目录
前言:
强烈建议先看栈的用法与实现
队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头

队列的实现
队列可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低,因为要从后面向前进行覆盖数据。
队列的定义
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
//size_t size;
}Queue;这里我们以单链表为基础,再定义一个头指针 head 一个尾指针 tail ,这两个指针才有意义。因为根据队列的性质,我们只会在队尾插,不会再队尾删。所以这个尾指针的价值就得到了完美的体现,实际中定义几个指针是看你的需求确定的
接口函数
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
实现接口函数
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL) //第一个元素
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head && pq->tail);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
return pq->head == NULL;
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}完整代码
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
//typedef struct QueueNode
//{
// QDataType data;
// struct QueueNode* next;
//}QNode, *PNode;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
//size_t size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
Queue.c
接口函数加 #include "Queue.h" 即可
栈与队列的OJ练习
强烈建议先看:数据结构 - c语言栈的基本操作
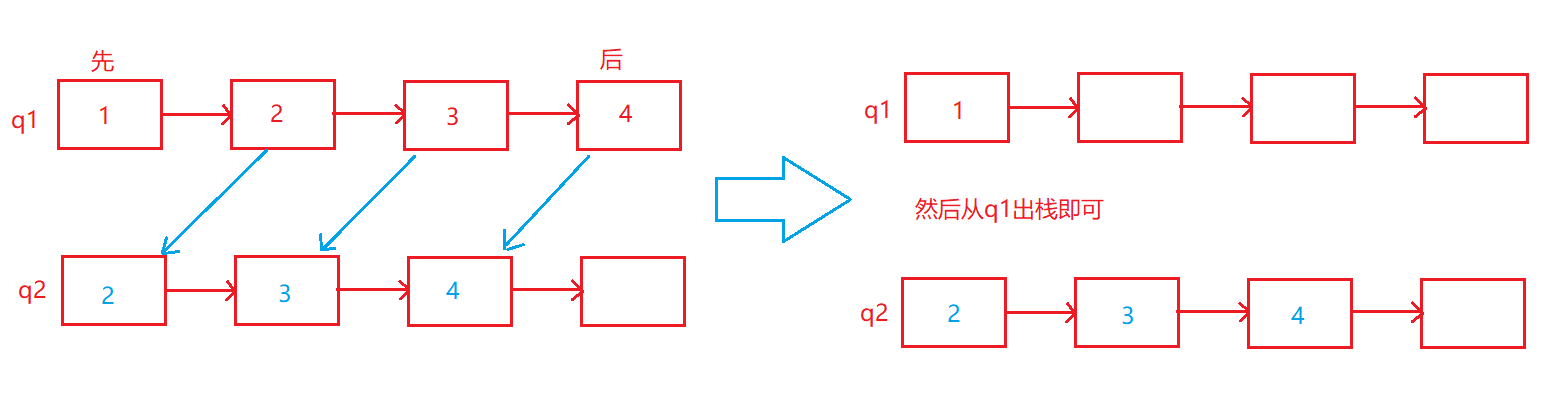
T1、用队列实现栈

思路:
1、入栈,push数据到不为空的队列
2、出栈,把不为空的队列的数据前N-1导入另一个空队列,最后剩下的一个删掉。

本质:保持一个队列存储数据,另外一个队列空着,要出栈时,空队列用来倒数据
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue*pq,QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue*pq);
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head =pq->tail = NULL;
}
QNode* BuyQNode(QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("fail malloc\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = BuyQNode(x);
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head= pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail&&pq->head);
if (pq->head->next==NULL)//处理只有一个节点的时候
{
free(pq->tail);
pq->tail = pq->head = NULL;
}
else//有多个节点
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
size_t size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur!= pq->tail->next)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head==NULL&&pq->tail==NULL;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
assert(pst);
QueueInit(&pst->q1);//这一行代码和后面这一行代码等价:QueueInit(&(pst->q1));
QueueInit(&pst->q2);//这一行代码和后面这一行代码等价:QueueInit(&(pst->q2));
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
Queue *emptyQ = &obj->q1;
Queue*nonEmptyQ = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyQ = &obj->q2;
nonEmptyQ = &obj->q1;
}
//把非空队列的前N个数据,导入空队列,剩下一个删掉
//就实现了后进先出
while(QueueSize(nonEmptyQ)>1)
{
QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(nonEmptyQ));//将非空队列的队头数据push到非空队列中
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);//将非空队列的队头数据出队
}
QDataType top = QueueFront(nonEmptyQ);
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
C++写法:

