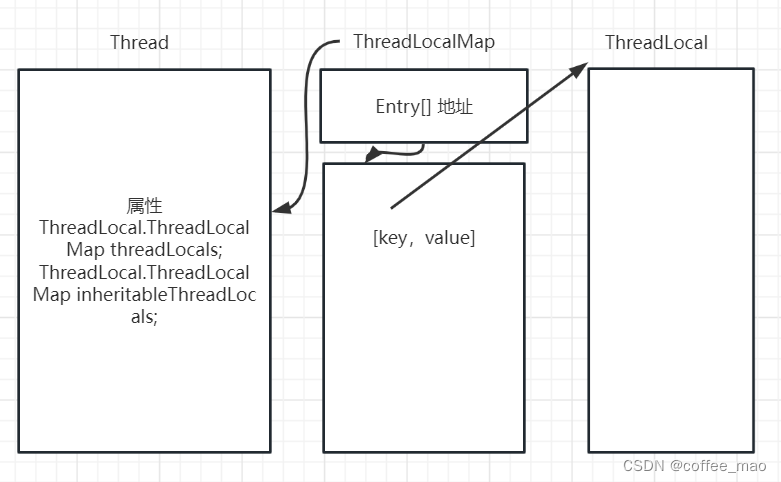
ThreadLocal 类似集合,但是内部是通过 map 的 (key,value) 的键值对存储的。当前线程获取到 threadLocals 这个属性,这个属性也就是 ThreadLocalMap 的键,map 中存储的是一个Entry 数组,Entry 存储每一个键值对。
JDK11 ThreadLocal 源码分析
// 类
class ThreadLocal
// 字段
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 1640531527;
// 无参构造方法
public ThreadLocal() {
}
// set()
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = this.getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
map.set(this, value);
} else {
this.createMap(t, value);
}
}
// createMap()
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
// getMap()
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
// get()
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = this.getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
T result = e.value;
return result;
}
}
return this.setInitialValue();
}
// remove()
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = this.getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null) {
m.remove(this);
}
}
// 静态内部类
static class ThreadLocalMap {
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
private Entry[] table;
private int size = 0;
private int threshold;
}
// Entry
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
this.value = v;
}
}
探究 ThreadLocal 的内存泄漏,以及如何解决
源码解释如下
如果 key threadlocal 为 null 了,这个 entry 就可以清除了。
ThreadLocal是一个弱引用,当为null时,会被当成垃圾回收 。
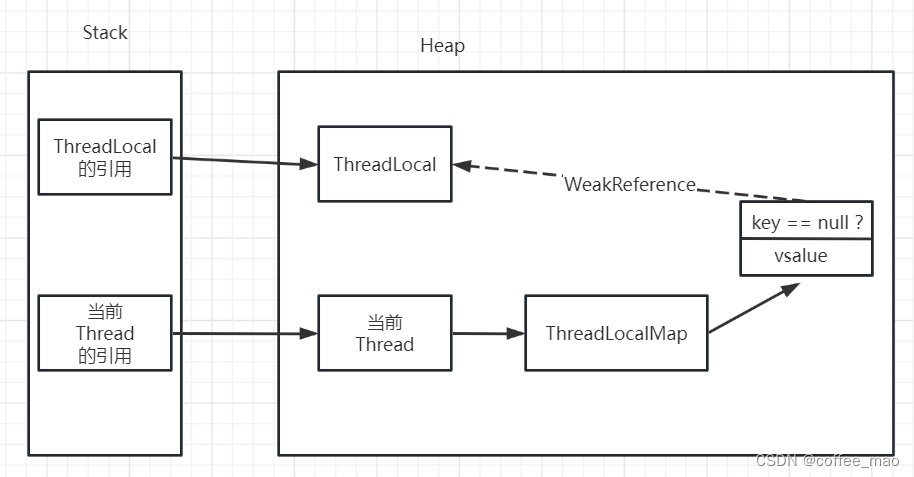
如图所示 ThreadLocal 是 null 了,也就是要被垃圾回收器回收了,但是此时我们的ThreadLocalMap(thread 的内部属性)生命周期和Thread的一样,它不会回收,这时候就出现了一个现象。那就是ThreadLocalMap的key没了,但是value还在,这就造成了内存泄漏。
解决方法:跟加锁解锁一样,在使用完ThreadLocal后,执行remove操作,避免出现内存溢出情况。
如果不
remove当前线程对应的value,就会一直存在这个值。
使用了线程池,可以达到“线程复用”的效果。但是归还线程之前记得清除ThreadLocalMap,要不然再取出该线程的时候,ThreadLocal变量还会存在。这就不仅仅是内存泄露的问题了,整个业务逻辑都可能会出错。
思考:为什么 key 不使用强应用
如果使用强引用,当
ThreadLocal对象的引用(强引用)被回收了,ThreadLocalMap本身依然还持有ThreadLocal的强引用,如果没有手动删除这个key,则ThreadLocal不会被回收,所以只要当前线程不消亡,ThreadLocalMap引用的那些对象就不会被回收, 可以认为这导致Entry内存泄漏。
二叉树的最小深度
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。 最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。 说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
树的这个类
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
解题思路
- 使用深度优先搜索的方法,遍历整棵树,记录最小深度。
对于每一个非叶子节点,我们只需要分别计算其左右子树的最小叶子节点深度。
代码
编写深度优先搜索的算法,在遍历每一个节点时候对比深度信息,对最小深度变量进行更新。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
int depth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(root.left != null){
depth = Math.min(dfs(root.left),depth);
}
if(root.right != null){
depth = Math.min(dfs(root.right),depth);
}
return depth+1;
}
}
- 广度优先搜索的方法,遍历整棵树。当我们找到一个叶子节点时,直接返回这个叶子节点的深度。广度优先搜索的性质保证了最先搜索到的叶子节点的深度一定最小。
代码
增加了一个队列节点的类,维护的是节点和对应深度的关系,统计的是当前节点和其深度,广度优先搜索一但节点的左右子树为空,那么此节点的深度就是二叉树的最小深度。
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return bfs(root);
}
class QueueNode{
TreeNode node;
int depth;
public QueueNode(TreeNode node,int depth){
this.node = node;
this.depth = depth;
}
}
private int bfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
Queue<QueueNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new QueueNode(root, 1));
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
QueueNode queueNode = queue.poll();
TreeNode node = queueNode.node;
int depth = queueNode.depth;
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) return depth;
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.left,depth+1));
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(new QueueNode(node.right,depth+1));
}
}
return 0;
}
}
日期转换Bug
日期设置为2023年12月31,注意Calendar.MONTH 月份是[0,11]
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args){
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR,2023);
calendar.set(Calendar.MONTH,11);
calendar.set(Calendar.DATE,31);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-dd");
String date = dateFormat.format(calendar.getTime());
