一,线程组
类似于在计算机使用文件夹管理文件,也可以使用线程组来管理线程。在线程组中定义一组相似(相关)的线程,在线程组中也可以定义子线程组。
Thread类有几个构造方法允许在创建线程时指定线程组,如果在创建线程时没有指定线程组则该线程就属于父线程所在的线程组。JVM在创建main线程时会为它指定一个线程组,因此每个java线程都有一个线程组与之关联,可以调用线程的getThreadGroup()方法返回线程组。
线程组开始是处于安全的考虑设计用来区分不同的Applet,然而ThreadGroup并未实现这一目标,在新开发的系统中,已经不常用线程组。现在一般会将一组相关的线程存入一个数组或一个集合中,如果仅仅是用来区分线程时,可以使用线程名称来区分,多数情况下可以忽略线程组。
1,创建线程组
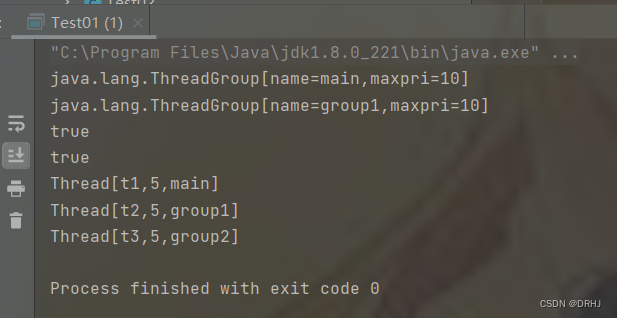
package com.drhj.thread_group;
/**
* 演示创建线程组
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/8 20:41
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//返回当前main线程的线程组
ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
System.out.println(mainGroup);
//定义线程组,如果不指定所属线程组,则自动归属到当前线程所属组中
ThreadGroup g1 = new ThreadGroup("group1");
System.out.println(g1);
//定义线程组,指定父线程组
ThreadGroup g2 = new ThreadGroup(mainGroup, "group2");
//g1与g2都是mainGroup线程组中的子线程组,调用getParent()返回父线程组
System.out.println(g1.getParent() == mainGroup);
System.out.println(g2.getParent() == mainGroup);
//创建线程时指定所属的线程组
Runnable r = () -> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
//创建线程时,如果没有指定线程组,则默认线程归属到父线程的线程组中
//在main线程中创建了t1线程,称main线程为父线程,t1线程为子线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(r, "t1");
System.out.println(t1); //中间的数表示优先级
//指定线程时,可以指定线程所属线程组
Thread t2 = new Thread(g1, r, "t2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(g2, r, "t3");
System.out.println(t2);
System.out.println(t3);
}
}
2,基本操作
activeCount() 返回当前线程组及子线程组中活动线程的数量(近似值)
activeGroupCount() 返回当前线程组及子线程组中活动线程组的数量(近似值)
enumerate(Thread[] list) 将当前线程组中的活动线程复制到参数数组中
enumerate(ThreadGroup[] list) 将当前线程组中的活动线程组复制到参数数组中
getMaxPriority() 返回线程组的最大优先级,默认是10
getName() 返回线程组的名称
getParent() 返回父线程组
interrupt() 中断线程组中所有的线程
isDaemon() 判断当前线程组是否为守护线程组
list() 将当前线程组中的活动线程打印出来
parentOf(ThreadGroup g) 判断当前线程是否为参数线程组的父线程组
setDaemon(boolean daemon) 设置线程组为守护线程组
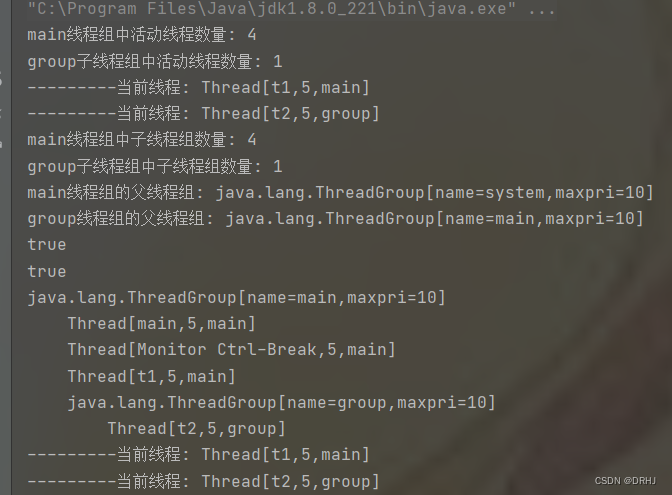
package com.drhj.thread_group;
/**
* 线程组的基础操作
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/9 20:07
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(); //返回当前线程组
//再定义线程组
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("group"); //默认group的父线程组是main线程组
