1. PostgreSQL体系结构概述
代码结构

其中,backend是后端核心代码,包括右边的几个dir:
access:处理数据访问方法和索引的代码。
bootstrap:数据库初始化相关的代码。
catalog:系统目录(如表和索引的元数据)的实现代码。
commands:实现SQL命令的代码。
executor:执行查询计划的代码。
foreign:处理外部数据源(如外部数据封装器和外部表)的代码。
jit:即时编译器优化代码。
lib:库函数。
libpq:PostgreSQL的C语言接口库。
main:后端主程序入口。
nodes:节点和树结构,用于内部查询表示。
optimizer:查询优化器代码。
parser:SQL解析器代码。
partitioning:分区表的处理代码。
postmaster:后端服务管理器。
regex:正则表达式处理代码。
replication:复制功能的代码。
rewrite:规则重写系统代码。
snowball:全文检索中用到的词干分析代码。
statistics:统计信息收集相关代码。
storage:数据存储相关代码。
tcop:交互式终端监控代码。
tsearch:全文搜索相关代码。
utils:工具函数,如数据类型转换等。
进程结构
pg的基本结构是进程,是多进程结构,这和基于pg的opengauss可能有所不同,og是单进程多线程。
与单进程多线程模型相比,多进程模型有一些优势和劣势:
优势:
- 稳健性:单个进程崩溃不会直接影响到运行在其他进程中的客户端会话。
- 安全:因为内存是隔离的,所以进程间的数据访问更加安全。
- 简单性:多进程模型通常更易于理解和调试。
劣势:
- 资源占用:每个进程都需要一定量的内存和系统资源,所以当并发连接数增加时,资源占用也会增加。
- 上下文切换:操作系统在多个进程间切换可能会带来额外的开销,尤其是在高并发环境下。
具体针对图中的各个部分来说是:
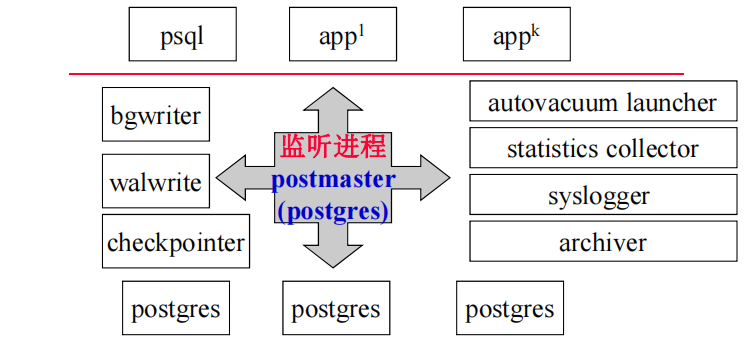
-
psql app1…
用于与 PostgreSQL 数据库进行交互和管理
-
Postmaster/Main Process:
这是主控进程,当PostgreSQL数据库启动时首先被创建。它负责监听并接受新的客户端连接请求,并为每个新的客户端连接产生一个新的服务器进程(backend process)。 -
Backend Processes:
为每个客户端连接创建的进程。每个客户端连接(如通过psql或其他应用程序)通常会有一个对应的后台进程。这些进程负责处理实际的SQL命令,并与数据库内的数据进行交互。 -
Background Writer (bgwriter):
这个进程负责将缓存中的脏页(已修改的页)定期写入磁盘。它可以减轻服务器进程的负担,因为这些进程可以将页标记为脏,但不必立即写入磁盘。 -
WAL Writer:
WAL(Write-Ahead Logging)写入器进程负责将事务日志记录写入到磁盘的WAL文件中。这是确保数据完整性的关键步骤,允许系统在崩溃后恢复到一致状态。 -
Checkpointer:
这个进程负责创建检查点,这是一个系统状态,数据库可以从该状态安全地恢复。它周期性地将当前状态写入到磁盘,并告知bgwriter哪些页可以被安全地写入。 -
Autovacuum Launcher:
这个守护进程监控数据库,定期启动autovacuum worker进程来执行清理任务。它负责删除旧版本的行(也称为元组),这些行由于更新和删除操作而不再可达。 -
Statistics Collector:
收集有关数据库操作的统计信息,这些信息可以用来优化查询计划。 -
Syslogger:
负责记录系统日志,包括错误消息、查询日志和其他系统事件。 -
Archiver:
当开启归档模式时,该进程负责复制WAL记录到指定的归档位置,以便可以用于数据恢复。
postmaster
具体的去查看postmaster.c,首先读注释
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* postmaster.c
* 该程序充当 POSTGRES 系统请求的中转站。前端程序发送启动消息
* 给 Postmaster,Postmaster 根据消息中的信息设置后台进程。
*
* Postmaster 还管理系统范围的操作,如启动和关闭。要注意的是,
* Postmaster 本身并不执行这些操作——它只是在适当的时候派生一个
* 子进程来执行。它还负责在后台进程崩溃时重置系统。
*
* Postmaster 在启动期间创建共享内存和信号量池,但通常不直接操作它们。
* 特别是,它不是 PGPROC 后台数组的成员,因此不能参与锁管理操作。
* 让 Postmaster 远离共享内存操作,使得它更简单更可靠。Postmaster 几乎总是能够
* 通过重置共享内存从单个后台进程的崩溃中恢复过来;如果它过多地与共享内存