System.out.println(date);
}
}
会发现格式之后的日期是2024年12月31日,问题是格式化的时候大写的Y记录的是星期所在的年份
解决方案
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
4 大引用
强引用:即便产生堆内存溢出,也不回收
static class Person{
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person); // Demo$Person@3567135c
System.gc();
System.out.println(person); //Demo$Person@3567135c
}
强引用基础上,将堆内存地址给别人,将person回收即是强引用删除,其他依旧引用,看是否还依旧指向他
软引用
一般情况之下和强引用一致,如果内存空间快满了,就垃圾进行回收
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person = new Person();
SoftReference<Person> softReference = new SoftReference<>(person);
System.out.println(softReference.get());
person = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(softReference.get());
}
运行结果,但是,如果存在空间就保留
Demo$Person@3567135c
Demo$Person@3567135c
弱引用
只要垃圾进行回收,就清理,在清理之后获取不到
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person = new Person();
WeakReference<Person> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(person);
System.out.println(weakReference.get()); // Demo$Person@3567135c
person = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference.get()); // null
}
虚引用
需要一个引用队列,构建两层,发现在强引用还没有清空的时候就已经获取不到了。
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person = new Person();
ReferenceQueue referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
PhantomReference phantomReference = new PhantomReference(person, referenceQueue);
System.out.println(phantomReference.get()); // null
person = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(phantomReference.get()); // null
}
抢红包算法
抢红包算法常用的有二分均值法和线段分割法
二分均值算法,每次红包剩余金额 / 剩余人数 * 2
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(redPackage(100, 10));
}
public static List redPackage(int totalMoney,int totalPerson){
ArrayList<Integer> distribution = new ArrayList<>();
int currentMoney = totalMoney,currentPerson = totalPerson;
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < totalPerson-1; i++) {
int money = random.nextInt(currentMoney/currentPerson*2-1)+1;
distribution.add(money);
currentPerson--;
currentMoney -= money;
}
distribution.add(currentMoney);
return distribution;
}
制作二维码
导入包core 3.3.3
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId>
<artifactId>core</artifactId>
<version>3.3.3</version>
</dependency>
MultiFormatWriter 画者,位矩阵作为二维码,通过I/O处理图片,将文件写入磁盘
public static void drawQRCode() throws WriterException, IOException {
// 绘制人
MultiFormatWriter mfw = new MultiFormatWriter();
// 二维码矩阵
String content = "瞅啥瞅,别乱骚二维码\nauthor:coffeemao";
BarcodeFormat qrCode = BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE;
int width = 600;
int height = 600;
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(EncodeHintType.CHARACTER_SET,"UTF-8");
map.put(EncodeHintType.ERROR_CORRECTION, String.valueOf(ErrorCorrectionLevel.H));
map.put(EncodeHintType.MARGIN, 2);
BitMatrix bitMatrix = mfw.encode(content,qrCode,width,height,map);
// I/O 处理
int black = Color.BLACK.getRGB();
int white = Color.WHITE.getRGB();
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(width,height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++) {
image.setRGB(i,j,bitMatrix.get(i,j) ? black : white);
}
}
File file = new File("E:\\Code\\Mybatis-Ex\\math\\src\\test\\image.jpg");
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",file);
}
邮件发送
导入依赖 mail.jar
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.mail/mail -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>mail</artifactId>
<version>1.4.7</version>
</dependency>
发送邮件的方法,开通邮箱的功能,获取授权码
public static void sendMail() throws MessagingException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.transport.protocol","smtp");
properties.put("mail.smtp.host","smtp.qq.com");
// 建立连接
Session session = Session.getInstance(properties);
// 模拟邮件
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress("2750506316@qq.com"));