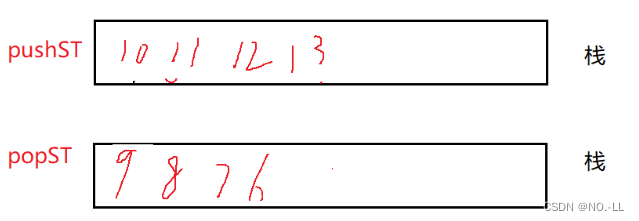
T2、用栈实现队列

思路:
建立两个栈,一个栈用来入队叫做pushST,一个栈用来出队,叫做popST;
在队popST中的数据进行操作(出队)时,如果popST中没有数据就将pushST中的数据都推送到popST中
typedef int STDataType;
//数组栈的实现
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;//栈顶的位置
int capacity;//容量
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST*ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity =ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//满了进行扩容
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 2 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType*new = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType)*newCapacity);
if (new == NULL)
{
printf("fail malloc\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = new;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top++] = x;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int SizeStack(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
void StackInit(ST*ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps,STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
int SizeStack(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
typedef struct {
ST pushST;
ST popST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue * myQueue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
assert(myQueue);
StackInit(&myQueue->pushST);
StackInit(&myQueue->popST);
return myQueue;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(&obj->pushST,x);//入队直接向pushST插入即可
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj){
assert(obj);
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))//push为空,就进行倒数据,就符合先进先出的顺序了
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
STDataType ret = StackTop(&obj->popST);//临时保存返回的数据
StackPop(&obj->popST);
return ret;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->popST);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)&&StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
StackDestory(&obj->pushST);
StackDestory(&obj->popST);
free(obj);
}
注意:在上面的代码中,在进行出队操作时,只要popST这个栈中有数据,那么我们就不进行倒数据的操作(即将pushST中的数据倒到popST这个栈中),只有当pop中的数据为空且我们要进行出队时才进行倒数据。
C++实现
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> in,out;
void in2out()
{
while(!in.empty())
{
out.push(in.top());
in.pop();
}
}
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(out.empty())
{
in2out();
}
int x=out.top();
out.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if(out.empty())
in2out();
return out.top();
}
bool empty() {
return in.empty()&&out.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/T3、设计循环队列
tail=rear;
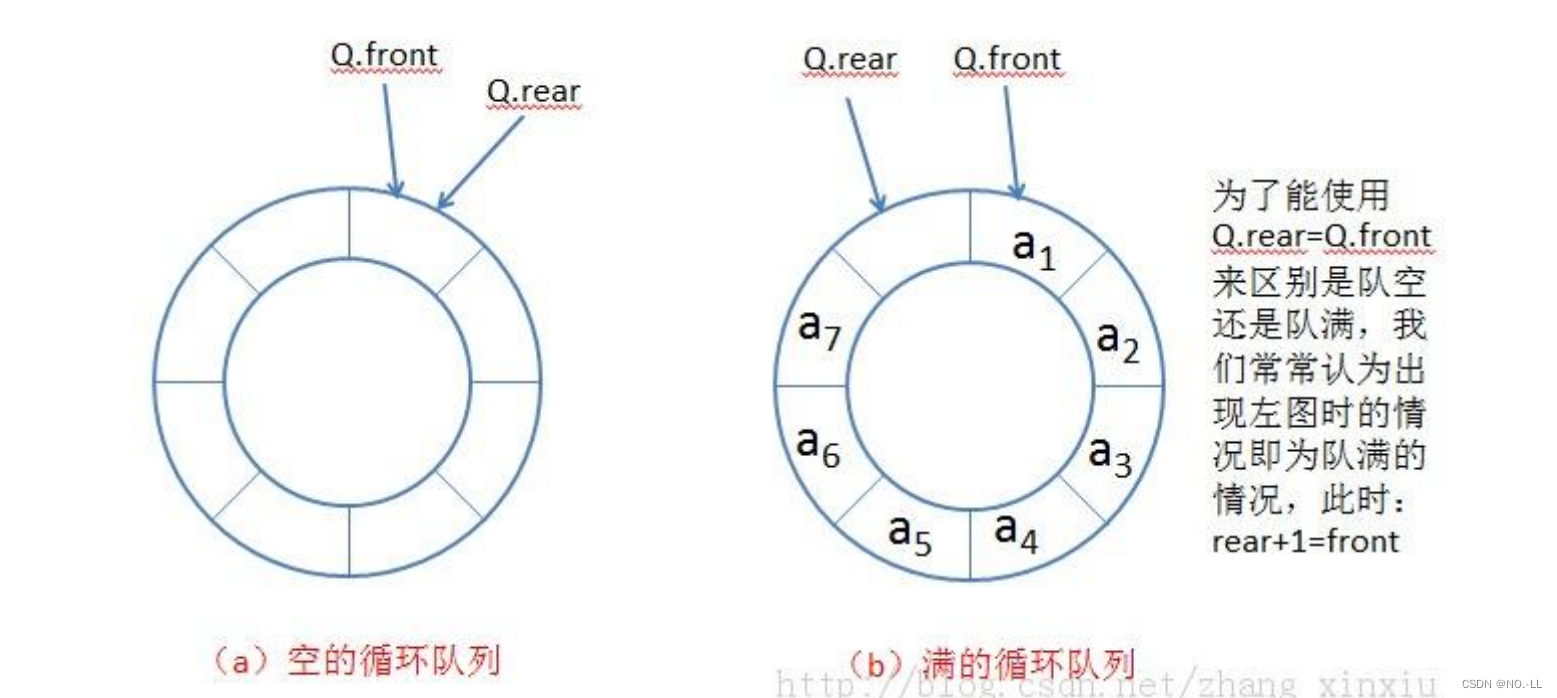
为了避免空和满混淆,无法区分,多开一个空间。
1. front = tail时是空
2. tail+1 = front时是满
然而我们是用链表实现,所以满会有两种情况:
1、
obj->tail = k && obj->head = 0
2、
obj->tail+1 = obj->head
typedef struct {
int *a;
int head;//循环队列的头
int tail;//循环队列的尾
int capacity;//循环队列元素的最大数目
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);//判断循环队列是否为空的声明
