目录
1. Regularized Linear Regression
1.2 Regularized linear regression cost function
1.3 Regularized linear regression gradient
3.1 Learning Polynomial Regression
3.2 Adjusting the regularization parameter
3.3 Selecting λ using a cross validation set
1. Regularized Linear Regression
内容:我们将用正则化线性回归,使用水库中水位的变化来预测从大坝流出的水量。
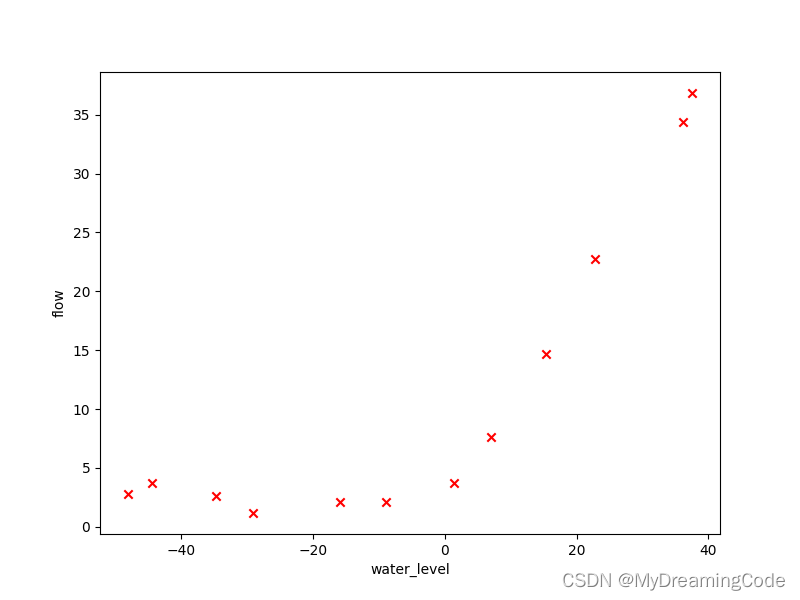
1.1 Visualizing the dataset
内容:水位—X;水流量—y。将数据分成训练集、交叉验证集以及测试集。
plot.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plotTrainingData(X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, marker='x', c='r')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from plot import * # 绘图
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
# print(X.shape, y.shape, Xval.shape, yval.shape, Xtest.shape, ytest.shape) #(12, 1) (12, 1) (21, 1) (21, 1) (21, 1) (21, 1)
plotTrainingData(X, y)
1.2 Regularized linear regression cost function
内容:计算带正则项的代价函数。
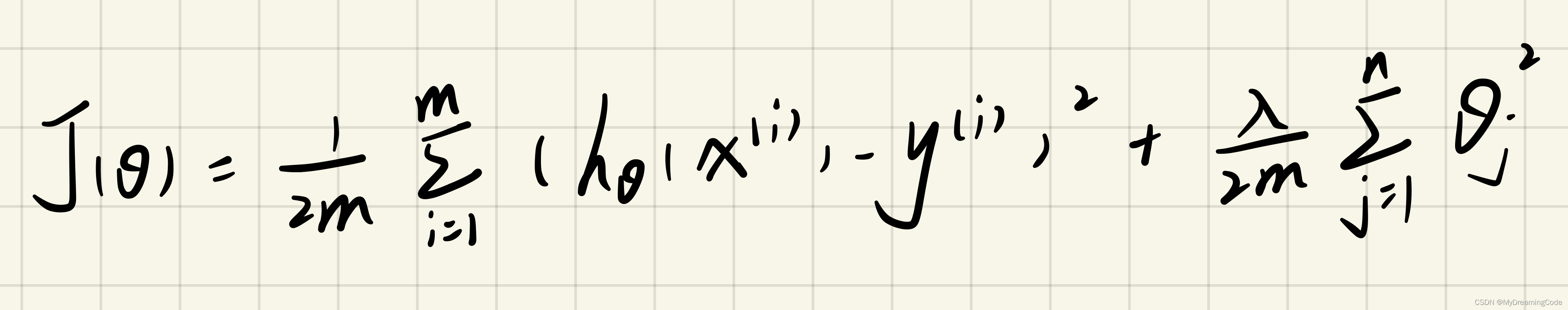
内容:正则化相当于在代价函数中增加了惩罚项,当theta(j)增大时,惩罚项也会增大。注意不需要将theta(0)进行正则化。
linearRegCostFunction.py
import numpy as np
def linearRegCostFunction(theta, X, y, learningRate):
theta = np.matrix(theta)
m = X.shape[0]
X = np.insert(X, 0, np.ones(m), axis=1)
reg = (learningRate / (2 * m)) * np.sum(np.power(theta[1:, :], 2))
return np.sum(np.power(X * theta.T - y, 2)) / (2 * m) + reg
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 正则化代价函数
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
theta = [1, 1]
learningRate = 1
print(linearRegCostFunction(theta, X, y, learningRate)) # 303.9515255535976
1.3 Regularized linear regression gradient
内容:求正则化线性回归的梯度。
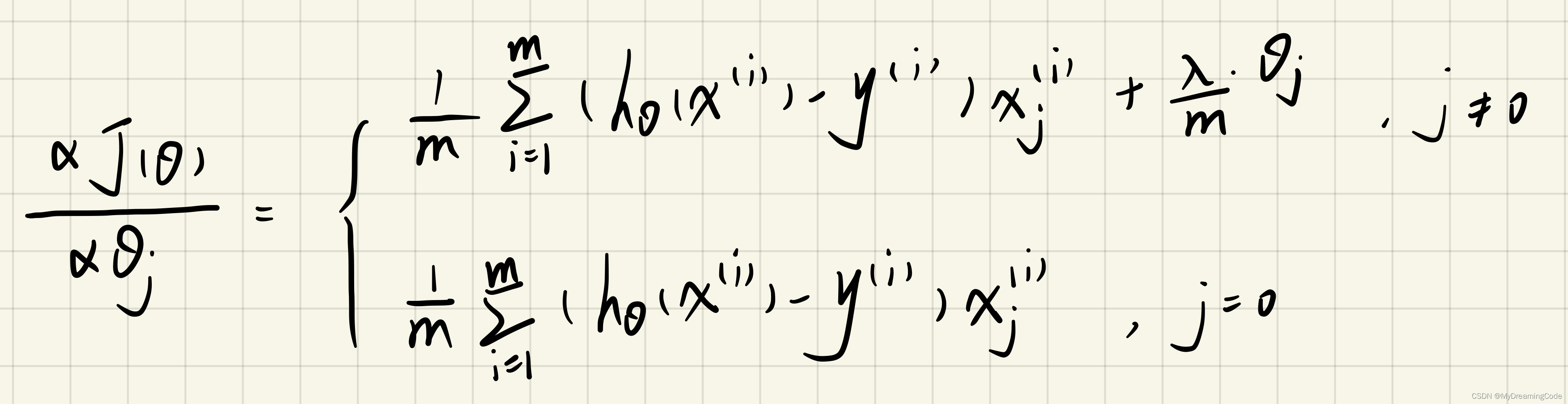
gradientReg.py
import numpy as np
def gradientReg(theta, X, y, learningRate):
m = X.shape[0]
X = np.matrix(X)
