Spring
Spring 是什么
-Spring 是于 2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的,IOC 和 AOP 的 Java 开发框架,它
是为了简化企业级应用开发而生的
轻量级
Spring 框架使用的 jar 都比较小,一般在 1M 以下或者几百 kb。Spring 核
心功能的所需的 jar 总共在 3M 左右。 Spring 框架运行占用的资源少,运行
效率高。
IOC
即 Inversion of Control,缩写为 IOC,就是由 Spring IoC 容器管理对象,而
非传统实现中由程序代码直接操控
AOP
面向切面编程。AOP 是一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。面向对象编程将程序抽象成各个层次的对象,而面向切面编程是将程序抽象成各个切面
一站式框架
Spring 本身也提供了数据访问功能和 web 功能,以及可以很好的管理其他框架
Spring体系结构
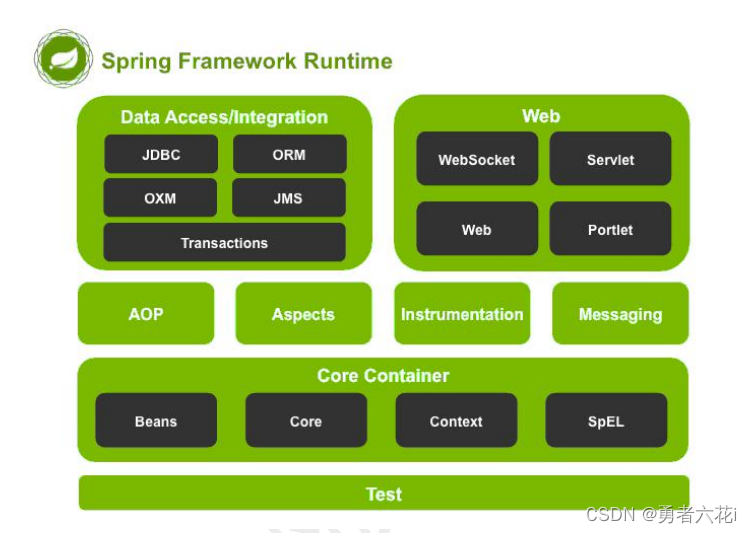
Core Container(核心容器):
Beans: 管理 Beans
Core: Spring 核心
Context: 配置文件
ExpressionLanguage: SpEL 表达式
AOP(切面编程)
AOP 框架: Aspects
Data Access(数据库整合):
JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, Transaction
Web(MVC Web 开发):
Web, Servlet, Portlet, Struts
Test(Junit 整合)
官网地址:https://spring.io/
SpringHelloWorld搭建
Maven 导入Spring核心基础jar
<!-- spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
编写Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.ff.spring.bean.User"> </bean>
</beans>
编写一个实体类
public class User{
private String name;
private int age;
public void work(){
System.out.println(this.name+"工作");
}
}
测试Spring
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
User user1 = new (User)applicationContext.getBean("User");
User user2 = new (User)applicationContext.getBean("User");
System.out.println(User1);
System.out.println(User2);
IOC控制翻转
见以前的文章
注解方式注入属性【DI:Dependency Injection】
@Autowired
@Autowired 是 Spring 提供的注解,可以写在字段和 setter 方法上。如果写在
字段上,那么就不需要再写 setter 方法。默认情况下它要求依赖对象必须存在,如果允许 null 值,可以设置它的 required 属性为 false。
byType 自动注入
该注解默认使用按类型自动装配 Bean 的方式。
byName 自动注入
如果我们想使用按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier 注解一起使用。
需要在引用属性上联合使用注解@Autowired 与@Qualifier。@Qualifier 的
value 属性用于指定要匹配的 Bean 的 id 值。
JDK 注解@Resource 自动注入
Spring 提供了对 jdk 中@Resource 注解的支持。@Resource 注解既可以按名称匹配 Bean,也可以按类型匹配 Bean。默认按照 ByName 自动注入
byName 注入引用类型属性
@Resource 注解指定其 name 属性,则 name 的值即为按照名称进行匹配
的 Bean 的 id
注解与XML对比
注解优点: 方便,直观,高效(代码少,没有配置文件的书写那么复杂)。
注解缺点:以硬编码的方式写入到 Java 代码中,修改是需要重新编译代码的。
xml 优点: 配置和代码是分离的,在 xml 中做修改,无需编译代码,只需重启服务器即可将新的配置加载。
xml 的缺点:编写麻烦,效率低,大型项目过于复杂
SpringJDBC
Spring 是个一站式框架:Spring 自身也提供了控制层的 SpringMVC 和 持久
层的 Spring JdbcTemplate。
- 下载 SpringJDBCTemplate的Jar包
<!-- spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 阿里数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
- 导入属性文件
<context:property-placeholder location=“config.properties”/> - 管理数据源对象
spring 管理与数据库链接 (数据源)
<bean id="dataSource"class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<propertyname="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${uname}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${pwd}"></property>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"></property>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="20"></property>
</bean>
- 在配置文件中创建 JdbcTemplate
