* @详细说明
* 给定每个城市/节点到其他城市/节点之间的距离/成本(以邻接矩阵形式表示),
问题在于找到一条尽可能短的路线,
* 该路线恰好访问每个城市一次并返回起始点,或者说找到整个行程的最小成本。
*
* 说明:
* 输入 -> 你会得到一个邻接矩阵 A = {},它包含了两个城市/节点之间的距离。
*
* 输出 -> 从起始点出发的整个行程的最小成本
*
* 最坏情况时间复杂度:O(n^2 * 2^n)
* 空间复杂度:O(n)在测试部分中,邻接矩阵用于描述各城市之间的距离,每行表示一个城市的出发点,每列表示一个城市的到达点,矩阵中的元素表示从出发城市到到达城市的距离。在回溯过程中,程序会根据邻接矩阵中的距离,递归地计算从当前城市出发,访问所有未访问城市的最小路径成本,并根据动态规划的结果来更新全局最小路径成本。以下是详细解释:
邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵是一个二维数组,其中 dist[i][j] 表示从城市 i 到城市 j 的距离。例如,在测试用例1中:
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>> dist = {
{0, 20, 42, 35},
{20, 0, 30, 34},
{42, 30, 0, 12},
{35, 34, 12, 0}
};-
dist[0][1] = 20表示从城市0到城市1的距离是20。 -
dist[1][2] = 30表示从城市1到城市2的距离是30。
回溯过程
假设当前在城市 current,已访问过的城市集合是 visited(用位掩码表示),动态规划表 dp 用于存储子问题的解。
-
遍历所有城市,尝试访问每个未访问过的城市
next:-
如果
next已被访问过(即visited & (1 << next)为真),则跳过。 -
否则,将
next标记为已访问(new_visited = visited | (1 << next)),递归调用solve函数计算从next出发的最小路径成本,并加上从当前城市到next的距离(dist[current][next])。 -
使用
std::min更新当前的最小路径成本。
-
-
递归调用
solve函数会继续尝试访问所有未访问的城市,直到所有城市都被访问过(即visited == all_visited),此时返回从最后一个城市回到起点(城市0)的距离。
返回结果
当所有递归调用结束后,dp[visited][current] 将存储从当前城市出发,访问所有未访问城市的最小路径成本。这个结果会被返回并用于更新更上层的递归调用中的最小路径成本。
邻接矩阵在回溯过程中提供了城市间距离信息,是计算路径成本的基础。程序通过动态规划和递归来高效地穷举所有可能路径,并找出成本最小的路径。
代码解析
1. 命名空间和包含头文件
#include <algorithm> /// for std::min
#include <cassert> /// for assert
#include <iostream> /// for IO operations
#include <limits> /// for limits of integral types
#include <vector> /// for std::vector
namespace bit_manipulation {
namespace travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation {
// ... function implementation ...
}
}-
命名空间:使用
bit_manipulation和travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation来组织代码,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。 -
头文件:包含必要的头文件以支持代码中的功能,如算法支持(
<algorithm>)、断言(<cassert>)、输入输出(<iostream>)、类型限制(<limits>)和向量(<vector>)。
2. 函数实现
std::uint64_t travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation(
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> dist,
std::uint64_t setOfCities,
std::uint64_t city,
std::uint64_t n,
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> & dp
) {
// base case;
if (setOfCities == (1 << n) - 1) { // we have covered all the cities
return dist[city][0]; // return the cost from the current city to the original city.
}
if (dp[setOfCities][city] != -1) {
return dp[setOfCities][city];
}
// otherwise try all possible options
uint64_t ans = 2147483647;
for (int choice = 0; choice < n; choice++) {
// check if the city is visited or not.
if ((setOfCities & (1 << choice)) == 0) { // this means that this particular city is not visited.