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);//判断循环队列是否为满的声明
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) //循环队列的初始化
{
MyCircularQueue*myCircularQ = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
assert(myCircularQ);
int *tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
assert(tmp);
myCircularQ->a = tmp;
myCircularQ->head = 0;
myCircularQ->tail = 0;
myCircularQ->capacity = k;
return myCircularQ;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) //向循环队列插入一个元素,如果成功插入则返回真。
{
assert(obj);
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))//满了的情况
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->tail] = value;
if(obj->tail==obj->capacity)//此时已经到达了开辟数组的最后一个位置,tail再进行++操作后会跳跃到第一个位置
{
obj->tail = 0;
}
else
{
++obj->tail;
}
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) //从循环队列中删除一个元素,如果成功删除则返回真。
{
assert(obj);
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))//循环队列中为空的情况
{
return false;
}
if(obj->head==obj->capacity)//循环队列中的head在开辟的最后的一个空间位置的情况,head要发生跳跃
{
obj->head = 0;
}
else
{
++obj->head;
}
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) //从队首获取元素,如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
{
assert(obj);
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))//队列元素为空的情况
return -1;
return obj->a[obj->head];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)//获取队尾元素,如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
{
assert(obj);
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))//循环队列元素为空的情况
return -1;
if(obj->tail==0)//尾在头的时候,就要返回最后一个空间的位置
{
return obj->a[obj->capacity];
}
else
{
return obj->a[obj->tail-1];//正常情况返回tail的前一个位置
}
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) //判断循环队列是否满
{
assert(obj);
return obj->tail==obj->head;//尾下标等于头下标的时候就是空
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) //判断循环队列是否满
{
assert(obj);
if(obj->tail==obj->capacity && obj->head==0)//判断的是尾下标指向最后一块空间,头下标在最靠前的空间
{
return true;
}
else
{
return obj->tail+1 ==obj->head;
}
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) //循环队列的销毁
{
assert(obj);
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
C++版本
class MyCircularQueue {
private:
int front;
int rear;
int capacity;
vector<int> elements;
public:
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this->capacity = k + 1;
this->elements = vector<int>(capacity);
rear = front = 0;
}
bool enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elements[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
bool deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[front];
}
int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
bool isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
bool isFull() {
return ((rear + 1) % capacity) == front;
}
};
栈和队列的用途
栈:用来解决括号匹配,逆波兰表达式的求解,递归改非递归等等。
队列:公平排队,广度优先遍历等等。

























 1290
1290











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