Runnable r = () -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("---------当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(r, "t1"); //默认在main线程组中创建线程
Thread t2 = new Thread(group, r, "t2"); //在指定的group线程组中创建线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
//打印线程组的相关属性
System.out.println("main线程组中活动线程数量: " + mainGroup.activeCount());
System.out.println("group子线程组中活动线程数量: " + group.activeCount());
System.out.println("main线程组中子线程组数量: " + mainGroup.activeCount());
System.out.println("group子线程组中子线程组数量: " + group.activeCount());
System.out.println("main线程组的父线程组: " + mainGroup.getParent());
System.out.println("group线程组的父线程组: " + group.getParent());
System.out.println(mainGroup.parentOf(mainGroup));
System.out.println(mainGroup.parentOf(group));
mainGroup.list();
}
}
2.1,复制线程组中的线程及子线程组
enumerate(Thread[] list) 将当前线程组和子线程组中所有的线程复制到参数数组中
enumerate(Thread[] list, boolean recurse),如果第二个参数设置为false,则只复制当前线程组中所有的线程,不复制子线程组中的线程
enumerate(ThreadGroup[] list) 将当前线程组中的活动线程组复制到参数数组中
enumerate(ThreadGroup[] list,boolean recurse) 第二个参数设置为false,则只负责当前线程组的子线程组
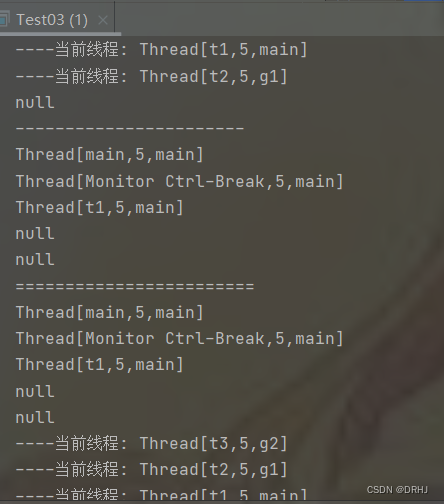
package com.drhj.thread_group;
/**
* 演示复制线程组中的内容
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/11 21:16
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(); //返回main线程的main线程组
//创建线程组
ThreadGroup g1 = new ThreadGroup("g1"); //默认group1的父线程组就是当前线程组main
ThreadGroup g2 = new ThreadGroup(mainGroup, "g2"); //默认group1的父线程组就是当前线程组main
Runnable r = () -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("----当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
//创建三个线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(r, "t1"); //默认在main线程组中创建线程
Thread t2 = new Thread(g1, r, "t2"); //在g1线程中创建线程
Thread t3 = new Thread(g2, r, "t3"); //在g2线程组中创建线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
//把main线程组中的线程复制到数组中
//先定义存储线程的数组,数组的长度为main线程组中活动线程的数量
Thread[] threadList = new Thread[mainGroup.activeCount()];
// mainGroup.enumerate(threadList);
//遍历threadList数组
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//只把main线程组中的线程复制到数组中,不包含子线程组的线程
mainGroup.enumerate(threadList, false);
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
//2)把main线程组中的子线程组复制到数组中
//定义数组存储线程组
ThreadGroup[] threadGroups = new ThreadGroup[mainGroup.activeGroupCount()];