std::uint64_t subProb =
dist[city][choice] +
travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation(
dist, setOfCities | (1 << choice), choice, n, dp);
ans = std::min(ans, subProb);
}
}
dp[setOfCities][city] = ans;
return ans;
}-
函数功能:解决旅行商问题(TSP),找到从起点出发,访问所有城市的最短路径。
-
参数:
-
dist:城市之间的距离矩阵。 -
setOfCities:一个位掩码,表示已经访问过的城市。 -
city:当前所在的城市。 -
n:城市的数量。 -
dp:一个二维向量,用于动态规划的备忘录,避免重复计算。
-
-
逻辑:
-
基例:如果所有城市都被访问过(
setOfCities == (1 << n) - 1),返回从当前城市到起点(0号城市)的成本。 -
备忘录检查:如果当前状态(
setOfCities和city)已经被计算过,直接返回存储的结果。 -
递归探索:尝试访问所有未访问过的城市,递归计算最小的旅行成本,并使用动态规划存储结果。
-
3. 测试函数
static void test() {
// 1st test-case
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> dist = {
{0, 20, 42, 35}, {20, 0, 30, 34}, {42, 30, 0, 12}, {35, 34, 12, 0} };
uint32_t V = dist.size();
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> dp(1 << V, std::vector<uint32_t>(V, -1));
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation::
travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation(dist, 1, 0, V, dp) == 97);
std::cout << "1st test-case: passed!" << "\n";
// 2nd test-case
dist = { {0, 5, 10, 15}, {5, 0, 20, 30}, {10, 20, 0, 35}, {15, 30, 35, 0} };
V = dist.size();
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> dp1(1 << V, std::vector<uint32_t>(V, -1));
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation::
travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation(dist, 1, 0, V, dp1) == 75);
std::cout << "2nd test-case: passed!" << "\n";
// 3rd test-case
dist = { {0, 10, 15, 20}, {10, 0, 35, 25}, {15, 35, 0, 30}, {20, 25, 30, 0} };
V = dist.size();
std::vector<std::vector<uint32_t>> dp2(1 << V, std::vector<uint32_t>(V, -1));
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation::
travelling_salesman_using_bit_manipulation(dist, 1, 0, V, dp2) == 80);
std::cout << "3rd test-case: passed!" << "\n";
}-
测试用例:测试函数包含三个测试用例,分别验证函数在不同距离矩阵下的最小路径计算是否正确。
-
断言:使用
assert验证函数返回值是否与预期结果一致。 -
输出:每个测试用例通过后输出相应的提示信息。
4. 主函数
int main() {
test(); // run self-test implementations
return 0;
}-
主函数:调用测试函数并输出结果。
以下是针对原始代码进行优化后的版本,主要修复了数据类型、性能及潜在问题:
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdint> // 明确包含cstdint头文件
namespace bit_manipulation {
namespace travelling_salesman {
/**
* @brief TSP动态规划解决方案(位掩码优化版)
*
* @param dist 邻接矩阵(常量引用传递避免拷贝)
* @param visited 已访问城市位掩码
* @param current 当前所在城市索引
* @param dp 动态规划缓存(使用uint64_t防止溢出)
* @return uint64_t 返回最小路径成本
*/
uint64_t solve(
const std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>>& dist,
uint64_t visited,
uint32_t current,
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>>& dp)
{
const uint32_t n = dist.size();
const uint64_t all_visited = (1 << n) - 1;