* 打交道,那么它也可能随着后台进程一起崩溃。
*
* 当收到请求消息时,我们现在立即执行 fork()。
* 子进程执行请求的认证,并在成功后变成一个后台进程。这允许认证代码
* 以简单的单线程方式编写(与过去需要的“穷人的多任务”代码相反)。
* 更重要的是,它确保了在非多线程库(如 SSL 或 PAM)阻塞时,
* 不会对其他客户端造成服务拒绝。
*
* 初始化:
* Postmaster 为后台设置共享内存数据结构。
*
* 同步:
* Postmaster 与后台共享内存,但应避免touch共享内存,以免在崩溃的
* 后台破坏锁或共享内存时变得卡住。同样,Postmaster 永远不应该
* 阻塞在来自前端客户端的消息上。
*
* 垃圾收集:
* 如果后台紧急退出和/或核心转储,Postmaster 会清理后台。
*
* 错误报告:
* 使用 write_stderr() 仅报告“交互式”错误(本质上是命令行上的错误参数)。
* 一旦启动了 postmaster,使用 ereport()。
*
*-------------------------------------------------------------------------
首先是定义了一些进程的type以及进程开始过程的一些状态
#define BACKEND_TYPE_NORMAL 0x0001 /* normal backend */
#define BACKEND_TYPE_AUTOVAC 0x0002 /* autovacuum worker process */
#define BACKEND_TYPE_WALSND 0x0004 /* walsender process */
#define BACKEND_TYPE_BGWORKER 0x0008 /* bgworker process */
#define BACKEND_TYPE_ALL 0x000F /* OR of all the above */
/* Startup process's status */
typedef enum
{
STARTUP_NOT_RUNNING,
STARTUP_RUNNING,
STARTUP_SIGNALED, /* we sent it a SIGQUIT or SIGKILL */
STARTUP_CRASHED
} StartupStatusEnum;
这里pg实际上使用了一个简单地state machine来控制startup shutdown和crash recovery
在postmasterMain函数里面,
1. 获取pid、starttime等信息
PostmasterPid = MyProcPid; captures the process ID of the postmaster.
PgStartTime = GetCurrentTimestamp(); records the startup time of the postmaster.
2. 分配内存管理上下文环境
PostmasterContext = AllocSetContextCreate(...); creates a memory context for the postmaster.
MemoryContextSwitchTo(PostmasterContext); switches to the newly created memory context.
3. *设置信号处理
pqsignal_pm(SIGCHLD, reaper);/* handle child termination */
pqsignal(SIGCHLD, handle_pm_child_exit_signal);
4. 初始化系统配置选项[默认值] // assign_hook()-typedef
InitializeGUCOptions();
5. 解析命令行参数
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "B:bC:c:D:d:EeFf:h:ijk:lN:OPp:r:S:sTt:W:-:")) != -1)
6. 根据postgresql.conf修改系统配置选项[小的解析器
/guc-file.l]
if (!SelectConfigFiles(userDoption, progname))
ExitPostmaster(2);
7. 监听socket端口
/*
* Establish input sockets.
*/
if (ListenAddresses)
{
8. 创建IPC资源[共享内存+信号灯]
CreateSharedMemoryAndSemaphores();
9. 处理pg_hba.conf和pg_ident.conf
/*
* Load configuration files for client authentication.