//把main线程组中的子线程组复制到数组中
System.out.println("========================");
mainGroup.enumerate(threadGroups);
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
}
}
2.2,线程组的批量中断
线程组的interrupt()可以给该线程组中所有的活动线程添加中断标志
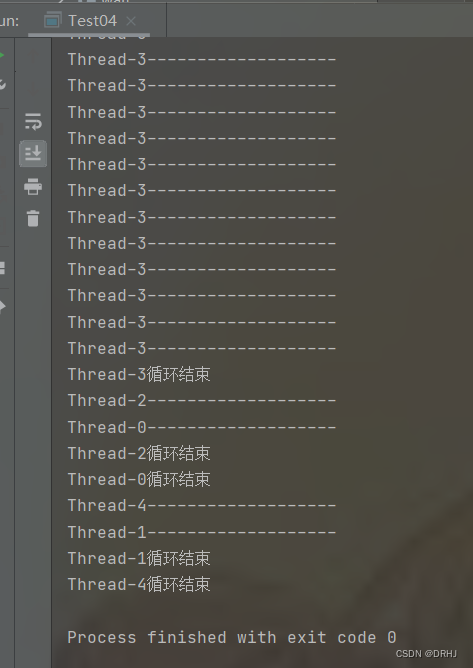
package com.drhj.thread_group;
/**
* 线程组的批量中断
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/17 21:02
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable r = () -> {
System.out.println("当前线程 -- " + Thread.currentThread() + " -- 开始循环");
//当线程没有被中断就一直循环
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-------------------");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(500);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// //如果中断睡眠中的线程,产生中断异常,同时会清除中断标志
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "循环结束");
};
//创建线程组
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("group");
//在group线程组中创建5个线程
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(group, r).start();
}
Thread.sleep(2000);
//中断线程组,会中断线程组中所有的线程
group.interrupt();
}
}
2.3,设置守护线程组
守护线程是为其他线程提供服务的,当JVM中只有守护线程时,守护线程会自动销毁,JVM会退出。
调用线程组的setDaemon(true)可以把线程组设置为守护线程组,当守护线程组中没有任何活动线程时,守护线程组会自动销毁。
注意线程组的守护属性,不影响线程组中线程的守护属性,或者说守护线程组中的线程可以是非守护线程
package com.drhj.thread_group;
/**
* 演示设置守护线程组
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/20 21:13
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("group");
//设置线程组为守护线程组
group.setDaemon(true);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(group, () -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- " + j);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
//main线程睡眠5s
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("main...end...");
}
}
二,捕获线程的执行异常
在线程的run方法中,如果有受检异常必须进行捕获处理,如果想要获得run()方法中出现的运行时异常信息,可以通过回调UncaughtExceptionHandler接口获得哪个线程出现了运行时异常。在Thread类中有关处理异常的方法有:
getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()获得全局的(默认的)UncaughtExceptionHandler;
getUncaughtExceptionHandler()获得当前线程的UncaughtExceptionHandler;
setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh)设置全局的UncaughtExceptionHandler;
setUncaughtExceptionHandler(Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh)设置当前线程的UncaughtExceptionHandler;