X = np.insert(X, 0, np.ones(m), axis=1)
y = np.matrix(y)
theta = np.matrix(theta)
grad = (((X * theta.T - y).T * X).T + learningRate * theta.T) / m
grad[0] = (X * theta.T - y).T * X[:, 0] / m
return grad
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from gradientReg import * # 正则化线性回归的梯度
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
theta = [1, 1]
learningRate = 1
gradient = gradientReg(theta, X, y, learningRate)
print(gradient)
# [[-15.30301567]
# [598.25074417]]
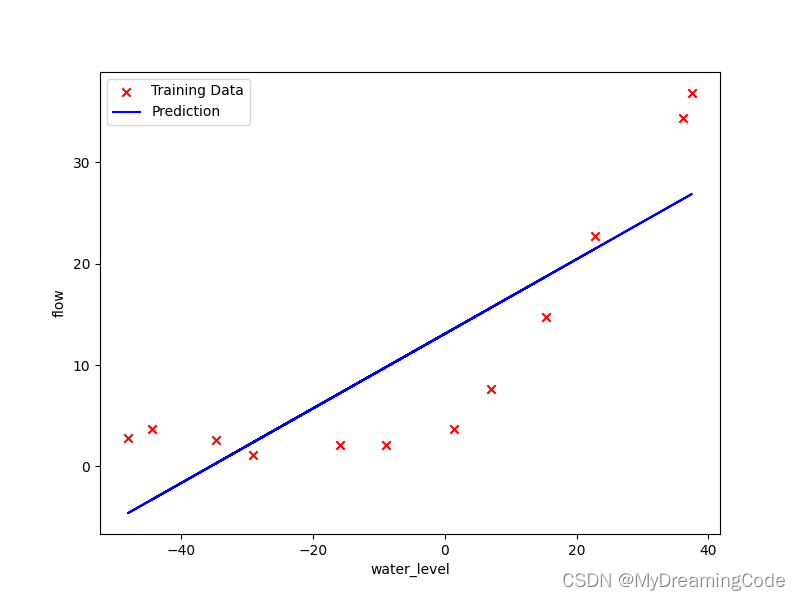
1.4 Fitting linear regression
内容:使用训练好的theta参数,可视化数据和拟合曲线。(因为theta在这里是二维的,正则化对它没有太大的作用,所以在这里可以让 λ=0)
plot.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plotTrainingData(X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, marker='x', c='r')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
plt.show()
def plotHypothesis(theta, X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker='x', label='Training Data')
ax.plot(X, theta[0] + theta[1] * X, c='b', label='Prediction')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize # 优化
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 代价函数
from gradientReg import * # 梯度
from plot import * # 绘制拟合曲线
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
theta = np.ones(X.shape[1] + 1)
final_theta = minimize(fun=linearRegCostFunction, x0=theta, args=(X, y, 0), method='TNC', jac=gradientReg)['x']
# print(final_theta) # [13.08790348 0.36777923]
plotHypothesis(final_theta, X, y)
2. Bias-Variance
内容:偏差与方差需要权衡,因为高偏差容易欠拟合,高方差容易过拟合,我们会绘制出学习曲线,来诊断高偏差或是高方差的问题。
2.1 Learning curves
内容:
(1)函数的自变量为训练集的子集;
(2)训练代价与验证集代价(无需正则化):

linearRegression.py
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 代价函数
from gradientReg import * # 梯度
def linearRegression(X, y, learningRate=1):
theta = np.ones(X.shape[1] + 1)