*/
if (!load_hba())
{
/*
* It makes no sense to continue if we fail to load the HBA file,
* since there is no way to connect to the database in this case.
*/
ereport(FATAL,
/* translator: %s is a configuration file */
(errmsg("could not load %s", HbaFileName)));
}
if (!load_ident())
{
/*
* We can start up without the IDENT file, although it means that you
* cannot log in using any of the authentication methods that need a
* user name mapping. load_ident() already logged the details of error
* to the log.
*/
}
10. 启动数据库[StartupDataBase] // StartChildProcess
StartupPID = StartupDataBase();
11. 进入监控循环
status = ServerLoop();
系统启动
postgre [opts]
- 保存环境变量
- 设置本地化
- 检查命令行参数
- 进入不同执行模式
- —boot:booststrap,初始化数据库
- —describe-config:显示系统配置
- —single:单用户模式启动
- :启动多用户模式
postgres@torresの机革:/usr/local/pgsql$ /usr/local/pgsql/bin/postgres --help
postgres is the PostgreSQL server.
Usage:
postgres [OPTION]...
Options:
-B NBUFFERS number of shared buffers
-c NAME=VALUE set run-time parameter
-C NAME print value of run-time parameter, then exit
-d 1-5 debugging level
-D DATADIR database directory
-e use European date input format (DMY)
-F turn fsync off
-h HOSTNAME host name or IP address to listen on
-i enable TCP/IP connections (deprecated)
-k DIRECTORY Unix-domain socket location
-N MAX-CONNECT maximum number of allowed connections
-p PORT port number to listen on
-s show statistics after each query
-S WORK-MEM set amount of memory for sorts (in kB)
-V, --version output version information, then exit
--NAME=VALUE set run-time parameter
--describe-config describe configuration parameters, then exit
-?, --help show this help, then exit
Developer options:
-f s|i|o|b|t|n|m|h forbid use of some plan types
-O allow system table structure changes
-P disable system indexes
-t pa|pl|ex show timings after each query
-T send SIGABRT to all backend processes if one dies
-W NUM wait NUM seconds to allow attach from a debugger
Options for single-user mode:
--single selects single-user mode (must be first argument)
DBNAME database name (defaults to user name)
-d 0-5 override debugging level
-E echo statement before execution
-j do not use newline as interactive query delimiter
-r FILENAME send stdout and stderr to given file
Options for bootstrapping mode:
--boot selects bootstrapping mode (must be first argument)
--check selects check mode (must be first argument)
DBNAME database name (mandatory argument in bootstrapping mode)
-r FILENAME send stdout and stderr to given file
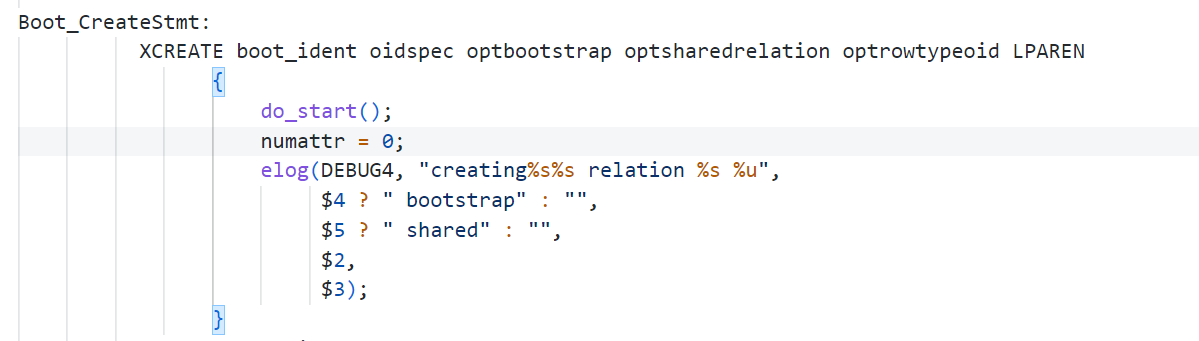
数据库创建和初始化
BKI:backend Interface 脚本文件:
- BKI文件就相当于一个模板文件,比如word空白文档的创建
- 位置: 安装目录下,其实src/backend/catalog/postgre.bki也有一个,create pg_proc 1255 bootstrap tableoid

- @bootstrap/bootstrap.c[+ bootparse.y],对BKI进行解析,在整个bootstrap目录下,进行解析、扫描、执行等
- 例子:建表
# PostgreSQL 16
# ( 上面是变化的,头处理一次,后面复用的吗oid=oid,重复的,属性的内容。
create pg_proc 1255 bootstrap rowtype_oid 81
(
oid = oid ,
proname = name ,
pronamespace = oid ,
proowner = oid ,
prolang = oid ,
procost = float4 ,
prorows = float4 ,