当线程运行过程中出现异常时,JVM会调用Thread类的dispatchUncaughtException(Throwable e)方法,该方法会调用getUncaughtExceptionHandler().uncaughtException(this, e);如果想要获得线程中出现的异常的信息,就需要设置线程的UncaughtExceptionHandler
package com.drhj.thread_exception;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* 演示设置线程UncaughtExceptionHandler
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/20 21:44
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//设置线程全局的回调接口
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e)->{
//t参数接收发生异常的线程,e就是该线程中的异常
System.out.println(t.getName() + "线程产生了异常:" + e.getMessage());
});
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始运行");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(12 / 0);
});
t1.start();
new Thread(()->{
String txt = null;
System.out.println(txt.length());
}).start();
}
}
三,注入Hook钩子线程
现在很多软件包括MySQL,Zookeeper,kafka等都存在Hook线程的校验机制,目的是校验进程是否已启动,防止重复启动程序。
Hook线程也称为钩子线程,当JVM退出的时候会执行Hook线程。经常在程序启动时创建一个.lock文件,用.lock文件检验程序是否启动,在程序退出(JVM退出)时删除该.lock文件,在Hook线程中除了防止重新启动进程外,还可以做资源释放,尽量避免在Hook线程中进行复杂的操作。
package com.drhj.hook;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 通过Hook线程防止程序重复启动
* Author: DRHJ
* Date: 2022/8/21 22:30
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//注入Hook线程,在程序退出时删除.lock文件
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("JVM退出,会启动当前Hook线程,在Hook线程中删除.lock文件");
getLockFile().toFile().delete();
}
});
//2)程序运行时,检查lock文件是否存在,如果lock文件存在,则抛出异常
if (getLockFile().toFile().exists()) {
throw new RuntimeException("程序已启动");
} else { //文件不存在,说明程序是第一次启动,创建lock文件
try {
getLockFile().toFile().createNewFile();
System.out.println("程序在启动时创建了lock文件");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//模拟程序运行
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("程序正在运行");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static Path getLockFile() {
return Paths.get("", "tmp.lock");
}
}
当第一次执行时我们是要执行100s后才删除文件,当中途断了后。

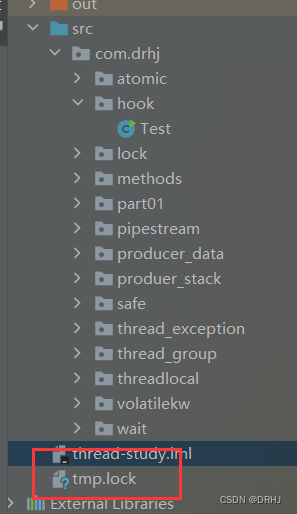
多了tmp.lock文件
当我们再次执行时,如下:
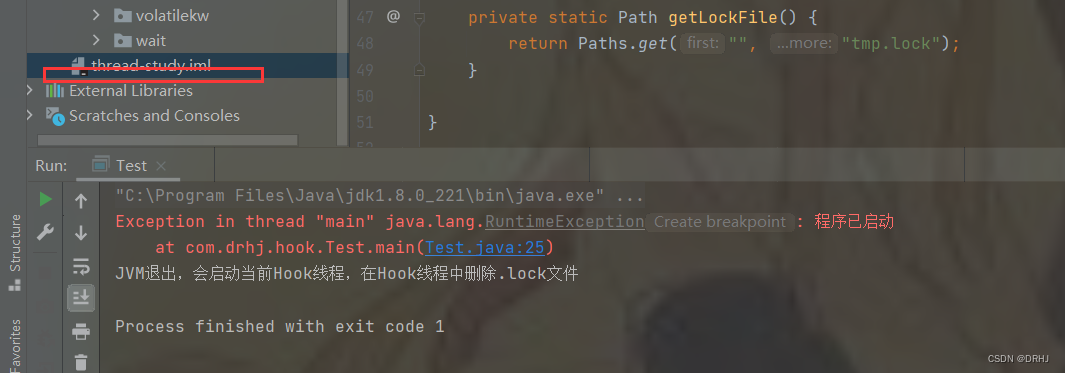
可见,文件已经删除。
当我们执行程序至结束,文件也是被删除的。
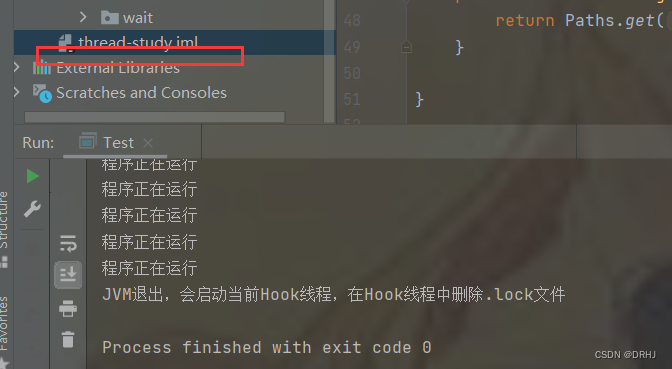























 373
373











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