res = minimize(fun=linearRegCostFunction, x0=theta, args=(X, y, learningRate), method='TNC', jac=gradientReg)
return res.x
learningCurve.py
from linearRegression import * # 线性回归
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 计算代价函数
from plot import * # 绘制学习曲线
def learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval):
m = X.shape[0]
train_cost = []
cv_cost = []
for i in range(1, m + 1):
# 随着训练集大小的不断增加,求出对应的最好的theta(能够使代价函数最小)
res = linearRegression(X[:i, :], y[:i], 0)
t = linearRegCostFunction(res, X[:i, :], y[:i], 0)
cv = linearRegCostFunction(res, Xval, yval, 0)
train_cost.append(t)
cv_cost.append(cv)
plotLearningCurve(X, train_cost, cv_cost)
plot.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plotTrainingData(X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, marker='x', c='r')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
plt.show()
def plotHypothesis(theta, X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker='x', label='Training Data')
ax.plot(X, theta[0] + theta[1] * X, c='b', label='Prediction')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
def plotLearningCurve(X, train_cost, cv_cost):
m = X.shape[0]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), train_cost, label='training cost')
ax.plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), cv_cost, label='cross validation cost')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('m(training set size)')
ax.set_ylabel('error')
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from learningCurve import * # 学习曲线
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval)
高偏差(欠拟合)的情况:
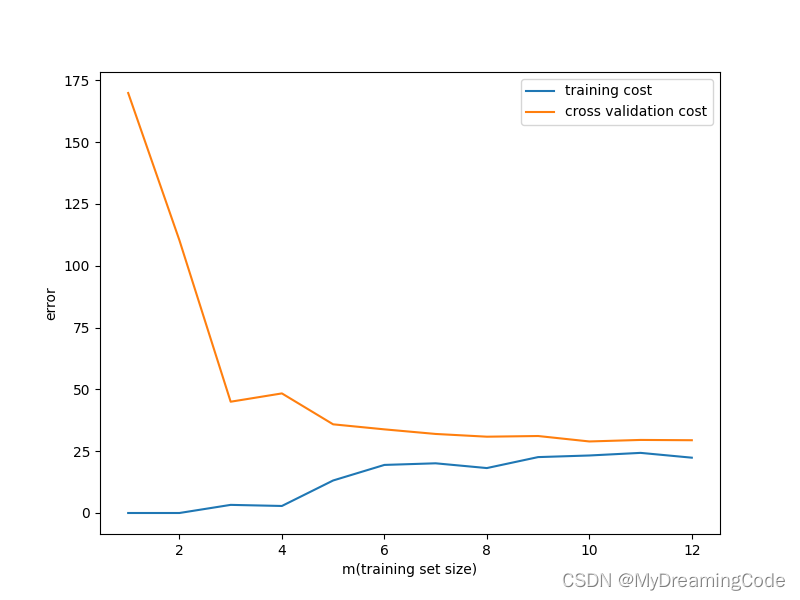
3. Polynomial regression
内容:线性回归模型对于数据的拟合有些差,容易出现欠拟合现象,我们需要再添加一些特征。

polyFeatures.py
import pandas as pd # 一种用于数据分析的扩展程序库
