接上篇line识别,本文的内容是cirle识别。类名:itkHoughTransform2DCirclesImageFilter。
不废话,上用法代码:
typedef itk::HoughTransform2DCirclesImageFilter<unsigned char, float> HoughTransformFilterType;
HoughTransformFilterType::Pointer hough = HoughTransformFilterType::New();
hough->SetInput(input_data);
hough->SetNumberOfCircles(1);
hough->SetMinimumRadius(10);
hough->SetMaximumRadius(300);
hough->SetVariance(5);
hough->SetSigmaGradient(1);
hough->SetDiscRadiusRatio(2);
hough->Update();输入:灰度图像
输出:
1.存放圆心的累加器数组;
2.一个存放坐标的数组,带有半径属性。
源码分析:
1..h中的私有变量
private:
HoughTransform2DCirclesImageFilter(const Self&);
void operator=(const Self&);
float m_SweepAngle; 扫描角度 0.0
double m_MinimumRadius; 最小半径 0
double m_MaximumRadius; 最大半径 10
double m_Threshold; 最小灰度下限 0
double m_SigmaGradient; 梯度参数 1
OutputImagePointer m_RadiusImage;
CirclesListType m_CirclesList;
unsigned int m_NumberOfCircles;
float m_DiscRadiusRatio; 需要排除的半径 1
float m_Variance; 设置高斯模糊器的方差 10
unsigned long m_OldModifiedTime; 0
unsigned long m_OldNumberOfCircles; 0template<typename TInputPixelType, typename TOutputPixelType>
void
HoughTransform2DCirclesImageFilter< TInputPixelType, TOutputPixelType>
::GenerateData()
{
// Get the input and output pointers
InputImageConstPointer inputImage = this->GetInput(0);
OutputImagePointer outputImage = this->GetOutput(0);
// Allocate the output
this->AllocateOutputs();
//输出图像涂黑
outputImage->FillBuffer(0);
//高斯导数图像函数?梯度图?高斯模糊器?
typedef GaussianDerivativeImageFunction<InputImageType> DoGFunctionType;
typename DoGFunctionType::Pointer DoGFunction = DoGFunctionType::New();
DoGFunction->SetInputImage(inputImage);
DoGFunction->SetSigma(m_SigmaGradient);
//半径图像???NO,统计投票结果
m_RadiusImage = OutputImageType::New();
m_RadiusImage->SetRegions( outputImage->GetLargestPossibleRegion() );
m_RadiusImage->SetOrigin(inputImage->GetOrigin());
m_RadiusImage->SetSpacing(inputImage->GetSpacing());
m_RadiusImage->SetDirection(inputImage->GetDirection());
m_RadiusImage->Allocate();
m_RadiusImage->FillBuffer(0);
//像素迭代器
ImageRegionConstIteratorWithIndex< InputImageType > image_it( inputImage, inputImage->GetRequestedRegion() );
image_it.Begin();
Index<2> index;
Point<float,2> point;
while( !image_it.IsAtEnd() )//逐点判断,一直迭代到最后一个点
{
if(image_it.Get()>m_Threshold)
{
point[0] = image_it.GetIndex()[0];
point[1] = image_it.GetIndex()[1];
//获得该点的梯度
typename DoGFunctionType::VectorType grad = DoGFunction->EvaluateAtIndex(image_it.GetIndex());
double Vx = grad[0];
double Vy = grad[1];
if( (vcl_fabs(Vx)>1) || (vcl_fabs(Vy)>1) ) // if the gradient is not flat 梯度不够平坦
{
double norm = vcl_sqrt(Vx*Vx+Vy*Vy);
Vx /= norm;
Vy /= norm;
for(double angle = -m_SweepAngle;angle<=m_SweepAngle;angle+=0.05)
{
double i = m_MinimumRadius;//先将预设最小半径
double distance;
do
{
//计算可能在圆上的点
index[0] = (long int)(point[0]-i*(Vx*vcl_cos(angle)+Vy*vcl_sin(angle)));
index[1] = (long int)(point[1]-i*(Vx*vcl_sin(angle)+Vy*vcl_cos(angle)));
//计算点与圆心的距离(疑似半径)
distance = vcl_sqrt((index[1]-point[1])*(index[1]-point[1])
+(index[0]-point[0])*(index[0]-point[0]) );
if(outputImage->GetRequestedRegion().IsInside( index ))
{
outputImage->SetPixel(index, outputImage->GetPixel(index)+1);
m_RadiusImage->SetPixel(index, (m_RadiusImage->GetPixel(index)+distance));//投票
}
i=i+1;//半径每次+1
} while( outputImage->GetRequestedRegion().IsInside( index )
&& (distance < m_MaximumRadius) );
}
}
}
++image_it;
}
// Compute the average radius
ImageRegionConstIterator< OutputImageType > output_it( outputImage, outputImage->GetLargestPossibleRegion() );
ImageRegionIterator< OutputImageType > radius_it( m_RadiusImage, m_RadiusImage->GetLargestPossibleRegion() );
output_it.Begin();
radius_it.Begin();
while( !output_it.IsAtEnd() )
{
if(output_it.Get()>0)
{
radius_it.Set(radius_it.Get()/output_it.Get());
}
++output_it;
++radius_it;
}
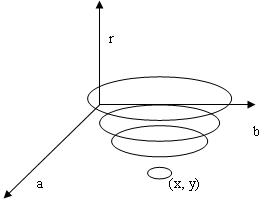
}已知圆的一般方程为:(x - a)^2 + (y - b)^2 = r^2
其中,(a, b)为圆心,r为圆的半径。
把X-Y平面上的圆转换到a-b-r参数空间,则图像空间中过(x, y)点圆对应参数空间中,高度r变化下的一个三维锥面,如下图:
这里摘抄一段网友的说法:
“ OpenCV内部提供了一个基于Hough变换理论的找圆算法,HoughCircle与一般的拟合圆算法比起来,各有优势:
优势:HoughCircle对噪声点不怎么敏感,并且可以在同一个图中找出多个圆;反观拟合圆算法,单纯的拟合结果容易受噪声点的影响,且不支持一个输入中找多个圆;
缺点:原始的Hough变换找圆,计算量很大,而且如果对查找圆的半径不加控制,不但运算量巨大,而且精度也不足,在输入噪声点不多的情况下,找圆效果远不如拟合找圆;为了提高找圆精度,相比拟合法,需要提供更多的参数加以控制,参数要求比较严格,且总体稳定性不佳;
OpenCV内的HoughCircles对基础的Hough变换找圆做了一定的优化来提高速度,它不再是在参数空间画出一个完整的圆来进行投票,而只是计算轮廓点处的梯度向量,然后根据搜索的半径R在该梯度方向距离轮廓点距离R的两边各投一点,最后根据投票结果图确定圆心位置。”
关键词:
投票

“佛说世间如梦如幻,一切都是刹那变化,我们执假为真,才不认识自己本来的面目。可大多数众生不知,就算知道了,还不是陷在其中不能自拔?”
---世间安得双全法,不负如来不负卿
1.http://www.opencv.org.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=34096
2.https://itk.org/Doxygen/html/group__ImageFeatureExtraction.html
3.http://blog.csdn.net/lee_cv/article/details/9163001
4.《基于Hough 变换的圆检测方法》























 158
158

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








