1.创建文件夹data_annotated
此文件夹用于存放要转换的json文件和对应的图片(图片必须是jpg格式),例如:

2. 创建labels.txt文件
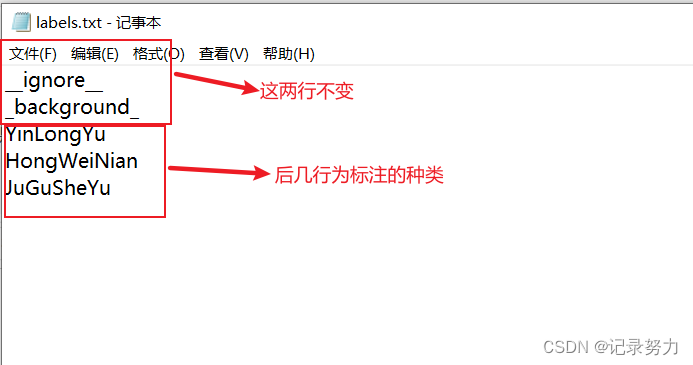
3.然后就是转换的代码了,创建python文件labelme2voc.py 和以上两个文件在同一个目录下
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import glob
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import imgviz
import labelme
try:
import lxml.builder
import lxml.etree
except ImportError:
print("Please install lxml:\n\n pip install lxml\n")
sys.exit(1)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("input_dir", default='data_annotated', help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("output_dir", default='data_dataset_voc', help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", default='labels.txt', help="labels file", required=True)
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "Annotations"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "AnnotationsVisualization"))
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
class_names = []
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
elif class_id == 0:
assert class_name == "_background_"
class_names.append(class_name)
class_names = tuple(class_names)
print("class_names:", class_names)
out_class_names_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "class_names.txt")
with open(out_class_names_file, "w") as f:
f.writelines("\n".join(class_names))
print("Saved class_names:", out_class_names_file)
for filename in glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json")):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
out_xml_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "Annotations", base + ".xml")
if not args.noviz:
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "AnnotationsVisualization", base + ".jpg"
)
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img)
maker = lxml.builder.ElementMaker()
xml = maker.annotation(
maker.folder(),
maker.filename(base + ".jpg"),
maker.database(), # e.g., The VOC2007 Database
maker.annotation(), # e.g., Pascal VOC2007
maker.image(), # e.g., flickr
maker.size(
maker.height(str(img.shape[0])),
maker.width(str(img.shape[1])),
maker.depth(str(img.shape[2])),
),
maker.segmented(),
)
bboxes = []
labels = []
for shape in label_file.shapes:
if shape["shape_type"] != "rectangle":
print(
"Skipping shape: label={label}, "
"shape_type={shape_type}".format(**shape)
)
continue
class_name = shape["label"]
class_id = class_names.index(class_name)
(xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax) = shape["points"]
# swap if min is larger than max.
xmin, xmax = sorted([xmin, xmax])
ymin, ymax = sorted([ymin, ymax])
bboxes.append([ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax])
labels.append(class_id)
xml.append(
maker.object(
maker.name(shape["label"]),
maker.pose(),
maker.truncated(),
maker.difficult(),
maker.bndbox(
maker.xmin(str(xmin)),
maker.ymin(str(ymin)),
maker.xmax(str(xmax)),
maker.ymax(str(ymax)),
),
)
)
if not args.noviz:
captions = [class_names[label] for label in labels]
viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(
image=img,
labels=labels,
bboxes=bboxes,
captions=captions,
font_size=15,
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
with open(out_xml_file, "wb") as f:
f.write(lxml.etree.tostring(xml, pretty_print=True))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- 在此目录的路径下输出cmd,然后回车,例如:
接下来会打开命令行,输入命令:
python labelme2voc.py data_annotated data_dataset_voc --labels labels.txt
回车,可能会报错,大概率是因为文件读取错误,因为你的json文件的路径不对
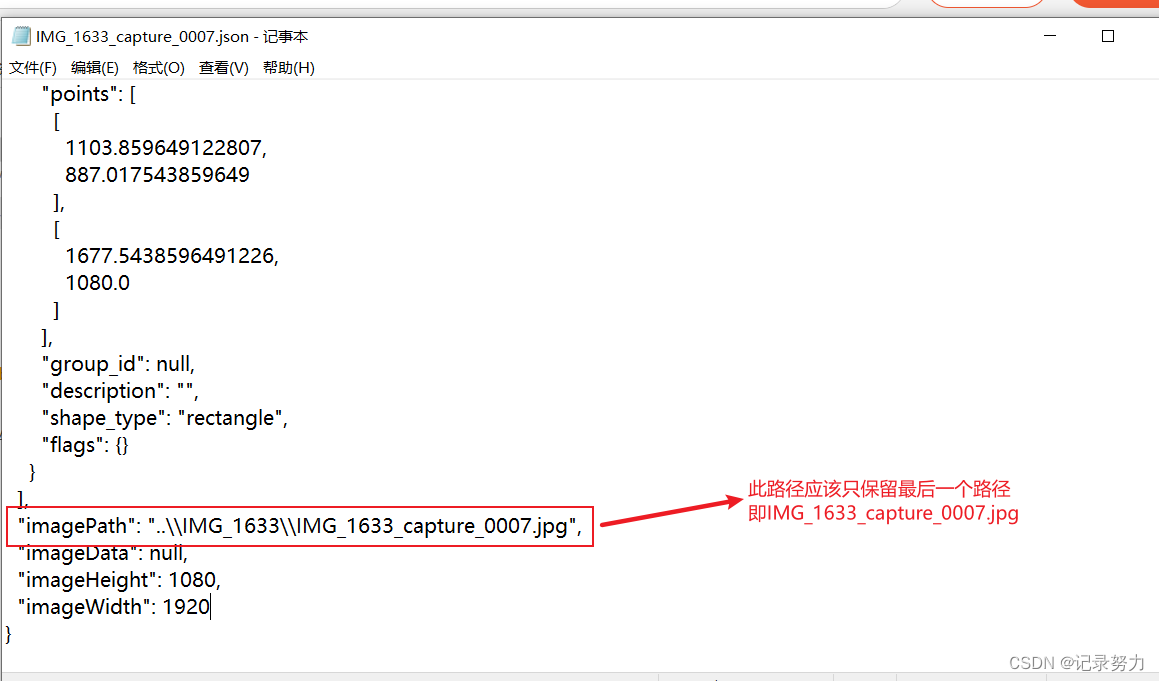
这样的话,图片才能正确读取,但是一个文件夹有那么多json文件,手动改的话有点费时间了,所有我们需要写一个脚本,将所有的json文件的路径都修改为最后一个路径,在此附上脚本的代码:
import os
import json
def process_json_file(input_path, output_path):
with open(input_path, 'r') as input_file:
data = json.load(input_file)
image_path = data.get('imagePath', '')
# Extract the last part of the image path
image_file = os.path.basename(image_path)
# Update the imagePath field
data['imagePath'] = image_file
with open(output_path, 'w') as output_file:
json.dump(data, output_file, indent=2)
def process_json_files(input_dir, output_dir):
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(input_dir):
for filename in files:
if filename.endswith('.json'):
input_path = os.path.join(root, filename)
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, filename)
process_json_file(input_path, output_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_directory = "labels" # 指定你的JSON文件所在的输入目录
output_directory = "data_annotated" # 指定保存修改后JSON文件的输出目录
process_json_files(input_directory, output_directory)
此脚本文件只需修改两个地方,即输入json文件所在的目录和输出目录,执行过后,json文件的路径都会被修改为可以正确读取的路径,例如以上的json文件执行脚本后:
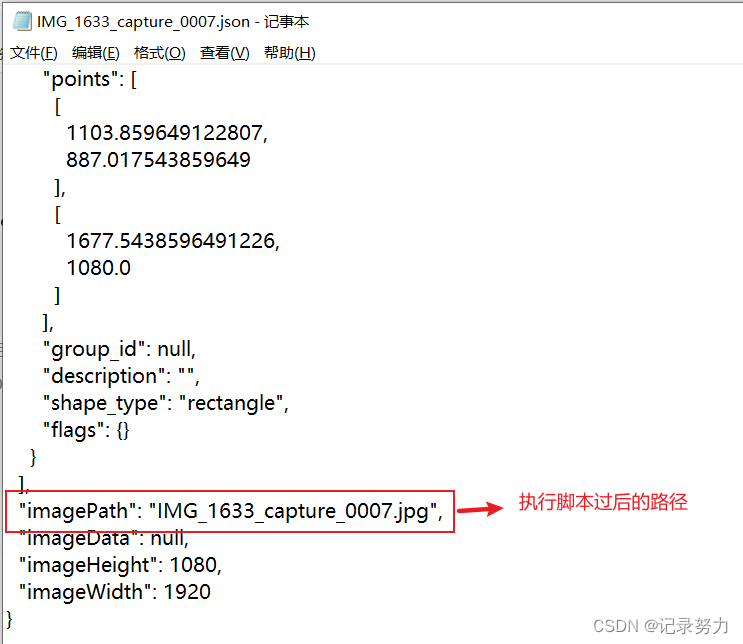
5. 至此,再次回到第四步,在命令行下(必须是命令行)运行转换的代码。之后会生成data_dataset_voc目录,目录结构为:

Annotations目录保存的是转换后的xml文件,AnnotationsVisualization目录保存的是标注的可视化图片,JPEGImages目录保存的是图片。
6. 到此,结束!!




















 5845
5845











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