import numpy as np
def polyFeatures(X, power):
# 注意F(i)的每一个对应值可以是一个一维数组,所以用ravel进行展开
data = {"F{}".format(i): np.power(X.ravel(), i) for i in range(1, power + 1)}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from polyFeatures import * # 增加特征
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
polyFeatures(X, 3)
F1 F2 F3
0 -15.936758 253.980260 -4047.621971
1 -29.152979 849.896197 -24777.006175
2 36.189549 1309.683430 47396.852168
3 37.492187 1405.664111 52701.422173
4 -48.058829 2309.651088 -110999.127750
5 -8.941458 79.949670 -714.866612
6 15.307793 234.328523 3587.052500
7 -34.706266 1204.524887 -41804.560890
8 1.389154 1.929750 2.680720
9 -44.383760 1969.918139 -87432.373590
10 7.013502 49.189211 344.988637
11 22.762749 518.142738 11794.353058
3.1 Learning Polynomial Regression
内容:
1. 将特征扩展到8阶(继续视为线性回归的处理方式);
2. 对特征进行规范化处理;
3. 计算训练集代价与验证集代价并画出学习曲线。
normalizeFeatures.py
def normalizeFeatures(feature):
# DataFrame.apply(func,axis=0,...)
# 1.func:函数或lambda表达式,应用于每行或每列
# 2.lambda表达式:函数式编程,使得apply处理数据时,参数可以传递给函数
# 3.axis:0(默认值)、index-处理每一列;1、columns-处理每一行
# 4.规范化处理:减去平均值,再除以标准差(np.std(..))
return feature.apply(lambda x: (x - x.mean()) / x.std())
polyFeatures.py
import pandas as pd # 一种用于数据分析的扩展程序库
import numpy as np
from normalizeFeatures import * # 特征规范化
def polyFeatures(X, power):
# 注意F(i)的每一个对应值可以是一个一维数组,所以用ravel进行展开
data = {"F{}".format(i): np.power(X.ravel(), i) for i in range(1, power + 1)}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_features = normalizeFeatures(df).values
return new_features
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from polyFeatures import * # 增加特征
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
X_poly = polyFeatures(X, 8) # 训练集扩充特征
Xval_poly = polyFeatures(Xval, 8) # 验证集扩充特征
print(X_poly[:3, :])