provariadic = oid ,
prosupport = regproc ,
prokind = char ,
prosecdef = bool ,
proleakproof = bool ,
proisstrict = bool ,
proretset = bool ,
provolatile = char ,
proparallel = char ,
pronargs = int2 ,
pronargdefaults = int2 ,
prorettype = oid ,
proargtypes = oidvector FORCE NOT NULL ,
proallargtypes = _oid ,
proargmodes = _char ,
proargnames = _text ,
proargdefaults = pg_node_tree ,
protrftypes = _oid ,
prosrc = text FORCE NOT NULL ,
probin = text ,
prosqlbody = pg_node_tree ,
proconfig = _text ,
proacl = _aclitem
)
# insert的省略,省略了into table 以及 values
insert ( 1242 boolin 11 10 12 1 0 0 0 f f f t f i s 1 0 16 2275 _null_ _null_ _null_ _null_ _null_ boolin _null_ _null_ _null_ _null_ )
边解析边处理
static void
bootstrap_template1(void)
{
PG_CMD_DECL;
char **line;
char **bki_lines;
char headerline[MAXPGPATH];
char buf[64];
/*
* get the lines from a text file
*
* The result is a malloc'd array of individually malloc'd strings.
*/
static char **
readfile(const char *path)
{
char **result;
FILE *infile;
StringInfoData line;
int maxlines;
int n;
if ((infile = fopen(path, "r")) == NULL)
pg_fatal("could not open file \"%s\" for reading: %m", path);
initStringInfo(&line);
maxlines = 1024;
result = (char **) pg_malloc(maxlines * sizeof(char *));
n = 0;
while (pg_get_line_buf(infile, &line))
{
/* make sure there will be room for a trailing NULL pointer */
if (n >= maxlines - 1)
{
maxlines *= 2;
result = (char **) pg_realloc(result, maxlines * sizeof(char *));
}
result[n++] = pg_strdup(line.data);
}
result[n] = NULL;
pfree(line.data);
fclose(infile);
return result;
}
char **result; vs char *result[];
运行和维护—Client App
-
数据库创建(fromTemplate)
- createdb [opts]
bin/scripts/createdb.c
-
空间整理(gc&analyze)
– vacuumdb [opts] -
数据导出/导入(backup)
– pg_dump [opts]
– pg_restore [opts]
数据字典
系统元数据在src/backend/catalog目录下,结构和接口声明在include/catalog下
pg class.h pg proc.h
pg_class.h 系统表catalog的关系的定义,
in/out 类比于 重载操作符,方便输入输出
{ oid => '1242', descr => 'I/O',
proname => 'boolin', prorettype => 'bool', proargtypes => 'cstring',
prosrc => 'boolin' },
{ oid => '1243', descr => 'I/O',
proname => 'boolout', prorettype => 'cstring', proargtypes => 'bool',
prosrc => 'boolout' },
pg_proc.h能被C编译器和pm程序所处理。
函数宏,预编译的阶段
/* Introduces a catalog's structure definition */
#define CATALOG(name,oid,oidmacro) typedef struct CppConcat(FormData_,name)
/* ----------------
* pg_proc definition. cpp turns this into
* typedef struct FormData_pg_proc
* ----------------
*/
CATALOG(pg_proc,1255,ProcedureRelationId) BKI_BOOTSTRAP BKI_ROWTYPE_OID(81,ProcedureRelation_Rowtype_Id) BKI_SCHEMA_MACRO
{
Oid oid; /* oid */
/* procedure name */
NameData proname;
/* OID of namespace containing this proc */
Oid pronamespace BKI_DEFAULT(pg_catalog) BKI_LOOKUP(pg_namespace);
/* procedure owner */
Oid proowner BKI_DEFAULT(POSTGRES) BKI_LOOKUP(pg_authid);
/* OID of pg_language entry */
Oid prolang BKI_DEFAULT(internal) BKI_LOOKUP(pg_language);
/*
* CppAsString
* Convert the argument to a string, using the C preprocessor.
