个人主页:仍有未知等待探索-CSDN博客
专题分栏:C++
请多多指教!
目录
一、标准库中的string
1、了解
1、string是表示字符串的字符串类
2、该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
2、string类常用接口说明
下面的函数都可以去下面的网址进行查文档,来看函数的功能。(接下来我会实现这个string类)
1、常见的构造函数
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| string() | 构造空的string类,即空字符串 |
| string(const char*s) | 用c_str()来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n, char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符c |
| string(const string& s) | 拷贝构造函数 |
2、容量操作
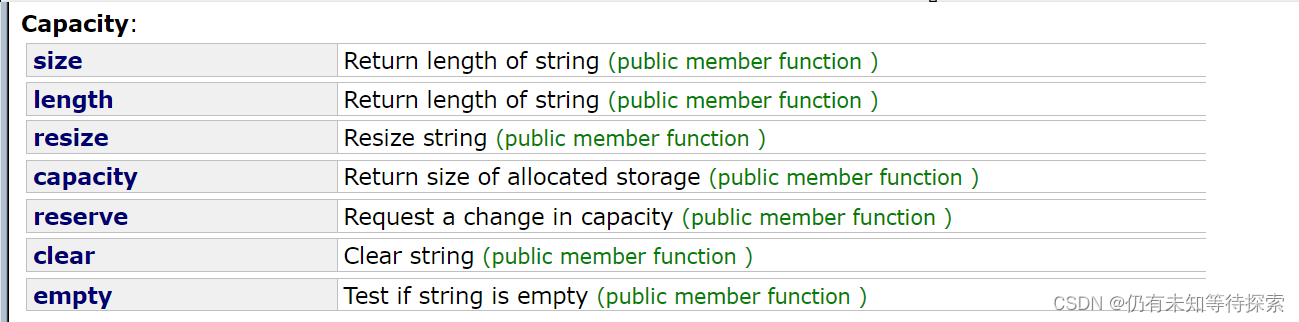
3、访问及遍历操作