[[-3.62140776e-01 -7.55086688e-01 1.82225876e-01 -7.06189908e-01
3.06617917e-01 -5.90877673e-01 3.44515797e-01 -5.08481165e-01]
[-8.03204845e-01 1.25825266e-03 -2.47936991e-01 -3.27023420e-01
9.33963187e-02 -4.35817606e-01 2.55416116e-01 -4.48912493e-01]
[ 1.37746700e+00 5.84826715e-01 1.24976856e+00 2.45311974e-01
9.78359696e-01 -1.21556976e-02 7.56568484e-01 -1.70352114e-01]]
plot.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from linearRegression import * # 得到最优theta
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 计算代价函数
from polyFeatures import * # 增加特征
def plotTrainingData(X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, marker='x', c='r')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
plt.show()
def plotHypothesis(theta, X, y):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker='x', label='Training Data')
ax.plot(X, theta[0] + theta[1] * X, c='b', label='Prediction')
ax.set_xlabel('water_level')
ax.set_ylabel('flow')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
def plotLearningCurve(X, train_cost, cv_cost):
m = X.shape[0]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), train_cost, label='training cost')
ax.plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), cv_cost, label='cross validation cost')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('m(training set size)')
ax.set_ylabel('error')
plt.show()
def plotPolyLearningCurve(X, y, X_poly, Xval_poly, yval, learningRate):
train_cost = []
cv_cost = []
m = X.shape[0]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
res = linearRegression(X_poly[:i, :], y[:i], 0) # 此时lambda=0可能会出现高方差,即过拟合现象。
t = linearRegCostFunction(res, X_poly[:i, :], y[:i], 0)
cv = linearRegCostFunction(res, Xval_poly[:i, :], yval[:i], 0)
train_cost.append(t)