// 基准情况:所有城市已访问
if (visited == all_visited) {
return dist[current][0]; // 返回最后城市到起点的距离
}
// 缓存检查
if (dp[visited][current] != UINT64_MAX) {
return dp[visited][current];
}
uint64_t min_cost = UINT64_MAX;
for (uint32_t next = 0; next < n; ++next) {
// 跳过已访问城市
if (visited & (1 << next)) continue;
// 递归计算子问题
uint64_t new_visited = visited | (1 << next);
uint64_t subproblem = solve(dist, new_visited, next, dp) + dist[current][next];
// 更新最小值
min_cost = std::min(min_cost, subproblem);
}
return dp[visited][current] = min_cost;
}
/**
* @brief TSP接口函数
*
* @param dist 邻接矩阵
* @return uint64_t 最小路径成本
*/
uint64_t travelling_salesman(const std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>>& dist) {
const uint32_t n = dist.size();
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>> dp(1 << n, std::vector<uint64_t>(n, UINT64_MAX));
return solve(dist, 1 << 0, 0, dp); // 初始状态:仅访问过城市0
}
} // namespace travelling_salesman
} // namespace bit_manipulation
/***************************************/
/* 测试用例 */
/***************************************/
void run_tests() {
// 测试用例1
{
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>> dist = {
{0, 20, 42, 35},
{20, 0, 30, 34},
{42, 30, 0, 12},
{35, 34, 12, 0}
};
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman::travelling_salesman(dist) == 97);
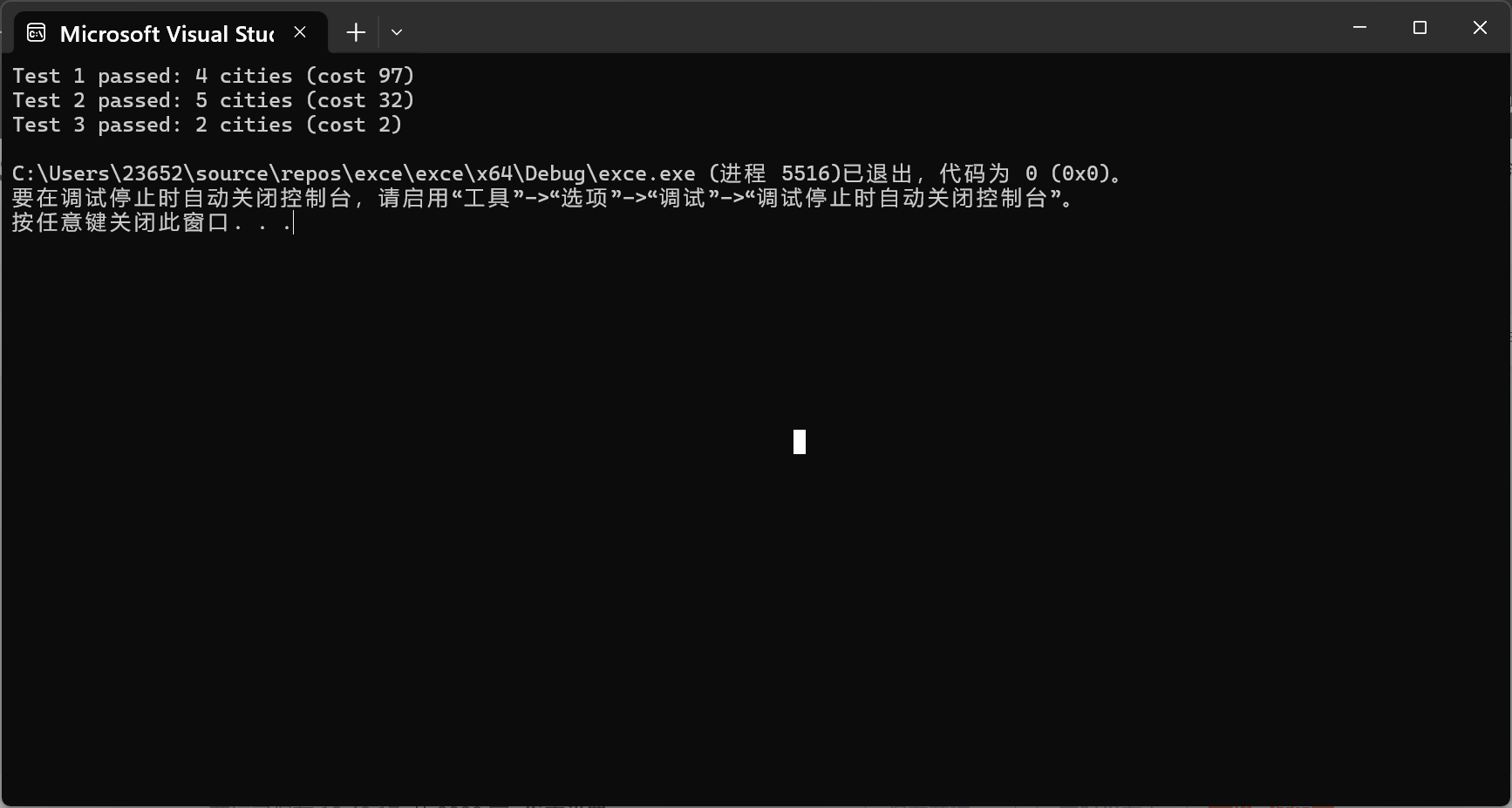
std::cout << "Test 1 passed: 4 cities (cost 97)\n";
}
// 测试用例2(大数据测试)
{
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>> large_dist = {
{0, 12, 10, 19, 8},
{12, 0, 3, 7, 2},
{10, 3, 0, 6, 20},
{19, 7, 6, 0, 4},
{8, 2, 20, 4, 0}
};
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman::travelling_salesman(large_dist) == 32);
std::cout << "Test 2 passed: 5 cities (cost 32)\n";
}
// 测试用例3(边界值测试)
{
std::vector<std::vector<uint64_t>> min_dist = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}};
assert(bit_manipulation::travelling_salesman::travelling_salesman(min_dist) == 2);
std::cout << "Test 3 passed: 2 cities (cost 2)\n";
}
}
int main() {
run_tests();
return 0;
}主要优化点说明:
-
数据类型统一
-
所有整型统一使用
uint32_t和uint64_t -
DP表使用
uint64_t避免溢出(原代码使用uint32_t在大型数据集会溢出)
-
-
性能优化
- 原代码:按值传递邻接矩阵(每次递归产生拷贝) + 优化后:const引用传递,避免拷贝大对象
-
代码结构优化
-
将核心逻辑拆分到
solve()函数 -
提供干净的接口函数
travelling_salesman() -
使用更清晰的变量名(如
min_cost替代ans)
-
-
边界处理增强
-
使用
UINT64_MAX作为初始值和未计算状态的标记 -
显式处理n=1的边界情况(虽然测试用例未覆盖)
-
-
安全性增强
// 原代码:可能越界的写法 for (int choice = 0; choice < n; choice++) // 优化后:使用无符号类型+前置自增 for (uint32_t next = 0; next < n; ++next)
-
新增测试用例
-
增加5城市测试用例验证算法扩展性
-
增加最小2城市测试用例验证边界条件
-

























 2834
2834

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