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
在类中获得 JdbcTemplate 对象,就可以直接使用
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate 中常用的方法:
execute:无返回值,可执行 ddl,增删改语句
update:执行新增、修改、删除语句;
queryForXXX:执行查询相关语句;
AOP面向切面编程
见以前的文章
SpringAOP的实现
对于 AOP 这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。Spring 就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。
AspectJ 是一个基于 Java 语言的 AOP 框架,它提供了强大的 AOP 功能,且其实现方式更为简捷,使用更为方便, 而且还支持注解式开发。所以,Spring 又将 AspectJ 的对于 AOP 的实现也引入到了自己的框架中
- 下载AOP相关jar
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
- 基于aspectj的xml配置方式实现
<bean id="aopdemo" class="com.ff.spring.aop.AopDemo"></bean>
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
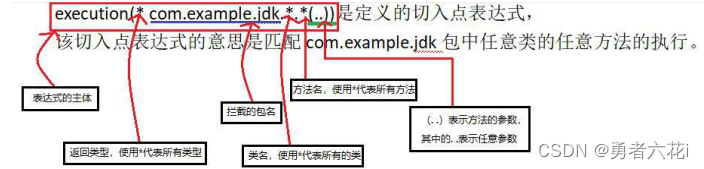
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(*
com.ff.spring.service.UserService.adduser(..))" id="adduser"/>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(*
com.ff.spring.service.UserService.*(..))" id="allmethod"/>
<!-- 配置通知和切入点 -->
<aop:aspect ref="aopdemo">
<aop:before method="savelog" pointcut-ref="adduser"/>
<aop:after method="savelog" pointcut-ref="adduser"/>
<aop:around method="aroundAdvice" pointcut-ref="adduser"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="exceptionAdvice" pointcut-ref="allmethod"
throwing="e" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
- AspectJ 中常用的通知有五种类型:
前置通知,后置通知,环绕通知,异常通知,最终通知
- 通知

基于注解方式的实现
启动 AspectJ 支持:<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
定义通知:
@Component
@Aspect
public class AOPDemo {
@Before("execution(* com.ff.spring.demo1.dao.UserDao.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("before");
}
@After("execution(* com.ff.spring.demo1.dao.UserDao.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("after");
}
@Around("execution(* com.ff.spring.demo1.dao.UserDao.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("start");
point.proceed();
System.out.println("end");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.ff.spring.demo1.dao.UserDao.*(..))",throwing = "e")
public void afterthrow(Throwable){
System.out.println("afterthrow");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.ff.spring.demo1.dao.UserDao.*(..))")
public void afterreturn(){
System.out.println("afterreturn");
}
}
Spring事务管理
事物可以看做是由对数据库若干操作组成的一个单元。
我们在开发企业应用时,对于业务人员的一个操作实际是对数据读写的多步操作的结合。由于数据操作在顺序执行的过程中,任何一步操作都有可能发生异常,异常会导致后续操作无法完成,此时由于业务逻辑并未正确的完成,之前成功操作数据的并不可靠,需要在这种情况下进行回退。
事务的作用就是为了保证用户的每一个操作都是可靠的,事务中的每一步操作都必须成功执行,只要有发生异常就回退到事务开始未进行操作的状态,这些操作要么都完成,要么都取消,从而保证数据满足一致性的要求
Spring 中的事务管理分为两种形式,一种是编程式事务,一种是声明式事务. 编 程 式 事 务 在 项 目 中 很 少 使 用 , 这 种 方 式 需 要 注 入 一 个 事 务 管 理 对 象TransactionTemplate ,然后在我们代码中需要提交事务或回滚事务时自己写代码实现. 声明式事务管理建立在 AOP 基础上,本质是对方法前后进行拦截,所以声明式事务是方法级别的。
Spring 声明式事物管理方式有两种:
基于 xml 配置
基于注解实现
Spring 针对不同的 dao 框架,提供了不同的实现类,Jdbc,mybatis 事物管理实现类是 DataSourceTransactionManager.