cv_cost.append(cv)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(8, 8)) # 子图:2行1列 即2*1=2个子图
# 1.绘制学习曲线
ax[0].plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), train_cost, label='training cost')
ax[0].plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), cv_cost, label='cross validation cost')
ax[0].set_xlabel('m(training set size)')
ax[0].set_ylabel('error')
ax[0].legend()
# 2.绘制拟合曲线
# a.np.linspace(a,b,c)生成[a,b)之间元素个数为c的序列
x = np.linspace(-50, 50, 100)
new_X_poly = np.insert(polyFeatures(x, 8), 0, np.ones(len(x)), axis=1)
h_theta = new_X_poly * np.matrix(linearRegression(X_poly, y, 0)).T
ax[1].plot(x, h_theta, c='b', label='fit_curve')
ax[1].scatter(X, y, c='r', marker='x', label='initial_x_y')
ax[1].set_xlabel('water_level')
ax[1].set_ylabel('flow')
ax[1].legend()
plt.show()
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from plot import * # 绘制多项式的拟合曲线以及学习曲线
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
X_poly = polyFeatures(X, 8) # 训练集扩充特征
Xval_poly = polyFeatures(Xval, 8) # 验证集扩充特征
plotPolyLearningCurve(X, y, X_poly, Xval_poly, yval, learningRate=0)
高方差(过拟合)的情况:
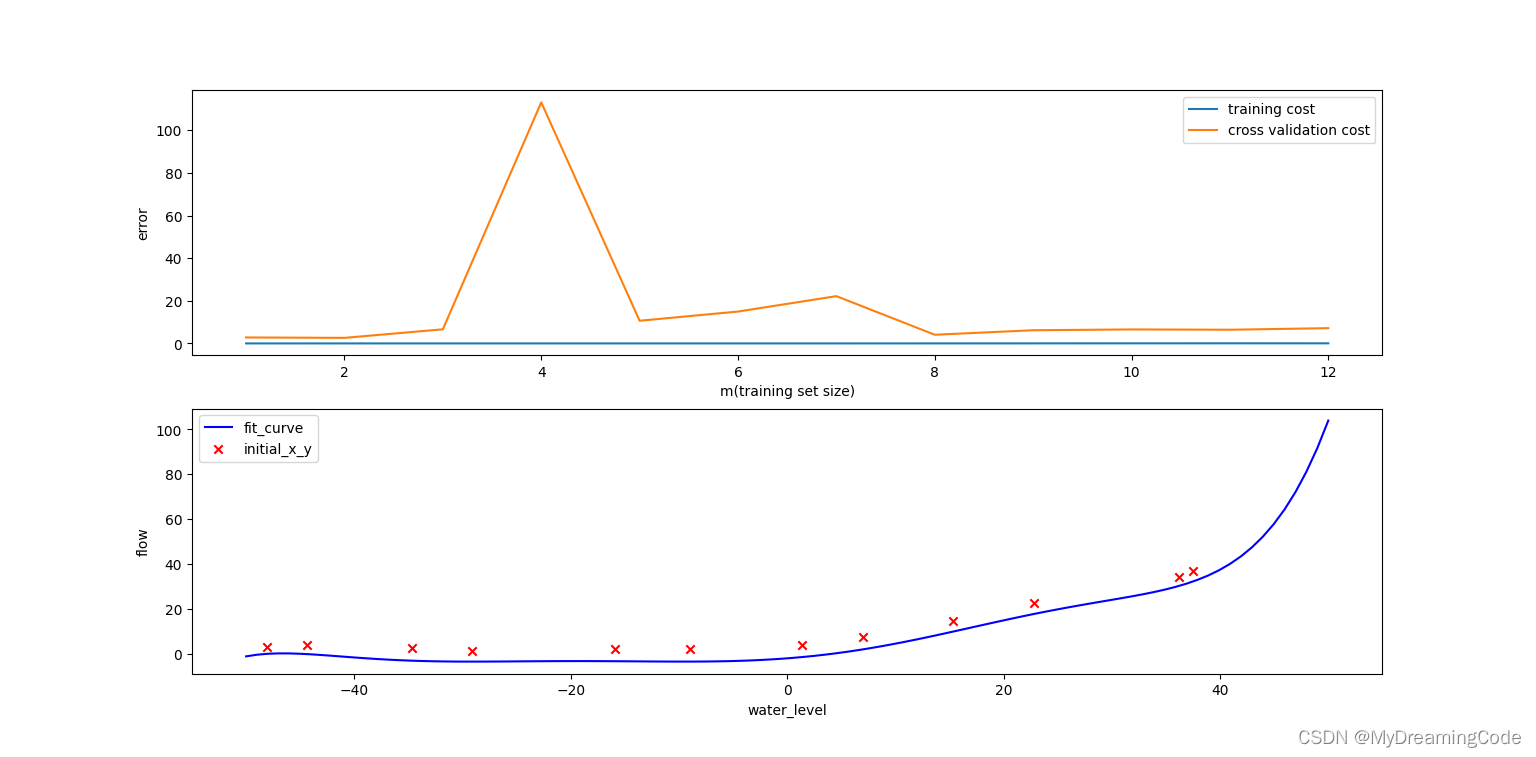
3.2 Adjusting the regularization parameter
内容:调整正则化的系数lambda。
A. lambda=1(即learningRate=1)的情况:
plot.py(部分代码):
def plotPolyLearningCurve(X, y, X_poly, Xval_poly, yval, learningRate):
train_cost = []
cv_cost = []
m = X.shape[0]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
res = linearRegression(X_poly[:i, :], y[:i], learningRate) # 此时lambda=0可能会出现高方差,即过拟合现象。
t = linearRegCostFunction(res, X_poly[:i, :], y[:i], 0)
cv = linearRegCostFunction(res, Xval_poly[:i, :], yval[:i], 0)
train_cost.append(t)
cv_cost.append(cv)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(8, 8)) # 子图:2行1列 即2*1=2个子图