4、修改操作

5、非成员函数

二、string类实现
实现string类能让我们更好的明白模板的使用,函数重载等等。
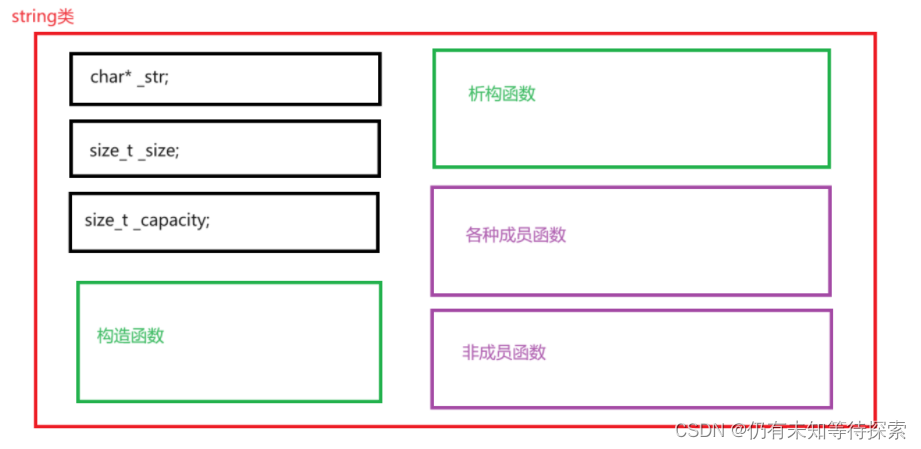
1、string类的大体框架
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
class string
{
public:
private:
char* _str; // string存的字符串
size_t _size; // string中字符串的长度
size_t _capacity; // string的容量
};2、构造和析构函数
string()
:_str(nullptr)
,_size(0)
,_capacity(0)
{}
string(const char* str)
:_size(strlen(str))
,_capacity(_size)
{
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string(const string& str)
:_str(new char[str._capacity + 1])
,_size(str._size)
,_capacity(str._capacity)
{
strcpy(_str, str._str);
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}3、迭代器
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
4、成员函数
string& operator=(const string& str)
{
char* tmp = new char[str._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, str._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = str._size;
_capacity = str._capacity;
return *this;
}
void reserve(int x)
{
if (_capacity < x)
{
char* tmp = new char[x + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = x;
}
}
void swap(string& str)
{
std::swap(_str, str._str);
std::swap(_size, str._size);
std::swap(_capacity, str._capacity);
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
void insert(int index, const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
assert(index >= 0 && index < _size);
if (_size + len >= _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity + len);
}
for (int i = _size - 1; i >= index; i -- )
{
_str[i + len] = _str[i];
}
for (int j = 0, i = index; j < str._size; j ++ ,i ++ )
{
_str[i] = str._str[j];
}
_size += len;
}
void insert(int index, char ch)
{
assert(index >= 0 && index < _size);
if (_size + 1 >= _capacity)
{
reserve(2 * _capacity);
_capacity *= 2;
}
for (int i = _size - 1; i >= index; i -- )
{
_str[i + 1] = _str[i];
}
_str[index] = ch;
_size ++ ;
}
void append(const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
_capacity = len * _size;
}
int end = _size;
for (int i = 0; i < str._size; i ++ ,end ++ )
{
_str[end] = str._str[i];
}
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(const string& str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void push_back(const char ch)
{
if (_size + 1 >= _capacity)
{
reserve(2 * _capacity);
}
_capacity *= 2;
_str[_size] = ch;
_size ++ ;
}
int size() const
{
return _size;
}
int capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
bool empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
void resize(int n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
for (int i = n; i < _size; i ++ )
{
_str[i] = '\0';
}
}
else if (n + 1 < _capacity)
{
for (int i = _size; i < n; i ++ )
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
}
else
{
reserve(n);
}
}
char& operator[](size_t index)
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
bool operator==(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret == 0;
}
bool operator!=(const string& str)
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool operator>(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret > 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& str)
{
return *this < str || *this == str;
}
bool operator>=(const string& str)
{
return *this > str || *this == str;
}
int find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (int i = pos; i < _size; i ++ )
{
if (_str[i] == c) return i;
}
return npos;
}
int find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{
char* p = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (p != nullptr)
{
return p - _str;
}
return npos;
}
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
int i = 0;
for (i = pos + len; i < _size; i ++ )
{
_str[i - len] = _str[i];
}
_str[i] = '\0';
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}5、非成员函数
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++ )
{
out << str._str[i];
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& str)
{
str.clear();
char ch = in.get();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i ++ ] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
str += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i != 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
str += buff;
}
return in;
}
}三、问题
1、深拷贝和浅拷贝问题
浅拷贝:也称位拷贝,编译器只是将对象中的值拷贝过来。如果对象中管理资源,最后就会导致多个对象共享同一份资源,当一个对象销毁时就会将该资源释放掉,而此时另一些对象不知道该资源已经被释放,以为还有效,所以当继续对资源进项操作时,就会发生发生了访问违规。
深拷贝:每个对象都有一份独立的资源,不要和其他对象共享。如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。一般情况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。
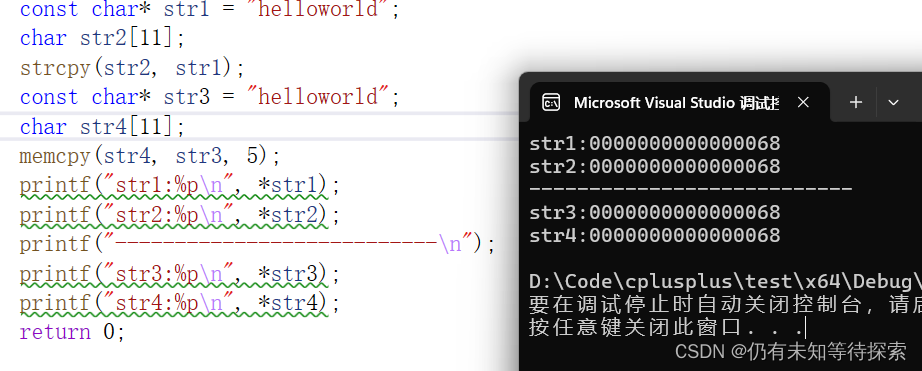
2、strcpy,memcpy
通过下面的例子也能清晰的看出来,这两个拷贝函数都是浅拷贝。所以在用的时候需要小心谨慎。