message.setRecipient(MimeMessage.RecipientType.TO,new InternetAddress("2750506316@qq.com"));
message.setSubject("测试Java程序邮件");
message.setSentDate(new Date());
message.setText("坚持每日编程!");
// 保存
message.saveChanges();
//发送
Transport transport = session.getTransport();
transport.connect("2750506316@qq.com","授权码");
transport.sendMessage(message,message.getAllRecipients());
// 关闭流
transport.close();
}
颠倒二进制位
颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
public class Solution {
// you need treat n as an unsigned value
public int reverseBits(int n) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32 && n != 0; i++){
res |= ((n&1) << (31-i));
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
注意 n >>= 1; 和 n >>>= 1;
使用 | 位运算符和+算术运算符是一致的
res += ((n&1) << (31-i));
其中熟悉 API 接口调用的直接使用Integer的方法直接返回
return Integer.reverse(n);
丢失的数字
题目描述
给定一个包含
[0, n]中n个数的数组nums,找出[0, n]这个范围内没有出现在数组中的那个数。
代码
数组容纳的数字是[0,n],这n个数求和即是总数的和,总数和与数组和求差即是缺失的数字。
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
return nums.length*(nums.length+1)/2 - Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
}
生产者和消费者模式
模拟仓库进出货物的线程竞争关系解决
WareHouse作为仓库具有进货物和出货物的功能。消费者和生产者模型进行添加和删除仓库元素。仓库使用静态代码块在最开始的时候进行初始货物的初始化。仓库集合使用可见性的关键字进行修饰,针对删除和增加货物的方法使用锁的关键字进行修饰。添加其他线程的唤醒功能,优化体验感。
static class WareHouse{
private static volatile List<String> wareHouse = new ArrayList<>();
static {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
wareHouse.add("a");
}
}
// 并发异常:Exception in thread "Thread-1" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 0 out of bounds for length 0
public synchronized void add(){
if (wareHouse.size() <= 30){
wareHouse.add("a");
}else {
try {
wait(10);
notifyAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public synchronized void remove(){
if (wareHouse.size() > 0){
wareHouse.remove(0);
}else {
try {
wait(10);
notifyAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
static class Producer extends Thread{
private String name;
private WareHouse wareHouse;
public Producer(String name,WareHouse wareHouse){
this.name = name;
this.wareHouse = wareHouse;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
wareHouse.add();
System.out.println(this.name + "添加了一个物品");
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
static class Customer extends Thread{
private String name;
private WareHouse wareHouse;
public Customer(String name,WareHouse wareHouse){
this.name = name;
this.wareHouse = wareHouse;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
wareHouse.remove();
System.out.println(this.name + "移出了一个物品");
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
WareHouse wareHouse = new WareHouse();
Producer p1 = new Producer("p1",wareHouse);
Customer c1 = new Customer("c1",wareHouse);
Customer c2 = new Customer("c2",wareHouse);
p1.start();
c1.start();
c2.start();
}
使用Lock锁实现,并且添加字段number防止虚假唤醒,减小锁的粒度,优化代码
static class WareHouse{
private static volatile List<String> wareHouse = new ArrayList<>();
static {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
wareHouse.add("a");
}
}
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
private int number = 0;
// 并发异常:Exception in thread "Thread-1" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 0 out of bounds for length 0
public void add(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 0){
// 等待
condition.await();
}
if (wareHouse.size() <= 30){
wareHouse.add("a");
}
number++;
condition.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void remove(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (number == 0){
// 等待
condition.await();
}
if (wareHouse.size() > 0){
wareHouse.remove(0);
}
number--;
condition.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}






















 718
718











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