# 1.绘制学习曲线
ax[0].plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), train_cost, label='training cost')
ax[0].plot(np.arange(1, m + 1), cv_cost, label='cross validation cost')
ax[0].set_xlabel('m(training set size)')
ax[0].set_ylabel('error')
ax[0].legend()
# 2.绘制拟合曲线
# a.np.linspace(a,b,c)生成[a,b)之间元素个数为c的序列
x = np.linspace(-50, 50, 100)
new_X_poly = np.insert(polyFeatures(x, 8), 0, np.ones(len(x)), axis=1)
h_theta = new_X_poly * np.matrix(linearRegression(X_poly, y, learningRate)).T
ax[1].plot(x, h_theta, c='b', label='fit_curve')
ax[1].scatter(X, y, c='r', marker='x', label='initial_x_y')
ax[1].set_xlabel('water_level')
ax[1].set_ylabel('flow')
ax[1].legend()
plt.show()main.py(修改一句)
plotPolyLearningCurve(X, y, X_poly, Xval_poly, yval, learningRate=1)
在学习曲线中可以看到,训练集的代价不再是0,即我们减轻了过拟合。
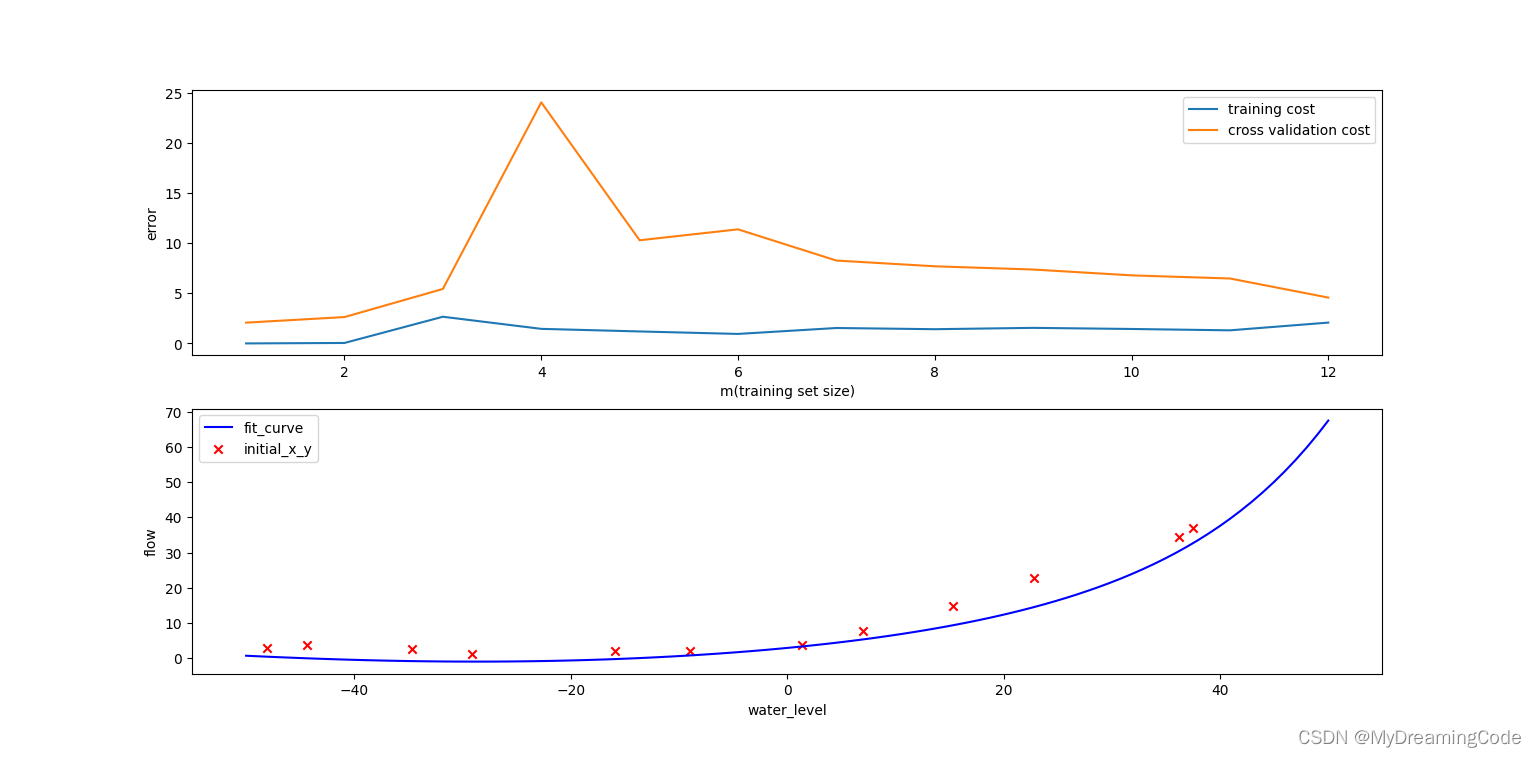
B. lambda=100(即learningRate=100)的情况:
main.py(修改一句)
plotPolyLearningCurve(X, y, X_poly, Xval_poly, yval, learningRate=100)
lambda惩罚项太大,出现了欠拟合的情况:
 3.3 Selecting λ using a cross validation set
3.3 Selecting λ using a cross validation set
内容:使用验证集来评价 λ 的好坏,选择好的 λ 后,在测试集上进行测试。lambda可以尝试0,0.001,0.003,0.01,0.03,0.1,0.3,1,3,10这些值。

chooseLambda.py
from plot import * # 绘制lambda与代价函数(训练集、验证集)的图像
def chooseLambda(X_poly, y, Xval_poly, yval):
l_candidate = [0, 0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10] # lambda候选值
train_cost = []
cv_cost = []
for l in l_candidate:
res = linearRegression(X_poly, y, l)
train_cost.append(linearRegCostFunction(res, X_poly, y, 0))
cv_cost.append(linearRegCostFunction(res, Xval_poly, yval, 0))
plotChooseLambda(l_candidate, train_cost, cv_cost)
plot.py(增加一个函数)
def plotChooseLambda(l_candidate, train_cost, cv_cost):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.plot(l_candidate, train_cost, label='training cost')
