1.定义
同往常一样,在实现队列之前先让我们看看什么叫做队列。
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据的操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列的特点是先进先出。进行插入操作的一端称为队尾,进行删除操作的一端则称为队头。示意图如下:
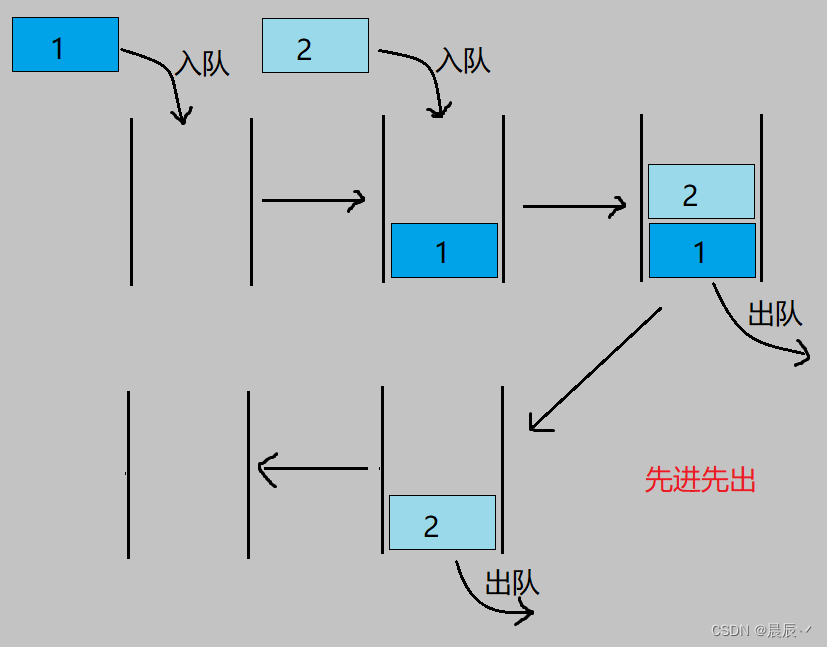
队列同样可以用数组和链表实现,但是如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据效率较低,因此在这里我们使用链表的方式来实现队列。
2. 代码实现
2.1 实现准备
在这里,由于我们实现函数时需要传入头尾两个结点,为了方便,在这里我们用两个结构体来分别表示队列和队列的结构。
typedef int QDataType;
//表示队列(链式结构)
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;//下个结点
QDataType data;//数据
}QNode;
//队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;//头指针
QNode* tail;//尾指针
int size;//个数
}Que;2.2 队列的初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//头尾结点置空
pq->size = 0;//元素个数置为0个
}2.3 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newNode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));//开辟新结点
if (newNode == NULL)//判断开辟是否成功
{
printf("malloc error.");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;//给新结点赋入想放的值
newNode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)//考虑队列为空的情况
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newNode;//下一个结点变为新开辟的结点
pq->tail = newNode;//尾结点指向新节点
}
pq->size++;//队列所含元素个数加一
}2.4 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//防止队列已经为空
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//队列内只含一个元素
{
free(pq->head);//free掉头节点
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//头尾指针置空
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;//存放下一个结点
free(pq->head);//free掉头节点
pq->head = next;//将头节点变为下一个结点
}
pq->size--;//元素个数减一
}2.5 获取头顶元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//防止队列为空
//直接返回头节点中的数据元素即可
return pq->head->data;
}2.6 获取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//防止队列为空
//直接返回尾结点数据元素即可
return pq->tail->data;
}2.7 获取队列中有效元素个数
由于我们在开始定义队列结构时用size储存了元素个数,因此这里只需要返回size的值。
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}2.8 判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;//若为空,则为ture,反之则为false
}2.9 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;//表示当前结点
while (cur)//当前结点不为空时循环
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//记录下一个结点
free(cur);//free掉当前结点
cur = next;//下一个结点变为当前结点
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//将头尾指针置空
pq->size = 0;//将元素个数置为0
}3.完整代码
3.1 Queue.h(头文件)
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;//头指针
QNode* tail;//尾指针
int size;//个数
}Que;
void QueueInit(Que* pq);//初始化
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);//销毁
void QueuePush(Que* pq,QDataType x);//插入
void QueuePop(Que* pq);//头删
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);//输出头元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);//输出尾元素
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);//判空
int QueueSize(Que* pq);//个数3.2 Queue.c(函数实现)
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newNode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error.");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newNode;
pq->tail = newNode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}3.3 test.c(测试)
#include "Queue.h"
void Test1()
{
Que q1;
QueueInit(&q1);
QueuePush(&q1, 1);
QueuePush(&q1, 2);
QueuePush(&q1, 3);
QueuePush(&q1, 4);
QueuePush(&q1, 5);
QueuePush(&q1, 6);
printf("%d\n", QueueBack(&q1));
printf("%d\n", QueueSize(&q1));
while (!QueueEmpty(&q1))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q1));
QueuePop(&q1);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q1);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}本次内容就到这里啦!感谢阅读!






















 1434
1434











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