* CppAsString2
* Convert the argument to a string, after one round of macro expansion.
* CppConcat
* Concatenate two arguments together, using the C preprocessor.
*
* Note: There used to be support here for pre-ANSI C compilers that didn't
* support # and ##. Nowadays, these macros are just for clarity and/or
* backward compatibility with existing PostgreSQL code.
*/
#define CppAsString(identifier) #identifier
#define CppAsString2(x) CppAsString(x)
#define CppConcat(x, y) x##y
主要代码阅读
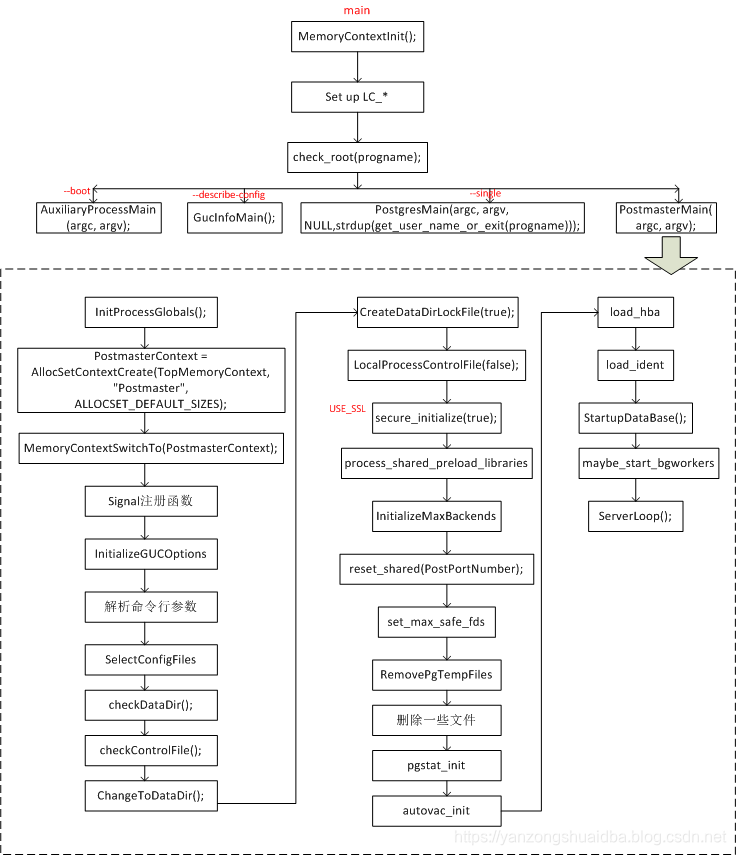
主要包括src/backend/postmaster/postmaster.c 上面以及简单解析了,还有就是src/backend/main/main.c 和 src/bin/initdb.c 和 src/backend/pg_ctl_pg_ctl.c
src/backend/main/main.c
/*
* 任何 Postgres 服务器进程的执行都是从这里开始。
*/
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
bool do_check_root = true;
reached_main = true;
// 在 Windows 平台上,如果后台进程崩溃,设置一个将被调用的处理函数。
#if defined(WIN32)
pgwin32_install_crashdump_handler();
#endif
// 获取程序名称。
progname = get_progname(argv[0]);
// 执行平台相关的启动准备。
startup_hacks(progname);
// 保存原始的 argv[] 数组的物理位置,以供 ps 显示使用。
argv = save_ps_display_args(argc, argv);
// 启动关键子系统:错误处理和内存管理。
MemoryContextInit();
// 设置本地化信息。
set_pglocale_pgservice(argv[0], PG_TEXTDOMAIN("postgres"));
// 初始化区域设置。
init_locale("LC_COLLATE", LC_COLLATE, "");
init_locale("LC_CTYPE", LC_CTYPE, "");
#ifdef LC_MESSAGES
init_locale("LC_MESSAGES", LC_MESSAGES, "");
#endif
init_locale("LC_MONETARY", LC_MONETARY, "C");
init_locale("LC_NUMERIC", LC_NUMERIC, "C");
init_locale("LC_TIME", LC_TIME, "C");
// 移除 LC_ALL 设置。
unsetenv("LC_ALL");
// 检查标准选项。
if (argc > 1)
{
if (strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "-?") == 0)
{
help(progname);
exit(0);
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "--version") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "-V") == 0)
{
fputs(PG_BACKEND_VERSIONSTR, stdout);
exit(0);
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "--describe-config") == 0)
do_check_root = false;
else if (argc > 2 && strcmp(argv[1], "-C") == 0)
do_check_root = false;
}
// 确保不是以 root 用户身份运行。
if (do_check_root)
check_root(progname);
/*
* Dispatch to one of various subprograms depending on first argument.