配置事物管理器
<!-- 配置 spring 事务管理类, 并注入数据源 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
注解方式
<!-- 开启注解事务管理 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
在 service 中控制事务
@Service(value=“userservice”)
@Transactional
声明式事务不生效的场景
@Transactional 应用在非 public 修饰的方法上
异常被 catch 捕获导致失效
出现编译期异常
@Transactional 事务传播行为设置错误
数据库引擎不支持事务
同一个类中,使用非代理对象调用一个有事务的方法,导致事务错误
Spring事务传播行为
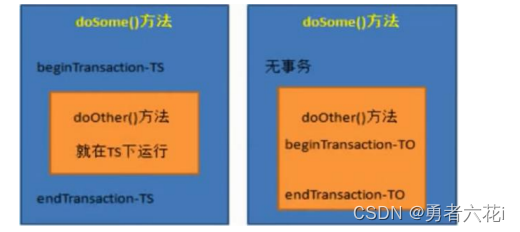
什么叫事务传播行为?
即然是传播,那么至少有两个东西,才可以发生传播。单体不存在传播这个行为。事务传播行为(propagation behavior)指的就是当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行。事务传播行为是 Spring 框架独有的事务增强特性,他不属于的事务实际提供方数据库行为. 例如:methodA 事务方法调用 methodB 事务方法时,methodB 是继续在调
用者 methodA 的事务中运行呢,还是为自己开启一个新事务运行,这就是由
methodB 的事务传播行为决定的。
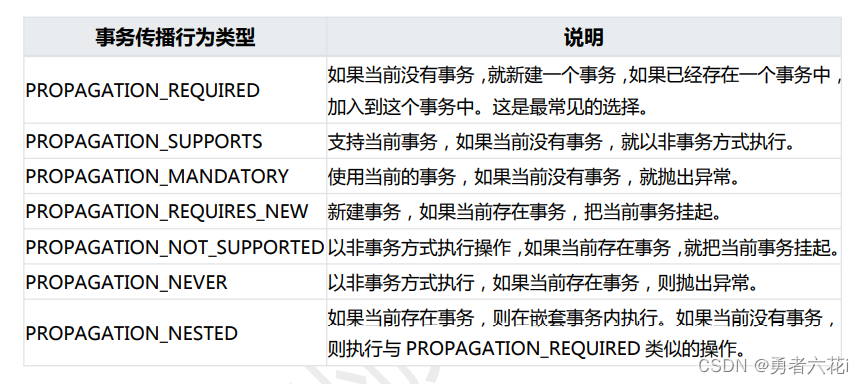
Spring 定义了七种传播行为:
-
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
指定的方法必须在事务内执行,若当前存在事务,加入到当前事务中,若当前没有事务,则创建一个新事务,这种传播行为是最常见的,也是 spring 默认的传播行为
-
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS
支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
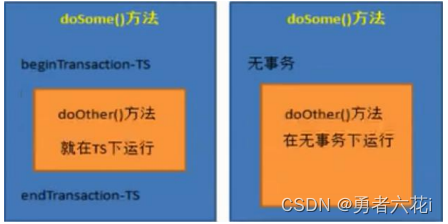
-
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
总是新建一个事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起,直到新建的事务结束。
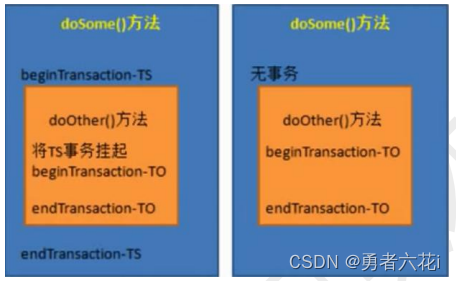
Spring集成Mybatis
Spring 集成 Mybatis 其核心是将 SqlSessionFactory 交由 Spring 管理,并由
Spring 管理对 dao 接口的代理实现。
导入 mybatis jar 包
- Spring 结合 mybatis 插件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
- 配置 sqlSessionFactor
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"></property>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="com/ff/*Mapper.xml">
</property>
</bean>
- 指定生成接口代理
<bean id="mapperFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.ff.ssm.dao"></property>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory">
</property>
</bean>
- 在 service 中注入 Dao 代理接口,此接口有 Spring
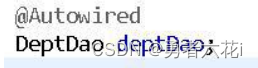





















 8万+
8万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