ax.plot(l_candidate, cv_cost, label='cross validation')
ax.set_xlabel('lambda λ')
ax.set_ylabel('cost')
ax.legend()
plt.show()main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from chooseLambda import * # 选择最合适的lambda
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
X_poly = polyFeatures(X, 8) # 训练集扩充特征
Xval_poly = polyFeatures(Xval, 8) # 验证集扩充特征
chooseLambda(X_poly, y, Xval_poly, yval)
cross validation的最小值在4附近,对应的lambda值约为1。
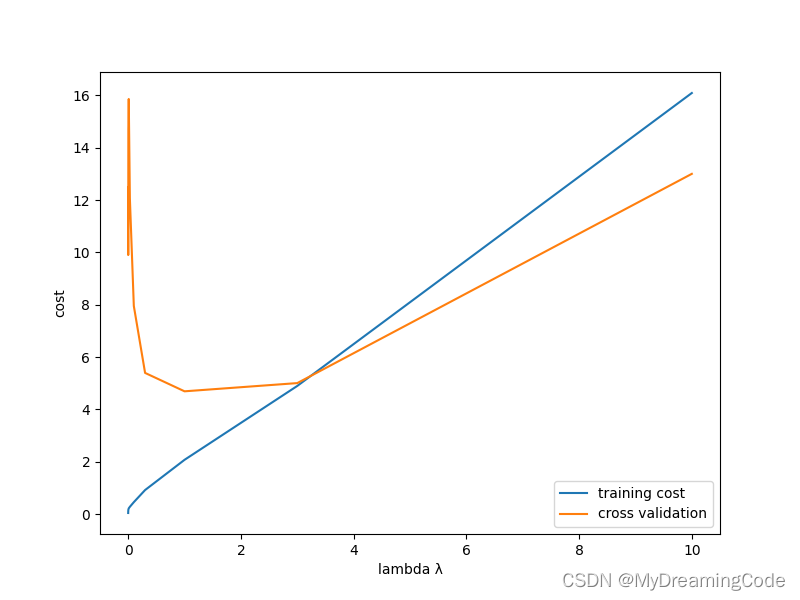
3.4 Computing test set error
内容:在测试集(之前从未被使用过的数据)上做评估。
testSet.py
from linearRegression import * # 计算出最优theta
from linearRegCostFunction import * # 计算代价函数
def testSet(X_poly, y, Xtest_poly, ytest):
l_candidate = [0, 0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10] # lambda候选值
for l in l_candidate:
theta = linearRegression(X_poly, y, l)
print("test cost(l={})={}".format(l, linearRegCostFunction(theta, Xtest_poly, ytest, l)))
main.py
from scipy.io import loadmat # 导入matlab格式数据
from polyFeatures import * # 扩展特征
from testSet import * # 在测试集上应用
data = loadmat('ex5data.mat')
X, y, Xval, yval, Xtest, ytest = data['X'], data['y'], data['Xval'], data['yval'], data['Xtest'], data['ytest']
X_poly = polyFeatures(X, 8)
Xtest_poly = polyFeatures(Xtest, 8)
testSet(X_poly, y, Xtest_poly, ytest)
test cost(l=0)=10.088273811962134
test cost(l=0.001)=10.936688556161654
test cost(l=0.003)=11.22874602267731
test cost(l=0.01)=10.992356113176701
test cost(l=0.03)=10.026774833897209
test cost(l=0.1)=8.624697841922986
test cost(l=0.3)=7.336693296833649
test cost(l=1)=7.477384083967169
test cost(l=3)=11.645564884360581
test cost(l=10)=27.71507101822064
此时,λ=0.3测得的代价函数最小,故λ=0.3为最优选择。





















 144
144











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