*/
if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--check") == 0)
BootstrapModeMain(argc, argv, true);
else if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--boot") == 0)
BootstrapModeMain(argc, argv, false);
#ifdef EXEC_BACKEND
else if (argc > 1 && strncmp(argv[1], "--fork", 6) == 0)
SubPostmasterMain(argc, argv);
#endif
else if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--describe-config") == 0)
GucInfoMain();
else if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--single") == 0)
PostgresSingleUserMain(argc, argv,
strdup(get_user_name_or_exit(progname)));
else
// 这里调用PostmasterMain
PostmasterMain(argc, argv);
// 这些函数不应该返回。
abort();
}
src/bin/initdb.c
initdb也是一个进程
比如可以这样/usr/local/pgsql/bin/initdb -D /usr/local/pgsql/data
src/backend/pg_ctl/pg_ctl.c
pg_ctl — start/stops/restarts the PostgreSQL server
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
static struct option long_options[] = {
// 长格式的命令行选项定义
// 例如,可以用 --pgdata 来指定数据目录
{"help", no_argument, NULL, '?'},
};
// 初始化日志系统,并设置本地化服务
pg_logging_init(argv[0]);
progname = get_progname(argv[0]);
set_pglocale_pgservice(argv[0], PG_TEXTDOMAIN("pg_ctl"));
start_time = time(NULL);
// 保存 argv[0],以便 do_start() 函数在需要时可以寻找 postmaster
argv0 = argv[0];
// 设置默认的 umask,直到检查 PGDATA 权限
umask(PG_MODE_MASK_OWNER);
// 支持即使以 root 用户身份运行时也能接收 --help 和 --version 参数
// 处理命令行选项,比如 -D 设置数据目录,-l 设置日志文件等
while ((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "cD:l:m:o:s:t:wW", long_options, &option_index)) != -1) {
switch (c) {
case 'D': // 数据目录选项
// ...设置 PGDATA 环境变量
break;
// ...处理其他选项
}
}
// 如果 optind 还没有超过 argc,那么处理操作命令,如 start, stop, restart
if (optind < argc) {
// 根据参数识别控制命令,如 "start"、"stop" 等
// 如果 ctl_command 已经被设置过了,则报错退出
// ...此处省略判断逻辑...
}
// 如果没有指定操作命令,则打印错误信息并给出建议
if (ctl_command == NO_COMMAND) {
// 错误处理...
}
// 设置环境变量 PGDATA 和其他相关的全局变量
// 根据控制命令执行相应操作
switch (ctl_command) {
case INIT_COMMAND:
// 执行初始化操作
do_init();
break;
// ...处理其他命令...
}
// 正常退出
exit(0);
}
补充-psql语法
数据库登录
使用postgres用户登录安装在本机的数据库:
$ psql -U postgres
Password for user postgres: //提示输入用户密码
输入用户密码后,登录成功
登录IP为192.168.1.3的服务器,并连接到名为"test"的数据库:
$ psql -U postgres -H 192.168.1.3 -d test
切换数据库
如果登录时未指定数据库,或需要切换到其它数据库,可以使用\c参数切换:
\c dbname
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的use dbname命令。
查看所有数据库
查看当前系统中有哪些数据库可以使用\l或\list参数:
\l
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的show databases命令。
查看数据库中的表
查看当前数据库中所有的表,使用\d参数:
\d
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的show tables命令。
查看表中的字段
查看指定表中的字段,使用\d dbtable参数:
\d mytable
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的desc dbtable或 show columns from dbtable命令。
查看表信息
查看表信息,使用\d+ dbtable参数:
\d+ mytable
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的describe dbtable命令。
退出登录
退出登录,使用\q参数:
\q
以上命令相当于mysql数据库的quit或\q命令。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lmmilove/article/details/122111192
补充-pg启动调用关系






















 306
306

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