四、总代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace my
{
class string
{
public:
string()
:_str(nullptr)
,_size(0)
,_capacity(0)
{}
string(const char* str)
:_size(strlen(str))
,_capacity(_size)
{
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
string(const string& str)
:_str(new char[str._capacity + 1])
,_size(str._size)
,_capacity(str._capacity)
{
strcpy(_str, str._str);
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
string& operator=(const string& str)
{
char* tmp = new char[str._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, str._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = str._size;
_capacity = str._capacity;
return *this;
}
void reserve(int x)
{
if (_capacity < x)
{
char* tmp = new char[x + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = x;
}
}
void swap(string& str)
{
std::swap(_str, str._str);
std::swap(_size, str._size);
std::swap(_capacity, str._capacity);
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
void insert(int index, const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
assert(index >= 0 && index < _size);
if (_size + len >= _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity + len);
}
for (int i = _size - 1; i >= index; i -- )
{
_str[i + len] = _str[i];
}
for (int j = 0, i = index; j < str._size; j ++ ,i ++ )
{
_str[i] = str._str[j];
}
_size += len;
}
void insert(int index, char ch)
{
assert(index >= 0 && index < _size);
if (_size + 1 >= _capacity)
{
reserve(2 * _capacity);
_capacity *= 2;
}
for (int i = _size - 1; i >= index; i -- )
{
_str[i + 1] = _str[i];
}
_str[index] = ch;
_size ++ ;
}
void append(const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
_capacity = len * _size;
}
int end = _size;
for (int i = 0; i < str._size; i ++ ,end ++ )
{
_str[end] = str._str[i];
}
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(const string& str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void push_back(const char ch)
{
if (_size + 1 >= _capacity)
{
reserve(2 * _capacity);
}
_capacity *= 2;
_str[_size] = ch;
_size ++ ;
}
int size() const
{
return _size;
}
int capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
bool empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
void resize(int n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
for (int i = n; i < _size; i ++ )
{
_str[i] = '\0';
}
}
else if (n + 1 < _capacity)
{
for (int i = _size; i < n; i ++ )
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
}
else
{
reserve(n);
}
}
char& operator[](size_t index)
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
bool operator==(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret == 0;
}
bool operator!=(const string& str)
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool operator>(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret > 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& str)
{
int ret = strcmp(_str, str.c_str());
return ret < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& str)
{
return *this < str || *this == str;
}
bool operator>=(const string& str)
{
return *this > str || *this == str;
}
int find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (int i = pos; i < _size; i ++ )
{
if (_str[i] == c) return i;
}
return npos;
}
int find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{
char* p = strstr(_str + pos, s);
if (p != nullptr)
{
return p - _str;
}
return npos;
}
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
int i = 0;
for (i = pos + len; i < _size; i ++ )
{
_str[i - len] = _str[i];
}
_str[i] = '\0';
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& str);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& str);
private:
char* _str; // string存的字符串
size_t _size; // string中字符串的长度
size_t _capacity; // string的容量
static const size_t npos = -1;
};
inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& str)
{
int len = str._size;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++ )
{
out << str._str[i];
}
return out;
}
inline istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& str)
{
str.clear();
char ch = in.get();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i ++ ] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
str += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i != 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
str += buff;
}
return in;
}
}谢谢大家!








 本文详细介绍了C++标准库中的string类,包括其构造方法、常用接口、容量操作、修改和访问功能,以及深浅拷贝的区别和strcpy/memcpy的使用注意事项。
本文详细介绍了C++标准库中的string类,包括其构造方法、常用接口、容量操作、修改和访问功能,以及深浅拷贝的区别和strcpy/memcpy的使用注意事项。















 5万+
5万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










